Abstract
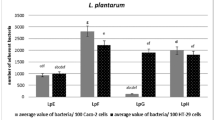
This study aimed to assess adhesion and anti-adhesion, aggregation, and surface properties of four selected oral Lactobacillus strains, L. fermentum SD7, L. paracasei SD1, L. rhamnosus SD4, and L. rhamnosus SD11, together with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Human cells, enterocytes Caco-2 and oral keratinocyte H357 were used, and various enteric and oral pathogens were included. Results showed that all Lactobacillus tested gave high adhesion and internalization in both Caco-2 and H357 cells similar to L. rhamnosus GG, and it suggests that such properties are strain dependent and specific to host cells. Anti-adhesion was different; it depended on the internalization ability of individual Lactobacillus and pathogenic strains to Caco-2 and H357. Coaggregation ability depended on autoaggregation of both the Lactobacillus and pathogenic strains. A positive correlation between surface charges and aggregation, and internalization and anti-adhesion of all Lactobacillus was found. In conclusion, results suggests that the selected Lactobacillus might be potential probiotics for usage in both the oral cavity and intestinal tract due to their abilities of aggregation, adherence and anti-internalization to both Caco-2 and H357 cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campana R, van Hemert S, Baffone W (2017) Strain-specific probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria and their interference with human intestinal pathogens invasion. Gut Pathog 9:12
Capurso L (2019) Thirty years of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: a review. Clin Gastroenterol 53(Suppl 1):S1–S41
Collado MC, Surono I, Meriluoto J, Salminen S (2007) Indigenous dadih lactic acid bacteria: cell-surface properties and interactions with pathogens. J Food Sci 72:M89–93
Collado MC, Meriluoto J, Salminen S (2008) Adhesion and aggregation properties of probiotic and pathogen strains. Eur Food Res Technol 226:1065–1073
Colloca ME, Ahumada MC, López ME, Nader-Macías ME (2000) Surface properties of lactobacilli isolated from healthy subjects. Oral Dis 6:227–233
Coppenhagen-Glazer S, Sol A, Abed J, Naor R, Zhang X, Han YW, Bachrach G (2015) Fap2 of Fusobacterium nucleatum is a galactose-inhibitable adhesin involved in coaggregation, cell adhesion, and preterm birth. Infect Immunol 83:1104–1113
Darilmaz DO, Beyatli Y, Yuksekdag ZN (2012) Aggregation and hydrophobicity properties of 6 dairy Propionibacteria strains isolated from homemade Turkish chesses. J Food Sci 71:M20–M24
Del Re B, Sgorbati B, Miglioli M, Palenzona D (2000) Adhesion, autoaggregation and hydrophobicity of 13 strains of Bifidobacterium longum. Lett Appl Microbiol 31:438–442
Falah F, Vasiee A, Behbahani BA, Yazdi FT, Moradi S, Mortazavi SA, Roshanak S (2019) Evaluation of adherence and anti-infective properties of probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum strain 4–17 against Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infection in humans. Microb Pathog 131:246–253
Gholizadeh P, Pormohammad A, Eslami H, Shokouhi B, Fakhrzadeh V, Kafil HS (2017) Oral pathogenesis of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Microb Pathog 113:303–311
Grigoryan S, Bazukyan I, Trchounian A (2018) Aggregation and adhesion activity of lactobacilli isolated from fermented products in vitro and in vivo: a potential probiotic strain. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 10:269–276
Kos B, Susković J, Vuković S, Simpraga M, Frece J, Matosic S (2003) Adhesion and aggregation ability of probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus M92. J Appl Microbiol 94:981–987
Li XJ, Yue LY, Guan XF, Qiao SY (2008) The adhesion of putative probiotic lactobacilli to cultured epithelial cells and porcine intestinal mucus. J Appl Microbiol 104:1082–1091
Lima BP, Shi W, Lux R (2017) Identification and characterization of a novel Fusobacterium nucleatum adhesin involved in physical interaction and biofilm formation with Streptococcus gordonii. Microbiologyopen 6:e444
Nadelman P, Magno MB, Masterson D, da Cruz AG, Maia LC (2018) Are dairy products containing probiotics beneficial for oral health? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig 22:2763–2785
Nakano MM (2018) Role of Streptococcus mutans surface proteins for biofilm formation. Jpn Dent Sci Rev 54:22–29
Olsen I, Progulske-Fox A (2015) Invasion of Porphyromonas gingivalis strains into vascular cells and tissue. J Oral Microbiol 7:28788
Piwat S, Teanpaisan R, Thitasomakul S, Thearmontree A, Dahlén G (2010) Lactobacillus species and genotypes associated with dental caries in Thai preschool children. Mol Oral Microbiol 25:157–164
Piwat S, Sophatha B, Teanpaisan R (2015) An assessment of adhesion, aggregation and surface charges of Lactobacillus strains derived from the human oral cavity. Lett Appl Microbiol 61:98–105
Pizarro-Cerdá J, Cossart P (2006) Bacterial adhesion and entry into host cells. Cell 124:715–727
Ren D, Li C, Qin Y, Yin R, Li X, Tian M, Du S, Guo H, Liu C, Zhu N, Sun D, Li Y, Jin N (2012) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus adherence to Caco-2 cells by lactobacilli and cell surface properties that influence attachment. Anaerobe 18:508–515
Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E (1980) Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 9:29–33
Rungsri P, Akkarachaneeyakorn N, Wongsuwanlert M, Piwat S, Nantarakchaikul P, Teanpaisan R (2017) Effect of fermented milk containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus SD11 on oral microbiota of healthy volunteers: a randomized clinical trial. J Dairy Sci 100:7780–7787
Teanpaisan R, Piwat S, Tianviwat S, Sophatha B, Kampoo T (2015) Effect of long-term consumption of Lactobacillus paracasei SD1 on reducing mutans streptococci and caries risk: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Dent J 3:43–54
Tuo Y, Yu H, Ai L, Wu Z, Guo B, Chen W (2013) Aggregation and adhesion properties of 22 Lactobacillus strains. J Dairy Sci 96:4252–4257
Vélez MP, De Keersmaecker SC, Vanderleyden J (2007) Adherence factors of Lactobacillus in the human gastrointestinal tract. FEMS Microbiol Lett 276:140–148
Veljović K, Popović N, Miljković M, Tolinački M, Terzić-Vidojević A, Kojić M (2017) Novel Aggregation promoting factor AggE contributes to the probiotic properties of Enterococcus faecium BGGO9-28. Front Microbiol 8:01843
Wannun P, Piwat S, Teanpaisan R (2014) Purification and characterization of bacteriocin produced by oral Lactobacillus paracasei SD1. Anaerobe 27:17–21
Wannun P, Piwat S, Teanpaisan R (2016) Purification, characterization, and optimum conditions of fermencin SD11, a bacteriocin produced by human orally Lactobacillus fermentum SD11. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179:572–582
Xu H, Jeong HS, Lee HY, Ahn J (2009) Assessment of cell surface properties and adhesion potential of selected probiotic strains. Lett Appl Microbiol 49:434–442
Zhang W, Wang H, Liu J, Zhao Y, Gao K, Zhang J (2013) Adhesive ability means inhibition activities for lactobacillus against pathogens and S-layer protein plays an important role in adhesion. Anaerobe 22:97–103
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Research Council of Thailand (DEN600045b), the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) through the Royal Golden Jubilee PhD program (PhD/0217/2553/AN.2), and the National Science and Technology Development Agency (Co-project, 2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sophatha, B., Piwat, S. & Teanpaisan, R. Adhesion, anti-adhesion and aggregation properties relating to surface charges of selected Lactobacillus strains: study in Caco-2 and H357 cells. Arch Microbiol 202, 1349–1357 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01846-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01846-7