Abstract
Summary
Our objective was to investigate the associations between polymorphisms in Wnt pathway genes and peak bone mineral density (BMD) and body composition in young Chinese men. Our study identified that WNT5B and CTNNBL1 for both BMD and body composition, and WNT4 and CTNNB1 gene polymorphisms contribute to the variation in BMD and body composition in young Chinese men, respectively.
Introduction
Our objective was to investigate the associations between polymorphisms in WNT4, WNT5B, WNT10B, WNT16, CTNNB1, and CTNNBL1 genes and peak bone mineral density (BMD), lean mass (LM), and fat mass (FM) in young Chinese men.
Methods
Using SNPscanTM kits, 51 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in the 6 genes were genotyped in a total of 1214 subjects from 399 Chinese nuclear families. BMD, total lean mass (TLM), and total fat mass (TFM) were measured using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The associations between the 51 SNPs and peak BMD and body composition [including the TLM, percentage lean mass (PLM), TFM, percentage fat mass (PFM), and the body mass index (BMI)] were analyzed through quantitative transmission disequilibrium tests (QTDTs).
Results
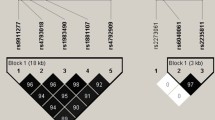
For peak BMD, we found significant within-family associations of rs2240506, rs7308793, and rs4765830 in the WNT5B gene and rs10917157 in the WNT4 gene with the lumbar spine BMD (all P < 0.05). We detected an association of rs11830202, rs3809269, rs1029628, and rs6489301 in the WNT5B gene and rs2293303 in the CTNNB1 gene with body composition (all P < 0.05). For the CTNNBL1 gene, six SNPs (rs6126098, rs6091103, rs238303, rs6067647, rs8126174, and rs4811144) were associated with peak BMD of the lumbar spine, femoral neck, or total hip (all P < 0.05). Furthermore, two of the six SNPs (rs8126174 and rs4811144) were associated with body composition.
Conclusions
This study identified WNT5B and CTNNBL1 for peak BMD and body composition in males from the Han Chinese ethnic group, and the results suggest a site-specific gene regulation. The WNT4 and CTNNB1 gene polymorphisms contribute to the variation in peak BMD and body composition, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Styrkarsdottir U, Halldorsson BV, Gretarsdottir S, Gudbjartsson DF, Walters GB, Ingvarsson T, Jonsdottir T, Saemundsdottir J, Center JR, Nguyen TV, Bagger Y, Gulcher JR, Eisman JA, Christiansen C, Sigurdsson G, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2008) Multiple genetic loci for bone mineral density and fractures. N Engl J Med 358:2355–2365
Mora S, Gilsanz V (2003) Establishment of peak bone mass. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 32:39–63
Koller DL, Zheng HF, Karasik D, Yerges-Armstrong L, Liu CT, McGuigan F, Kemp JP, Giroux S, Lai D, Edenberg HJ, Peacock M, Czerwinski SA, Choh AC, McMahon G, St PB, Timpson NJ, Lawlor DA, Evans DM, Towne B, Blangero J, Carless MA, Kammerer C, Goltzman D, Kovacs CS, Prior JC, Spector TD, Rousseau F, Tobias JH, Akesson K, Econs MJ, Mitchell BD, Richards JB, Kiel DP, Foroud T (2013) Meta-analysis of genome-wide studies identifies WNT16 and ESR1 SNPs associated with bone mineral density in premenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 28:547–558
Ferrari S (2008) Human genetics of osteoporosis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 22:723–735
Brown LB, Streeten EA, Shapiro JR, McBride D, Shuldiner AR, Peyser PA, Mitchell BD (2005) Genetic and environmental influences on bone mineral density in pre- and post-menopausal women. Osteoporos Int 16:1849–1856
Peacock M, Koller DL, Hui S, Johnston CC, Foroud T, Econs MJ (2004) Peak bone mineral density at the hip is linked to chromosomes 14q and 15q. Osteoporos Int 15:489–496
Kelly PJ, Nguyen T, Hopper J, Pocock N, Sambrook P, Eisman J (1993) Changes in axial bone density with age: a twin study. J Bone Miner Res 8:11–17
DiGirolamo DJ, Kiel DP, Esser KA (2013) Bone and skeletal muscle: neighbors with close ties. J Bone Miner Res 28:1509–1518
Sadie-Van GH, Crowther NJ, Hough FS, Ferris WF (2013) The interrelationship between bone and fat: from cellular see-saw to endocrine reciprocity. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:2331–2349
Kaji H (2014) Interaction between muscle and bone. J Bone Metab 21:29–40
Christodoulides C, Lagathu C, Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig A (2009) Adipogenesis and WNT signalling. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20:16–24
Karasik D, Kiel DP (2010) Evidence for pleiotropic factors in genetics of the musculoskeletal system. Bone 46:1226–1237
Xiao WJ, He JW, Zhang H, Hu WW, Gu JM, Yue H, Gao G, Yu JB, Wang C, Ke YH, Fu WZ, Zhang ZL (2011) ALOX12 polymorphisms are associated with fat mass but not peak bone mineral density in Chinese nuclear families. Int J Obes 35:378–386
Monroe DG, McGee-Lawrence ME, Oursler MJ, Westendorf JJ (2012) Update on Wnt signaling in bone cell biology and bone disease. GENE 492:1–18
von Maltzahn J, Chang NC, Bentzinger CF, Rudnicki MA (2012) Wnt signaling in myogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 22:602–609
Laudes M (2011) Role of WNT signalling in the determination of human mesenchymal stem cells into preadipocytes. J Mol Endocrinol 46:R65–R72
Tamanini S, Idolazzi L, Gatti D, Viapiana O, Fassio A, Rossini M (2013) Insight into the WNT system and its drug related response. Reumatismo 65:219–230
Maruotti N, Corrado A, Neve A, Cantatore FP (2013) Systemic effects of Wnt signaling. J Cell Physiol 228:1428–1432
Estrada K, Styrkarsdottir U, Evangelou E, Hsu YH, Duncan EL, Ntzani EE, Oei L, Albagha OM, Amin N, Kemp JP, Koller DL, Li G, Liu CT, Minster RL, Moayyeri A, Vandenput L, Willner D, Xiao SM, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Zheng HF, Alonso N, Eriksson J, Kammerer CM, Kaptoge SK, Leo PJ, Thorleifsson G, Wilson SG, Wilson JF, Aalto V, Alen M, Aragaki AK, Aspelund T, Center JR, Dailiana Z, Duggan DJ, Garcia M, Garcia-Giralt N, Giroux S, Hallmans G, Hocking LJ, Husted LB, Jameson KA, Khusainova R, Kim GS, Kooperberg C, Koromila T, Kruk M, Laaksonen M, Lacroix AZ, Lee SH, Leung PC, Lewis JR, Masi L, Mencej-Bedrac S, Nguyen TV, Nogues X, Patel MS, Prezelj J, Rose LM, Scollen S, Siggeirsdottir K, Smith AV, Svensson O, Trompet S, Trummer O, van Schoor NM, Woo J, Zhu K, Balcells S, Brandi ML, Buckley BM, Cheng S, Christiansen C, Cooper C, Dedoussis G, Ford I, Frost M, Goltzman D, Gonzalez-Macias J, Kahonen M, Karlsson M, Khusnutdinova E, Koh JM, Kollia P, Langdahl BL, Leslie WD, Lips P, Ljunggren O, Lorenc RS, Marc J, Mellstrom D, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Olmos JM, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Reid DM, Riancho JA, Ridker PM, Rousseau F, Slagboom PE, Tang NL, Urreizti R, Van Hul W, Viikari J, Zarrabeitia MT, Aulchenko YS, Castano-Betancourt M, Grundberg E, Herrera L, Ingvarsson T, Johannsdottir H, Kwan T, Li R, Luben R, Medina-Gomez C, Palsson ST, Reppe S, Rotter JI, Sigurdsson G, van Meurs JB, Verlaan D, Williams FM, Wood AR, Zhou Y, Gautvik KM, Pastinen T, Raychaudhuri S, Cauley JA, Chasman DI, Clark GR, Cummings SR, Danoy P, Dennison EM, Eastell R, Eisman JA, Gudnason V, Hofman A, Jackson RD, Jones G, Jukema JW, Khaw KT, Lehtimaki T, Liu Y, Lorentzon M, McCloskey E, Mitchell BD, Nandakumar K, Nicholson GC, Oostra BA, Peacock M, Pols HA, Prince RL, Raitakari O, Reid IR, Robbins J, Sambrook PN, Sham PC, Shuldiner AR, Tylavsky FA, van Duijn CM, Wareham NJ, Cupples LA, Econs MJ, Evans DM, Harris TB, Kung AW, Psaty BM, Reeve J, Spector TD, Streeten EA, Zillikens MC, Thorsteinsdottir U, Ohlsson C, Karasik D, Richards JB, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Uitterlinden AG, Ralston SH, Ioannidis JP, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F (2012) Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 56 bone mineral density loci and reveals 14 loci associated with risk of fracture. Nat Genet 44:491–501
Hsu YH, Kiel DP (2012) Clinical review: genome-wide association studies of skeletal phenotypes: what we have learned and where we are headed. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E1958–E1977
Medina-Gomez C, Kemp JP, Estrada K, Eriksson J, Liu J, Reppe S, Evans DM, Heppe DH, Vandenput L, Herrera L, Ring SM, Kruithof CJ, Timpson NJ, Zillikens MC, Olstad OK, Zheng HF, Richards JB, St PB, Hofman A, Jaddoe VW, Smith GD, Lorentzon M, Gautvik KM, Uitterlinden AG, Brommage R, Ohlsson C, Tobias JH, Rivadeneira F (2012) Meta-analysis of genome-wide scans for total body BMD in children and adults reveals allelic heterogeneity and age-specific effects at the WNT16 locus. PLoS Genet 8, e1002718
Koller DL, Ichikawa S, Lai D, Padgett LR, Doheny KF, Pugh E, Paschall J, Hui SL, Edenberg HJ, Xuei X, Peacock M, Econs MJ, Foroud T (2010) Genome-wide association study of bone mineral density in premenopausal European-American women and replication in African-American women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1802–1809
Ichikawa S, Koller DL, Padgett LR, Lai D, Hui SL, Peacock M, Foroud T, Econs MJ (2010) Replication of previous genome-wide association studies of bone mineral density in premenopausal American women. J Bone Miner Res 25:1821–1829
Jabbour L, Welter JF, Kollar J, Hering TM (2003) Sequence, gene structure, and expression pattern of CTNNBL1, a minor-class intron-containing gene—evidence for a role in apoptosis. Genomics 81:292–303
Liu YJ, Liu XG, Wang L, Dina C, Yan H, Liu JF, Levy S, Papasian CJ, Drees BM, Hamilton JJ, Meyre D, Delplanque J, Pei YF, Zhang L, Recker RR, Froguel P, Deng HW (2008) Genome-wide association scans identified CTNNBL1 as a novel gene for obesity. Hum Mol Genet 17:1803–1813
Andreasen CH, Mogensen MS, Borch-Johnsen K, Sandbaek A, Lauritzen T, Almind K, Hansen L, Jorgensen T, Pedersen O, Hansen T (2009) Studies of CTNNBL1 and FDFT1 variants and measures of obesity: analyses of quantitative traits and case–control studies in 18,014 Danes. BMC Med Genet 10:17
Tan LJ, Zhu H, He H, Wu KH, Li J, Chen XD, Zhang JG, Shen H, Tian Q, Krousel-Wood M, Papasian CJ, Bouchard C, Perusse L, Deng HW (2014) Replication of 6 obesity genes in a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies from diverse ancestries. PLoS ONE 9, e96149
Yu JB, Ke YH, He JW, Zhang H, Hu WW, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Gu JM, Fu WZ, Gao G, Yue H, Xiao WJ, Zhang ZL (2010) No association between LRP5 gene polymorphisms and bone and obesity phenotypes in Chinese male-offspring nuclear families. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:1464–1469
Yue H, He JW, Ke YH, Zhang H, Wang C, Hu WW, Gu JM, Fu WZ, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Zhang ZL (2013) Association of single nucleotide polymorphism Rs2236518 in PRDM16 gene with BMI in Chinese males. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:710–716
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68:978–989
Wang C, Zhang Z, Zhang H, He JW, Gu JM, Hu WW, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Fu WZ, Yue H, Ke YH, Zhang ZL (2012) Susceptibility genes for osteoporotic fracture in postmenopausal Chinese women. J Bone Miner Res 27:2582–2591
Zhang ZL, He JW, Qin YJ, Hu YQ, Li M, Zhang H, Hu WW, Liu YJ, Gu JM (2008) Association between myostatin gene polymorphisms and peak BMD variation in Chinese nuclear families. Osteoporos Int 19:39–47
Allison DB (1997) Transmission-disequilibrium tests for quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet 60:676–690
Spielman RS, McGinnis RE, Ewens WJ (1993) Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Am J Hum Genet 52:506–516
Xia F, Zhou JY, Fung WK (2011) A powerful approach for association analysis incorporating imprinting effects. Bioinformatics 27:2571–2577
Qin YJ, Shen H, Huang QR, Zhao LJ, Zhou Q, Li MX, He JW, Mo XY, Lu JH, Recker RR, Deng HW (2003) Estrogen receptor alpha gene polymorphisms and peak bone density in Chinese nuclear families. J Bone Miner Res 18:1028–1035
Zhang H, He JW, Gao G, Yue H, Yu JB, Hu WW, Gu JM, Hu YQ, Li M, Fu WZ, Liu YJ, Zhang ZL (2010) Polymorphisms in the HOXD4 gene are not associated with peak bone mineral density in Chinese nuclear families. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:977–983
Ke YH, Xiao WJ, He JW, Zhang H, Yu JB, Hu WW, Gu JM, Gao G, Yue H, Wang C, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Fu WZ, Zhang ZL (2012) Association of ALOX15 gene polymorphisms with obesity-related phenotypes in Chinese nuclear families with male offspring. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:201–207
Yue H, He JW, Zhang H, Wang C, Hu WW, Gu JM, Ke YH, Fu WZ, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Wu SH, Zhang ZL (2012) Contribution of myostatin gene polymorphisms to normal variation in lean mass, fat mass and peak BMD in Chinese male offspring. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:660–667
Gao G, Zhang ZL, He JW, Zhang H, Yue H, Hu WW, Gu JM, Fu WZ, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Yu JB (2010) No association of the polymorphisms of the frizzled-related protein gene with peak bone mineral density in Chinese nuclear families. BMC Med Genet 11:1
Kanazawa A, Tsukada S, Sekine A, Tsunoda T, Takahashi A, Kashiwagi A, Tanaka Y, Babazono T, Matsuda M, Kaku K, Iwamoto Y, Kawamori R, Kikkawa R, Nakamura Y, Maeda S (2004) Association of the gene encoding wingless-type mammary tumor virus integration-site family member 5B (WNT5B) with type 2 diabetes. Am J Hum Genet 75:832–843
Salpea KD, Gable DR, Cooper JA, Stephens JW, Hurel SJ, Ireland HA, Feher MD, Godsland IF, Humphries SE (2009) The effect of WNT5B IVS3C> G on the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in UK Caucasian subjects. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 19:140–145
Zmuda JM, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Moffett SP, Klei L, Kammerer CM, Roeder K, Cauley JA, Kuipers A, Ensrud KE, Nestlerode CS, Hoffman AR, Lewis CE, Lang TF, Barrett-Connor E, Ferrell RE, Orwoll ES (2011) Genetic analysis of vertebral trabecular bone density and cross-sectional area in older men. Osteoporos Int 22:1079–1090
James AW (2013) Review of signaling pathways governing MSC osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation. Scientifica (Cairo) 2013, 684736
Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, Suva LJ, Lane TF, Hankenson KD, MacDougald OA (2005) Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:3324–3329
Van Camp JK, Beckers S, Zegers D, Boudin E, Nielsen TL, Andersen M, Roef G, Taes Y, Brixen K, Van Hul W (2013) Genetic association study of WNT10B polymorphisms with BMD and adiposity parameters in Danish and Belgian males. Endocrine 44:247–254
Zheng HF, Tobias JH, Duncan E, Evans DM, Eriksson J, Paternoster L, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Lehtimaki T, Bergstrom U, Kahonen M, Leo PJ, Raitakari O, Laaksonen M, Nicholson GC, Viikari J, Ladouceur M, Lyytikainen LP, Medina-Gomez C, Rivadeneira F, Prince RL, Sievanen H, Leslie WD, Mellstrom D, Eisman JA, Moverare-Skrtic S, Goltzman D, Hanley DA, Jones G, St PB, Xiao Y, Timpson NJ, Smith GD, Reid IR, Ring SM, Sambrook PN, Karlsson M, Dennison EM, Kemp JP, Danoy P, Sayers A, Wilson SG, Nethander M, McCloskey E, Vandenput L, Eastell R, Liu J, Spector T, Mitchell BD, Streeten EA, Brommage R, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Brown MA, Ohlsson C, Richards JB, Lorentzon M (2012) WNT16 influences bone mineral density, cortical bone thickness, bone strength, and osteoporotic fracture risk. PLoS Genet 8, e1002745
Karasik D, Ferrari SL (2008) Contribution of gender-specific genetic factors to osteoporosis risk. Ann Hum Genet 72:696–714
Zhang ZL, Qin YJ, Huang QR, Hu YQ, Li M, He JW, Zhang H, Liu YJ, Hu WW (2006) Bone mineral density of the spine and femur in healthy Chinese men. Asian J Androl 8:419–427
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2014CB942903), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81170803 and 81370978), the Frontier Technology Joint Research Program of the Shanghai municipal hospitals (SHDC 12013115), the Shanghai Leading Talents Award (051), the Science and Technology Commission of Chongqing municipality (CSTC2013jcyjC00009), the Science, and the Technology Commission of Shanghai municipality (14JC1405000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital, and signed informed consent forms were obtained from all subjects.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
(DOCX 107 kb)
Table S2
(DOCX 103 kb)
Table S3
(DOCX 105 kb)
Table S4
(DOCX 102 kb)
Table S5
(DOCX 102 kb)
Table S6
(DOCX 103 kb)
Table S7
(DOCX 104 kb)
Table S8
(DOCX 102 kb)
Table S9
(DOCX 104 kb)
Table S10
(DOCX 107 kb)
Table S11
(DOCX 103 kb)
Table S12
(DOCX 103 kb)
Table S13
(DOCX 104 kb)
Table S14
(DOCX 105 kb)
Table S15
(DOCX 101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, H. et al. Polymorphisms in Wnt signaling pathway genes are associated with peak bone mineral density, lean mass, and fat mass in Chinese male nuclear families. Osteoporos Int 27, 1805–1815 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3457-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3457-7