Abstract
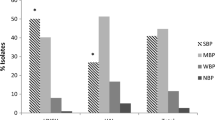
The genus Pseudomonas mainly includes opportunistic pathogens that rely on type IV pili as an important virulence factor, which is associated with adherence and biofilm formation. Pseudomonas infections are well known to be persistent and resilient in nature largely because of the tendency of the species to form biofilms. This study aimed at analyzing environmental strains of Pseudomonas genus with respect to their ability to execute twitching and swarming motilities as well as with respect to their ability to form biofilms both in the presence as well as in the absence of furanone, a substance that has the potential to prevent the formation of biofilms. Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and strains belonging to other species of the genus were analyzed. Twitching and swarming motility assays and biofilm-formation assays, both in the presence as well as in the absence of furanone, were performed. In twitching assay strains belonging to P. aeruginosa outperformed those belonging to other species. Interestingly, it was seen that the presence of furanone had a negative impact on formation of twitching and swarming motility zones. In the case of biofilm assays, it was observed that the presence of furanone resulted in an observable decrease in the degree of adhesion in 30% of the analyzed strains. Thus, from our results, it can be concluded that, as compared to other species, the strains belonging to P. aeruginosa exhibit a higher potential for twitching motility and similar performance in swarming motility and biofilm formation. It can also be concluded that furanone has the potential to interfere with both motilities as well as with biofilm formation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora SK, Neely AN, Blair B, Lory S, Ramphal R (2005) Role of motility and flagellin glycosylation in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn wound infections. Infect Immun 73:4395–4398
Beatson SA, Whitchurch CB, Semmler ABT, Mattick JS (2002) Quorum sensing is not required for twitching motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184:3598–3604
Boyd C, Smith TJ, El-Kirat-Chatel S, Newell PD, Dufrêne YF, O’Toole GA (2014) Structural features of the Pseudomonas fluorescensbiofilm adhesin LapA required for LapG-dependent cleavage, biofilm formation, and cell surface localization. J Bacteriol 196:2775–2788
Breidenstein EBM, Fuente-Núñez C, Hancock REW (2011) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: all roads lead to resistance. Trends Microbiol 19:419–426
Burrows LL (2012) Pseudomonas aeruginosa twitching motility: type IV pili in action. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:493–520
Chiang P, Burrows L (2003) Biofilm Formation by hyperpiliated mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 185:2374–2378
Chiang P, Habash M, Burrows LL (2005) Disparate subcellular localization patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type IV pilus ATPases involved in twitching motility. J Bacteriol 187:829–839
Chibeu A, Ceyssens PJ, Hertveldt K, Volckaert G, Cornelis P, Matthijs S, Lavigne R (2009) The adsorption of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage KMV is dependent on expression regulation of type IV pili genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 296:210–218
Daniels R, Vanderleyden J, Michiels J (2004) Quorum sensing and swarming migration in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:261–289
De Kievit TR, Gillis R, Marx S, Brown C, Iglewski BH (2001) Quorum-Sensing genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: their role and expression patterns. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1865–1873
Docquier JD, Riccio ML, Mugnaioli C, Luzzaro F, Endimiani A, Toniolo A, Amicosante G, Rossolini GM (2003) IMP-12, a new plasmid-encoded metallo-β-lactamase from a Pseudomonas putida clinical isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:1522–1528
Fuentefria DB, Ferreira AE, Corção G (2011) Antibiotic-resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa from hospital wastewater and superficial water: are they genetically related? J Environ Manag 92:250–255
Hentzer M, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Heydorn A, Andersen JB, Parsek MR, Rice SA, Eber L, Molin S, Høiby N, Kjelleberg S, Givskov M (2002) Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 148: 87–102
Kim SG, Yoon YH, Choi JW, Rha KS, Park YH (2012) Effect of furanone on experimentally induced Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation: in vitro study. Intern J Pediat Otorhinol 76:1575–1578
Klausen M, Heydorn A, Ragas P, Lambertsen L, Aaes-Jørgensen A, Molin S, Tolker-Nielsen T (2003) Biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa wild type, flagella and type IV pili mutants. Mol Microbiol 48:1511–1524
Kohler T, Curty LK, Barja F, van Delden C, Pechère JC (2000) Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on cell-to-cell signaling and requires flagella and pili. J Bacteriol 182:5990–5996
Murray TS, Kazmierczak BI (2008) Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits sliding motility in the absence of type IV pili and flagella. J Bacteriol 190:2700–2708
O´Toole GA, Kolter R (1998) Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple convergent signaling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28:449–461
Rasmussen TB, Manefield M, Andersen JB, Eber L, Anthoni U, Christophersen C, Steinberg P, Kjelleberg S, Givskov M (2000) How Delisea pulchra furanones affect quorum sensing and swarming motility in Serratia liquefaciens MG1. Microbiology 146:3237–3244
Shrout J, Chopp DL, Just CL, Hentzer M, Givskov M, Parsek MR (2006) The impact of quorum sensing and swarming motility on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation is nutritionally conditional. Mol Microbiol 62:1264–1277
Sperandio D, Decoin V, Latour X, Mijouin L, Hillion M, Feuilloley MGJ, Orange N, Merieau A (2012) Virulence of the Pseudomonas fluorescens clinical strain MFN1032 towards Dictyostelium discoideum and macrophages in relation with type III secretion system. BMC Microbiol 12:223
Spindler A, Otton LM, Fuentefria DB, Corção G (2012) Beta-lactams resistance and presence of class 1 integron in Pseudomonas spp. isolated from untreated hospital effluents in Brazil. Antonie van Leeuw 102:73–81
Stepanovic S, Vukovic D, Dakic I, Savic B, Svabic-Vlahovic M (2000) A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol Meth 40:175–179
Tremblay J, Déziel E (2008) Improving the reproducibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa swarming motility assays. J Basic Microbiol 48:509–515
Whiteley M, Bangera MG, Bumgarner RE, Parsek MR, Teitzel GM, Lory S, Greenberg EP (2001) Gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Lett Nat 413:860–864
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Djamel DRIDER.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otton, L.M., da Silva Campos, M., Meneghetti, K.L. et al. Influence of twitching and swarming motilities on biofilm formation in Pseudomonas strains. Arch Microbiol 199, 677–682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1344-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1344-7