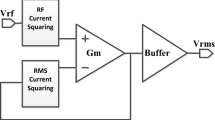
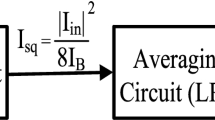
Abstract
A new realization of root mean square (RMS) detector comprising two controlled current conveyors, metal-oxide-semiconductor transistors and a single grounded capacitor is presented in this paper, without any external resistors and components matching requirements added. The proposed circuit can be used for measuring the RMS value of periodic, band-limited signals. Inherently, the circuit is well suited for IC implementation. The errors related to signal processing and errors bound were investigated and provided. To verify the theoretical analysis, the circuit PSpice simulations have also been included, showing good agreement with the theory. The maximum power consumption of the converter is \(\sim \)4.28 mW, at \(\pm \)1.25 V supply voltages.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Northrop RB (1990) Analog electronics circuits. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Heavey P, Whitney C (2004) RMS measuring principles in the application of protective relaying and metering. In: Proceedings of the 57th annual conference protective relay engineering, pp 469–489
Pogliana U (1997) Precision measurement of AC voltage below 20 Hz at IEN. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 46(2):369–372
Germer H (2001) High-precision AC measurements using the Monte-Carlo method. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 50(2):457–460
Yoon W-K, Deveney MJ (1998) Power measurement using the wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 47(5):1205–1210
Novotny M, Sedlacek M (2008) RMS value measurement based on classical and modified digital signal processing algorithms. Measurement 41(3):236–250
True RMS detector (2002) National semiconductor application note AN008474
DSCA33 ISOLATED True RMS Input Module (2011) AN101 Dataforth Corporation, USA
Frey DR (2004) Exact analysis of implicit RMS converters. Electron. Lett. 40(5):283–284
Abulma’atti MT (2009) Improved analysis of implicit RMS detectors. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 58(3):502–505
High Precision, Wide-Band RMS-to-DC Converter (2011) Analog devices application note AD637
Precision Wide Bandwidth, RMS-to-DC Converter (2004) Linear technology application note LTC1968
Mulder J, Serdijn WA, Woerd AC, Roermund AHM (1996) Dynamic translinear RMS-DC converter. Electron Lett 32:2067–2068
Mulder J, Serdijn WA, Roermund AHM (1997) An RMS-DC converter base don the dynamic translinear principle. IEEE Solid-State Circuits 32:1146–1150
Surakampontron W, Kumwachara K (1999) A dual translinear-based RMS-to-DC converter. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 47:456–464
Wasseneaar RF, Seevinck E, van Leeuwen MG, Speelman CJ, Holle E (1998) New techniques for high-frequency RMS-to-DC conversion based on a multifunctional V-to-I convertor. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 23(3):802–815
Milanović V, Gaitan M, Bowen ED, Tea NH, Zaghlou ME (1997) Thermoelectric power sensors for microwave applications by commercial CMOS fabrication. IEEE Electron Device Lett 18(9):450–452
Sedra AS, Smith KC (1970) A second-generation current conveyor and its applications. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory CT–17(1):132–134
Yuce E, Minaei S, Tokat S (2007) Root-mean-square measurement of distinct voltage signals. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 56(6):2782–2787
Fabre A, Saaid O, Wiest F, Boucheron C (1995) Current controllable bandpass filter based on translinear conveyors. Electron Lett 31:1727–1728
Pal K (1989) Modified current conveyors and their applications. Microelectron J 20:37–40
Soliman AM (1998) Modified current conveyor filters: classification and review. Microelectron J 29:133–149
Tangsrirat W, Surakampontorn W (2007) High output impendance current-mode universal filter employing dual-output current-controlled conveyors and grounded capacitors. AEU-Int J Electron Commun 61:127–131
Fabre A, Saaid O, Barthelemy H (1995) On the frequency limitations of the circuits based on the second generation current conveyors. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 7(2):113–129
Petrovic P, Zupunski I (2013) RMS detector of periodic, band-limited signals based on usage of DO-CCIIs. Measurement 46(9):3073–3083
Petrović P (2012) Root-mean-square measurement of periodic, band-limited signals. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on instrumentation and measurement technology (I2MTC), pp 323–327
Maneatis JG (1996) Low-jitter process-independent DLL and PLL based on self-biased techniques. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 31(11):1723–1732
Ingels M (1999) A 1-Gb/s, 0.7-\(\mu \)m CMOS optical receiver with full rail-to-rail output swing. IEEE J Soid. State Circuits 34(7):971–977
Grewing C, Winterberg K, Waasen S, Friedrich M, Puma GL, Wiesbauer A, Sandner C (2004) Fully integrated distributed power amplifier in CMOS technology, optimized for UWB transmitters. In: Proceedings of the radio frequency integrated circuits symposium, pp 87–90
Petrovic P, Stevanovic M (2006) Measuring of active power of synchronously sampled AC signals in presence of interharmnoics and subharmonics. IEE Proc Electr Power Appl 153(2):227–235
Zhang T, Eisenstadt WR, Fox RM, Yin Q (2006) Bipolar RMS power detectors. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 41(9):2188–2192
Rumberg B, Graham DW (2012) A low-power magnitude detector for analysis of transient-rich signals. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 47(3):676–685
Abdul-Karim MAH, Taha SMR, Omran SS (1987) Microprocessor-based implicit RMS meter. Int J Electron 62(6):953–959
Minaei S, Sayin OK, Kuntman H (2006) A new CMOS electronically tuneable current conveyor and its application to current-mode filters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I 53(7):1448–1457
GUM-Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (1993) ISO-1993
Prommee P, Angkeaw K, Somdunyakanok M, Dejhan K (2009) CMOS-based near zero-offset multiple inputs max-min circuits and its applications. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 61:93–105
Achigui HJ, Fayomi C, Massicotte D, Boukadoum M (2011) Low-voltage, high-speed CMOS analog latched voltage comparator using the “flipped voltage follower” as input stage. Microelectron J 42:785–789
Precision CMOS analog switches (1994) MAXIM, data sheet
Single positive-edge-triggered D-type flip-flop SN74LVC1G80 (2007) Texsas Instruments, data sheet
Annema AJ, Goksun GA (2012) 0.0025mm2 bandgap voltage reference for 1.1 V supply in standard 0.16 \(\mu \)m CMOS. In: Proceedings of 2012 IEEE international solid-state circuits conference, pp 364–366
Prommee P, Angkeaw K, Somdunyakanok M, Dejhan K (2009) CMOS-based near zero-offset multiple inputs max-min circuits and its applications. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 61:93–105
Banba H, Shiga H, Umezawa A, Miyaba T, Tanzawa T, Atsumi S, Sakui K (1999) A CMOS bandgap reference circuit with sub-1V operation. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 34(5):670–674
Kaewdang K, Kumwachara K, Surakampontorn W (2009) A translinear-based true RMS-to-DC converter using only npn BJTs. AEU-Int J Electron Commun 63(6):472–477
Yhang T, Eisenstadt WR, Fox RM, Yin Q (2006) Bipolar RMS power detectors. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 41(9):2188–2192
Spencer RR (1991) Analog implementation of artificial neural networks. Proc IEEE Int Symp Circuits Syst 2:1271–1274
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank to the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Serbia for its support of this work provided within the projects 42009 and OI-172057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrović, P.B. Current-tunable current-mode RMS detector. Electr Eng 97, 65–74 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-014-0313-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-014-0313-2