Abstract
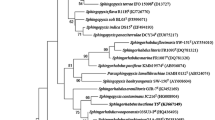
An aerobic, Gram-negative, yellow-pigmented, non-motile rod-shaped bacterium designated KMM 9574T was isolated from a sand sediment sample collected from the Sea of Japan seashore. Comparative 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that strain KMM 9574T belonged to the genus Sphingorhabdus sharing a highest sequence similarity to Sphingorhabdus marina JCM 14161T 96.8 %. Strain KMM 9574T was characterized by the major ubiquinone Q-10, and by the predominance of C18:1 ω7c, C16:0 2-OH, C16:1 ω7c, C17:1, followed by C15:0 2-OH and C14:0 2-OH in its fatty acid profile. Polar lipids consisted of phosphatidylcholine, sphingoglycolipid, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, an unknown phospholipid, and an unknown lipid. The DNA G+C content was 56.5 mol %. Based on phylogenetic analysis and distinctive phenotypic characteristics, strain 9574T is concluded to represent a novel species of the genus Sphingorhabdus, for which the name Sphingorhabdus pacificus sp. nov., is proposed. The type strain of the species is strain KMM 9574T (= NRIC 0922T = JCM 30177T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baik KS, Choe HN, Park SC, Hwang YM, Kim EM, Park C, Seong CN (2013) Sphingopyxis rigui sp. nov. and Sphingopyxis wooponensis sp. nov., isolated from wetland freshwater, and emended description of the genus Sphingopyxis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1297–1303
Bruns A, Rohde M, Berthe-Corti L (2001) Muricauda ruestringensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultatively anaerobic, appendaged bacterium from German North sea intertidal sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1997–2006
Collins MD, Shah HN (1984) Fatty acid, menaquinone and polar lipid composition of Rothia dentosacariosa. Arch Microbiol 137:247–249
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Jogler M, Chen H, Simon J, Rohde M, Busse HJ, Klenk HP, Tindall BJ, Overmann J (2013) Description of Sphingorhabdus planktonica gen. nov., sp. nov. and reclassification of three related members of the genus Sphingopyxis in the genus Sphingorhabdus gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1342–1349
Kim BS, Lim YW, Chun J (2008) Sphingopyxis marina sp. nov. and Sphingopyxis litoris sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2415–2419
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA Gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Mitchell K, Fallon RJ (1990) The determination of ubiquinone profiles by reversed-phase high performance thin-layer chromatography as an aid to the speciation of Legionellaceae. J Gen Microbiol 136:2035–2041
Owen J, Hill LR, Lapage SP (1969) Determination of DNA base composition from melting profiles in dilute buffers. Biopolymers 7:503–516
Park JM, Park S, Jung YT, Kim H, Lee JS, Yoon JH (2014) Sphingorhabdus arenilitoris sp. nov., isolated from a coastal sand and reclassification of Sphingopyxis rigui as Sphingorhabdus rigui comb. nov. and Sphingopyxis wooponensis as Sphingorhabdus wooponensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol doi:10.1099/ijs.0.064378-0 in press
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Romanenko LA, Tanaka N, Frolova GM, Mikhailov VV (2009) Sphingomonas japonica sp. nov., isolated from marine crustacean Paralithodes camtschatica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1179–1182
Romanenko LA, Tanaka N, Svetashev VI (2013) Devosia submarina sp. nov., isolated from deep sea surface sediments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3079–3085
Sasser M (1990) Microbial identification by gas chromatographic analysis of fatty acid methyl esters (GC-FAME).Technical Note 101. Newark, DE: MIDI
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Nakamura LK, Komagata K (1997) Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticus to the genus Paenibacillus and emended description of the genus Paenibacillus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:289–298
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. DC, American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, Washington, pp 607–655
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Yoon JH, Oh TK (2005) Sphingopyxis flavimaris sp. nov., isolated from sea water of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:369–373
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Moriya Ohkuma, Japan Collection of Microorganisms, JCM, Japan, for providing Sphingorhabdus type strains for comparative analyses. This study was supported by a grant from the RSF “Biodiversity and biotechnological potential of marine bacteria and fungi” no. 14-14-00030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
The DDBJ/GenBank/EMBL accession number of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain KMM 9574T is AB936074.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanenko, L.A., Tanaka, N., Svetashev, V.I. et al. Sphingorhabdus pacificus sp. nov., isolated from sandy sediments of the Sea of Japan seashore. Arch Microbiol 197, 147–153 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-014-1033-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-014-1033-8