Abstract
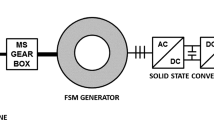
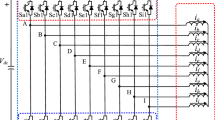
In this paper a unified approach for several synchronous machine current waveform optimization problems is presented. It is shown that the problems of ohmic losses minimization with and without the constraint of constant torque waveform admit solutions which can be described by the same equation in different vector spaces. The constraint of open-circuited neutral node is also investigated and it is shown that in the unified framework only a minor modification of the solution is needed irrespectively of the presence of the constant torque constraint. The ohmic losses and the torque ripple of the various waveforms are compared in the case of a permanent magnet synchronous generator used in a variable speed wind turbine. The optimal waveforms are also compared to non-optimal waveforms obtained using a diode rectifier.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman SJ (2003) Electric machinery fundamentals. McGraw-Hill, New York
Fitzgerald AE, Kingsley C Jr, Umans S (2002) Electric machinery. McGraw-Hill, New York
Wu AP, Chapman PL (2005) Simple expressions for optimal current waveforms for permanent-magnet synchronous machine drives. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 20(1):151–157
Chen S, Song A, Sekiguchi T (2000) High efficiency and low torque ripple control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on the current tracking vector of electromotive force. In: 2000 IEEE industry applications conference, vol 3, pp 1725–1729
Yang Y-P, Luh Y-P, Lee C-M (2002) A Novel Design of Optimal Phase Current Waveform for an Electric Vehicle Wheel Motor. Electric Power Comp Syst 30(7):705–721
Clenet S, Lefevre Y, Sadowski N, Astier S, Lajoie-Mazenc M (1993) Compensation of permanent magnet motors torque ripple by means of current supply waveshapes control determined by finite element method. IEEE Trans Magn 29(2):2019–2023
Favre E, Cardoletti L, Jufer M (1993) Permanent-magnet synchronous motors: a comprehensive approach to cogging Torque suppression. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 29(6):1141–1149
Hanselman DC (1994) Minimum Torque ripple, maximum efficiency excitation of brushless permanent magnet motors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 41(3):292–300
Chapman PL, Sudhoff SD, Whitcomb CA (1999) Optimal Current Control Strategies for Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Conversion 14(4):1043–1050
Zeng J, Degobert P, Hautier JP (2005) Minimum Torque ripple control of permanent magnet synchronous motor in the stationary reference frame. In: Electric machines and drives 2005 IEEE international conference on, pp 667–673
Morimoto S (1994) Loss minimization control of permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 41(5):511–517
Pinilla M, Martinez S (2011) Selection of main design variables for low-speed permanent magnet machines devoted to renewable energy conversion. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 26(3):940–945
Krizan J, Sudhoff S (2013) A design model for salient permanent-magnet machines with investigation of saliency and wide-speed-range performance. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 28(1):95–105
I. M. Gelfand and S. V. Fomin, Calculus of Variatons, Prentice Hall, 1963, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charalampidis, A.C., Chaniotis, A.E. & Kladas, A.G. Current waveform optimization techniques for synchronous machines and numerical evaluation in the case of a PMSM wind turbine generator. Electr Eng 99, 525–533 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0374-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0374-5