Abstract
We investigate the impact of the reduction of non-tidal loading (NTL) in the computation of secular terrestrial reference frames (TRFs) from Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) observations. There are no conventional models for NTL in the geodetic community yet, but the Global Geophysical Fluid Center prepared a set of corresponding site displacements for the 2020 realizations of the International Terrestrial Reference System. We make use of these data, which comprise the total NTL consisting of non-tidal atmospheric, oceanic, and hydrological loading. The displacement series contain linear trends (i.e., offsets plus drifts), and since these affect the estimated linear station positions and the realized geodetic datum in a secular TRF, we remove the trends before reducing the NTL in our computations. The displacements are applied at two different levels of the parameter estimation process: the observation and the normal equation level. This way, we can analyze whether the latter offers a suitable approximation if the original observations have not been reduced by NTL. We find that the TRF statistics are hardly affected by the NTL. The largest impact is given for the secular motion of antennas with short observation time spans. The application level is basically irrelevant for the linear antenna positions, but it leads to differences in the rates of the jointly estimated Earth orientation parameters (EOPs). Secular TRF solutions and session solutions deviate with respect to the parameterization of the antenna coordinates, and thus also with respect to the correlations between the estimated antenna parameters and the EOPs. Due to this, the consistently estimated EOP series also show differences. However, for both solution types the reduction of the NTL leads to a change of the annual signal in the EOP series.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) regularly publishes conventions for the geophysical models applied in the analysis of the four geodetic space techniques: Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI), Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR), the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), and Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite (DORIS). The latest version, the IERS Conventions 2010 (Petit and Luzum 2010), contains models for the tidal deformation of the Earth’s crust due to the gravitational forces of external bodies like the Sun and the Moon (e.g., Earth tides) or the rotation of the Earth (e.g., pole tides). The document further recognizes the existence of non-tidal deformations, which are generated from the redistribution of air and water masses in the Earth system that is not driven by the aforementioned tidal forces. This non-tidal loading (NTL) is usually separated into atmospheric, oceanic, and hydrological components. For example, if the barometric pressure increases (decreases) at a site due to atmospheric fluctuation, the Earth’s elastic surface is pushed down (lifted up) there. Such vertical displacements can have a magnitude of a few centimeters, also for the other two NTL components. Likewise, horizontal displacements are gene-rated, even though their sizes are about 2–5 times smaller. These magnitudes as well as the relevance of NTL for the geodetic space techniques have been shown in many stu-dies during the last decades (e.g., Rabbel and Zschau 1985; van Dam and Wahr 1987; MacMillan and Gipson 1994; van Dam et al. 2001; Tregoning and van Dam 2005a; Dach et al. 2010; Williams and Penna 2011; Eriksson and MacMillan 2014). However, there still are no recommended geophysical or empirical models for site displacements due to NTL in the current IERS Conventions. The various existing mo-dels show significant differences especially for the non-tidal oceanic and the hydrological loading (e.g., Roggenbuck et al. 2015; Glomsda et al. 2022), so they have been rated to not be sufficiently accurate. Only the International VLBI Service for Geodesy and Astrometry (IVS, Nothnagel et al. 2017) requests its Analysis Centers (ACs) to consider non-tidal atmospheric loading in the processing of VLBI observations, since the agreement is quite strong for the respective models nowadays.
A major application of the analysis results of the geodetic space techniques is the realization of the International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS), which co-rotates with the Earth. Such realizations, called Terrestrial Reference Frames (TRFs), contain the time-dependent coordinates of reference points (i.e., markers of the VLBI, SLR, GNSS, and DORIS observing stations) fixed to the Earth’s crust. In secular TRFs, these coordinates change linearly with time, and hence any instantaneous, nonlinear deformations of the Earth should ideally be reduced in the analysis. However, the official contributions of the technique services IVS, International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS, Pavlis et al. 2021), International GNSS Service (IGS, Johnston et al. 2017), and International DORIS Service (IDS, Willis et al. 2010) to the realizations of the ITRS are not yet reduced by NTL.
To account for the non-tidal signals, the three IERS ITRS Combination Centers at the Institut national de l’information géographique et forestière (IGN, France), NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL, USA), and the Deutsches Geodäti-sches Forschungsinstitut der Technischen Universität München (DGFI-TUM, Germany) take distinct measures. In its two latest versions of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF), the IGN estimated annual and semi-annual signals for the position time series of the four geodetic space techniques (both ITRF2014, Altamimi et al. 2016, and ITRF2020, Altamimi et al. 2023), as well as additional periodic signals for the first 8 draconitic harmonics of the Global Positioning System (GPS) for the position time series of the IGS stations (ITRF2020 only). After all, the ITRS realizations by IGN are based on a combination at the solution level. On the other hand, the ITRS realizations by DGFI-TUM, named DTRF, are combined at the normal equation level. DTRF2014 (Seitz et al. 2022) and DTRF2020Footnote 1 are reduced by NTL at the normal equation level, too, namely by the application of dedicated site displacements derived from geophysical mo-dels and provided by the Global Geophysical Fluid Center (GGFC). Finally, the ITRS realizations by JPL, named JTRF (e.g., JTRF2014, Abbondanza et al. 2017), are no secular TRFs (like the ITRS realizations by IGN and DGFI-TUM) but epoch frames consisting of time series of reference points, which naturally contain nonlinear behavior.
Collilieux et al. (2009) have analyzed the application of site displacements due to NTL at the solution level for the ITRF combination. Their results were generally promising, but not significant enough to adapt this approach for the subsequent ITRF2014 or ITRF2020. The insufficient accuracy of the loading models was identified to be a major limitation. Seitz et al. (2022) describe the application at the normal equation level for the DTRF, and they also find that the reduction of NTL is basically beneficial, in particular for mitigating annual signals in the datum parameters. The application at observation level, i.e., the reduction of NTL directly in the functional models of the geodetic space techniques, has mostly been discussed for daily or weekly single-technique solutions (e.g., Tregoning and van Dam 2005b; van Dam et al. 2012; Eriksson and MacMillan 2014). Only few studies (e.g., Böhm et al. 2009 for VLBI) compute single-technique secular TRFs when reducing NTL. As long as the distinct technique services do not consider NTL consistently, and no institution processes all techniques jointly, the analysis of a combined (secular) TRF with NTL applied at the observation level is not possible.
Our study will not completely fill this gap, either. Ne-vertheless, we generate several VLBI-only secular TRFs, which reduce NTL at both the observation and the normal equation level. We make use of the same geophysical NTL models as will be applied in the DTRF2020 (compare Glomsda et al. 2022), which represent recent updates and should be more accurate than the models used in the previous decades. We examine the discrepancies between the application levels and hence the suitability of a reduction of NTL at the normal equation level in a secular TRF solution. This might provide insights for the inter-technique combination as well. In previous studies (Glomsda et al. 2020, 2021), we already investigated the impact of NTL in VLBI single-session solutions, and we found that the results for both levels were similar and systematically beneficial. However, we will check whether there are qualitative differences between the two types of solutions here. In particular, we will focus on the Earth orientation parameters (EOPs).
In Sect. 2, we start with a description of the input data, i.e., the VLBI observations and the site displacements obtained from the geophysical models. The theory of the computation of single-technique secular TRFs and the reduction of nonlinear displacements is summarized in Sect. 3. The main results regarding the impact of the reduction of NTL on the estimated antenna offsets and velocities and the EOPs are presented in Sect. 4, before the final conclusions are drawn in Sect. 5.
2 Input data
2.1 VLBI observations
In this study, we basically use the same legacy VLBI observations that have been considered as input to the ITRS 2020 realizations. These comprise all 24 h VLBI sessions with at least three antennas involved between August 1979 and December 2020.Footnote 2 The official contribution by the IVS is a combination of the reprocessed normal equations for these sessions provided by the distinct IVS ACs (Hellmers et al. 2022). All ACs had to apply consistent geophysical models in their processing—in particular, the VLBI observations must not be reduced by any NTL. Since we are going to apply NTL at the observation level, however, we are not able to use the IVS contribution. Instead, we have to set up our own single-session normal equations (compare Sect. 3.1), generated with the DGFI-TUM Orbit and Geodetic parameter estimation Software (DOGS; Gerstl et al. 2000; Kwak et al. 2017).
We did not exactly recycle our IVS input (DGFI-TUM is an operational AC of the IVS), but we included a few model updates for the new normal equations, which are not expected to have an impact on our results. Most importantly, we chose the ITRF2020 for the a priori antenna positions. Furthermore, we applied the latest DGFI-TUM ocean tide model EOT20 (Hart-Davis et al. 2021), and we increased the resolution of the estimated tropospheric gradients from 24 to 6 h. Finally, the Galactic aberration of the radio source positions (see, e.g., MacMillan et al. 2019) is no longer considered by a direct shift of the a priori positions taken from the International Celestial Reference Frame 3 (ICRF3, Charlot et al. 2020), but by a delay correction in the theoretical VLBI model. The other geophysical and technique-specific models are in line with the IERS Conventions 2010 and the IVS requirements for the ITRS 2020 realization.
We could not include the full set of the aforementioned legacy sessions, because some of them either failed in the single-session reprocessing already, or their results were corrupting our subsequent secular TRF solutions. In the end, we used 5878 (out of 6519) sessions between 1980 and 2020.
2.2 Non-tidal loading data
Concerning the NTL data, we picked the contribution to the ITRS 2020 realizations by the GGFC (Boy 2021). The same data will be applied in the DTRF2020 and have been analyzed extensively by Glomsda et al. (2022). They consist of site displacements for the relevant geodetic observing stations, which have been derived from surface pressure anomalies by the common global convolution with weighting Green’s functions (see, e.g., Farrell 1972, or Petrov and Boy 2004). The driving geophysical and meteorological models for the pressure anomalies are ECMWF (European Center for Medium-range Weather Forecasts) ERA5 (Hersbach et al. 2020) for the non-tidal atmospheric and hydrological loading, and the Toulouse Unstructured Grid Ocean model (TUGO-m, see Carrère and Lyard 2003, and Mémin et al. 2020) for the non-tidal oceanic loading. The site displacements for these NTL components are available separately, but Boy (2021) ensured the conservation of mass when they are combined.
Time series of the combined site displacements (CM frame) generated from non-tidal atmospheric, oceanic, and hydrological loading for the VLBI antenna NOTO in Italy. The original values (blue) have been corrected for the linear trend (black) to obtain the detrended series (red). Top: up, middle: North, bottom: East direction
All displacements are provided in the center of figure of the solid Earth (CF) frame, and in the center of mass of the total Earth system (CM) frame, which includes the atmosphere and the hydrosphere. The differences
between the CF and CM displacements \(\varvec{\delta }_\textrm{NTL}\) at a site \(\varvec{S}\) and an epoch \(t\) yield the geocenter motion contributions \(\varvec{g}_\textrm{NTL}(t)\) generated by NTL, which are equal for all sites. Geocenter motion is the time series of the distance between the origins of the CF and CM frames (see, e.g., Dong et al. 2003), and it plays a crucial role in the realization of the ITRS (see Altamimi et al. 2016, or Seitz et al. 2022). For the DTRF2020, we will apply the site displacements of the CM frame (see Glomsda et al. 2022), as the center of mass is the origin of the ITRS (realized by SLR). For VLBI, the choice of the frame is basically irrelevant (see, e.g., Eriksson and MacMillan 2014, and Glomsda et al. 2021), because this technique depends on the baselines between each two radio antennas. When computing the difference between two antennas’ positions \(\varvec{S}_1\) and \(\varvec{S}_2\), which have been shifted by displacements \(\varvec{\delta }_\textrm{NTL}\), the site-independent translation \(\varvec{g}_\textrm{NTL}\) cancels, such that
To recycle the NTL data used for the DTRF2020, we applied the CM displacements in this study, too. The CF displacements, however, can be computed with Eq. (1) and the geocenter motion contribution time series, which is also provided by Boy (2021).
The time series of the site displacements and the corresponding geocenter motion contribution contain linear trends (i.e., offsets plus drifts, compare Glomsda et al. 2022), in particular for the hydrological component. Such trends distort the estimated station offsets and velocities of secular TRFs, i.e., a part of the linear station motions will be captured by the NTL. To avoid this for both the DTRF2020 and the VLBI-only secular TRFs generated in this study, the trends are removed from the displacement time series before the latter are applied (compare Fig. 1). If the trends were not removed, the pure linear station motions could not be obtained from the secular TRF without getting hold of the displacement data and correcting the motions for these trends.
Finally, since the input data for the ITRS 2020 realizations have not been reduced by NTL at the observation level, only the normal equations of the distinct geodetic space techniques can be reduced during the computation of the DTRF2020. At the normal equation level, however, the temporal resolution of the site displacements gets lower. Originally, the data by Boy (2021) have a resolution of 1 h, but only one displacement value can be applied per site coordinate and normal equation. Hence, average values have to be computed for the reduction in the DTRF2020. For VLBI and GNSS, this would be the average displacement (per antenna) for each 24 h observing session. For SLR and DORIS, on the other hand, these would even be 7-day (15-day in the early years of SLR) averages.
3 VLBI-only terrestrial reference frames
3.1 Single-session solutions
At first, observation and normal equations are set up for the single VLBI sessions with DOGS-RI (Radio Interferometry). The estimated variables comprise constant antenna coordinates, constant radio source coordinates, linear Earth rotation parameters (ERPs), constant celestial pole offsets, as well as piecewise linear clock and tropospheric parameters. The estimation process itself is based on the Gauss–Markov model (see, e.g., Koch 1999), which we will recap briefly.
The linearized observation equations of each session \(s\) are given by
with the matrix of partial derivatives \(A^s_{ij} = \partial f(t_i) / \partial x^s_j\) of the theoretical VLBI delay model \(f\) w.r.t. the parameters \(x_j^s\) (\(j=1,\ldots ,n^s\)), the vector \(\varvec{\varDelta x}^s\) of corrections to the a priori parameter values in vector \(\varvec{x}^{s,0}\), and the vector
of observed minus computed delays. The optimum solution for the single session \(s\) in terms of the minimum sum of squared residuals in the vector
is given by the solution of the normal equation
where \(\varvec{N}^s = (\varvec{A}^s)^T \varvec{P}^s \varvec{A}^s\) is called the normal equation matrix with right-hand side \(\varvec{y}^s = (\varvec{A}^s)^T \varvec{P}^s \varvec{l}^s\). \(\varvec{N}^s_D\) is a matrix of datum constraints (usually no-net-translation, NNT, for antenna coordinates, and no-net-rotation, NNR, for antenna and radio source coordinates), which are necessary to regularize the normal equation matrix. \(\varvec{P}^s\) is a (usually diagonal) weight matrix filled with the reciprocals of the squared formal errors of the real observations \(b^s_i\) (\(i=1,\ldots ,m^s\)). Finally, the a posteriori variance factors of the single-session solutions are
and the covariance matrix of the vector of estimates \(\varvec{x}^s = \varvec{x}^{s,0} + \varvec{\varDelta x}^s\) is given by
3.2 Secular terrestrial reference frame
When computing the single-session and secular TRF solutions with DOGS-CS (Combination and Solution) for this study, we reduce the clock and tropospheric parameters, and we fix the radio source coordinates to their a priori values. For our secular TRFs, we additionally transform the constant antenna coordinates \(p(t_s)\) at the session epochs \(t_s\) into linear ones, parameterized by an offset \(o(t_0)\) at a suitable reference epoch \(t_0\) and a constant velocity \(d\) (compare Angermann et al. 2004; Seitz et al. 2022):
As a consequence, the left-hand side of the observation equation (3) is modified,
with matrix
(see Bloßfeld 2015; for ease of notation, we restrict the formulas to the antenna coordinates in \(\varvec{p}\)). Likewise, the normal equation system is transformed,
and the new a priori values fulfill \(\varvec{o}^{s,0} + \varvec{B}^s \varvec{d}^{s,0} = \varvec{p}^{s,0}\).
The secular TRF can now be obtained from the combination of the single-session normal equation systems. The \(q\) transformed, datum-free, and session-wise components are stacked like this:
where the normal equation matrices \(\varvec{N}^s\) and right hand sides \(\varvec{y}^s\) have been extended by rows and columns of zeros to match a dimension equal to the total number of estimated parameters \(n\). With an a priori variance factor \(\sigma _0^2\), the weight matrix of the combination is given by
The datum constraints in a matrix \({{\varvec{N}}}_{\!\!D}\) are only applied to the stacked normal equation system, and they now consist of NNT and NNR conditions for the antenna positions and velocities. Finally, the secular TRF solution is obtained by solving
for the transformed and stacked parameter vector \(\varvec{x}\), and the a posteriori variance factor is computed as
with the residual vector \(\varvec{v}\). \(\hat{\sigma }_0^2\) contributes to the covariance matrix of the estimates analogous to Eq. (8).
3.3 Application of site displacements
As mentioned before, reducing NTL means reducing the (VLBI) observations by the respective site displacements at one of the following levels:
-
1.
The observation level, where the original site displacements are directly considered in the linearized observation equations (see, e.g., van Dam and Wahr 1987, or Petrov and Boy 2004). This is the most rigorous approach.
-
2.
The normal equation level, where the normal equation system is modified with average displacements (see, e.g., Glomsda et al. 2020, or Seitz et al. 2022). This is only an approximate approach.
-
3.
The solution level, where the site displacements are simply removed from either the final coordinate estimates (see, e.g., Böhm et al. 2009, or Williams and Penna 2011), or from the input coordinates to a secular TRF combination at solution level (Collilieux et al. 2009).
In the following, we present some theoretical implications of the reduction of site displacements in a (VLBI-only) secular TRF. Glomsda et al. (2021) have done this for single-session solutions. In this study, however, we will only treat the first two levels.
3.3.1 Observation level
If site displacements are applied at the observation level of the Gauss–Markov model, the theoretical delay function \(f\) changes to \({\tilde{f}}\). Following Glomsda et al. (2021), we end up with new normal equation systems for each session \(s\),
and consequently a new stacked normal equation system for the secular TRF:
3.3.2 Normal equation level
Applying average site displacements in a vector \(\varvec{\bar{\delta }}^s_\textrm{NTL}\) at the normal equation level means approximating the new theore-tical (delay) function by
(see Seitz et al. 2022). As a consequence, the right-hand side of the normal equation system converts to
while the normal equation matrices \(\varvec{N}^s\) remain unchanged. The new stacked system becomes
3.3.3 Comparison of application levels
Comparing Eqs. (18) and (21), we identify several potential sources for deviations between the secular TRFs with NTL reduced at the observation and the normal equation level, respectively:
-
the loss of temporal resolution by the average displacement vector \(\varvec{\bar{\delta }}^s_\textrm{NTL}\) in Eq. (19).
-
the differences in the single-session normal equation matrices, \(\varvec{{\tilde{N}}}^s\) vs. \(\varvec{N}^s\).
-
the differences in the single-session observation matrices, \(\varvec{\tilde{A}}^s\) vs. \(\varvec{A}^s\), which affect the estimated antenna parameters in Eq. (10).
Glomsda et al. (2021) show that \(\varvec{\tilde{A}}^s \approx \varvec{A}^s\), and hence \(\varvec{{\tilde{N}}}^s \approx \varvec{N}^s\) for most \(s\). As a consequence, the impact of the application level on the estimated antenna positions will mostly be low in VLBI single-session analysis, especially if the temporal variation of the displacements is small du-ring a session (which holds for the hydrological loading in particular, compare Glomsda et al. 2020). However, the contingently small discrepancies per session might accumulate to a significant deviation of the new matrix \(\varvec{{\tilde{N}}}\) from \(\varvec{N}\) in a secular TRF solution. In addition, the new offset and velocity parameters \(\varvec{{\tilde{o}}}^s\) and \(\varvec{{\tilde{d}}}^s\) depend on \(\varvec{\tilde{A}}^s\), respectively.
On the other hand, a linear station motion is estimated in a secular TRF. Seasonal and other variations in single-session positions are hence averaged out, at least if the coordinate time series are long enough (e.g., more than \(2.5\) years according to Blewitt and Lavallée 2002). As a consequence, the differences between the application levels might be averaged out as well. Significant deviations might rather be observable for the jointly estimated EOPs, which are not bound to a linear motion across all sessions.
3.3.4 Comparison of solution types
An eminent difference between single-session and secular TRF solutions is given by the datum constraints. There is a separate matrix \(\varvec{N}_D^s\) for each session \(s\), and Böhm et al. (2009) and Glomsda et al. (2021) claim that the choice of datum stations determines how the (NTL) site displacements are transformed into changes in the estimated antenna coordinates. Hence, there is a network effect in the position time series created from single-session solutions. In the computation of a secular TRF, on the other hand, the datum constraints \(\varvec{N}_{\!\!D}\) are only applied after the stacking of the datum-free normal equation systems. These constraints are defined for a fixed set of stable stations and across all sessions. As a consequence, there is no comparable network effect related to the NTL, at least no time-dependent one.
3.4 Secular TRF computation details
In this work, we basically generate all VLBI-only secular TRFs according to the approach described in Sect. 3.2. Some more details, however, need to be mentioned.
A few antennas do not reveal a long-term linear motion across their whole observation period, because their positions have been abruptly shifted by earthquakes. After these events, the antenna coordinates follow nonlinear motions due to post-seismic deformation (PSD; compare Altamimi et al. 2016) of the Earth’s crust. Such deviations from the constant velocity \(d\) need to be accounted for, and we apply the same approach as will be used for the DTRF2020. Namely, we model the PSD by exponential or logarithmic functions, or by combinations of the latter, for each corresponding antenna coordinate separately. The resulting site displacements are valid for certain periods after each earthquake, and all normal equations of VLBI sessions that take place during these periods and contain an affected antenna are corrected for these displacements before being stacked.
The introduction of antenna velocities according to Eqs. (9) and (12) is only performed after the single-session normal equations have been corrected for PSD. As a priori values \(o^0\) and \(d^0\) for the new antenna offsets at the reference epoch and the velocities, we use the values of the previous DTRF2014 and zero, respectively. The reference epoch \(t_0\) is set to 2010.0, like for the DTRF2020. For each observation period before and after a position series discontinuity, new offsets and velocities need to be set up. As a consequence, a single antenna can have several so-called solution numbers (A01, A02,...), which are valid at distinct intervals. Next to the ones created by earthquakes, there are also other antenna-specific discontinuities (compare Seitz et al. 2022). For example, we introduced a break at 2017-10-18 for the \(20\) m antenna at Ny Alesund, Svalbard, due to post-glacial uplift (Kierulf et al. 2022), and another one at 2011-11-10 for the \(40\) m antenna at Yebes, Spain, due to the introduction of the gravitational deformation model (Nothnagel et al. 2014).
We are not estimating parameters for all antennas in our set of single sessions. In particular, we reduce all solution numbers that participate in less than 20 sessions to obtain sufficiently stable results. In the end, we estimate offsets and velocities for 119 solutions of 84 antennas.
As already mentioned in Sect. 3.2, the remaining free parameters are the linear antenna positions and the EOPs. The datum constraints \(\varvec{N}_{\! D}\) consist of NNT and NNR conditions w.r.t. the offsets and velocities of 33 steady antennas. The EOPs have been loosely constrained with standard deviations of \(10\) mas, \(50\) mas, and \(5\) ms for the nutation (\(DX_\textrm{CIP}, DY_\textrm{CIP}\)), polar motion (\(dx_\textrm{pol}\), \(dy_\textrm{pol}\), as well as their rates), and Earth rotation (\(\varDelta \textrm{UT}1, \textrm{LOD}\)) parameters, respectively. These values ensure numerical stability but keep the diversity of the estimated standard deviations between the EOPs.
4 Impact of non-tidal loading on TRF
4.1 NTL scenarios
In Table 1, we summarize the distinct VLBI-only secular TRF scenarios that we investigate in this study. REF is the refe-rence scenario, where no NTL is reduced at all. The formulas and notations of Sects. 3.1 and 3.2 belong to this case. In scenario ATM, we reduce only non-tidal atmospheric loading (i.e., the ECMWF ERA5 data with the inverted barometer hypothesis for the atmospheric pressure above the oceans, compare Boy 2021) at the observation level. This is the setup for the regular, non-ITRS IVS contributions. All three (atmospheric, oceanic, hydrological) components of NTL are reduced at the observation level in scenario SUM. As with scenario ATM, the linear trends have been removed from the corresponding site displacements (compare Sect. 2.2). Finally, in scenario NEQ, we reduce the combined and detrended NTL data at the normal equation level, as is done for the DTRF2020.
4.2 Solution statistics and formal errors
Original (top) and relative (bottom) changes in the formal errors of the estimated x-coordinate velocities for our NTL scenarios (blue: ATM, red: SUM, yellow: NEQ) w.r.t. the reference scenario REF. The corresponding antennas (x-axes) are ordered by the length of their observation periods. The straight lines indicate the ratios between the a posteriori variance factors of the NTL scenarios and the scenario REF
In Table 2, we summarize the statistics for the distinct secular TRF solutions. They do not change significantly after the reduction of any NTL, so the least-squares optimization for a secular TRF appears to be rather insensitive to this effect. At least, we observe an improvement in the weighted square sum of residuals \(\varvec{v}^T \varvec{P} \, \varvec{v}\) in each case. The best, i.e., smallest, value is obtained when all three NTL components are considered (SUM), and the values are quite close for the two application levels (SUM and NEQ).
The ratios between the a posteriori variance factors \(\hat{\sigma }_0^2\) of the NTL scenarios and the reference scenario will determine the size of the change in the formal errors, i.e., the standard deviations of the estimated parameters. Namely, the para-meter covariance matrix is given by
From these equations, we see that the formal errors are additionally affected by the new entries in the combined normal equation matrix \(\varvec{{\tilde{N}}}\) when the NTL is reduced at the observation level.
In Fig. 2, we show the changes in formal errors for the estimated x-coordinate velocities after the reduction of NTL. The absolute changes are very small (with a magnitude of a few micrometers per year, compare the top panel), and the relative changes are basically located on the lines representing \((\hat{\sigma }_0^\textrm{NTL})^2 / (\hat{\sigma }_0^\textrm{REF})^2\) (bottom panel). However, there is some additional variation for the scenarios where the covariance matrix of the secular TRF contains \(\varvec{{\tilde{N}}}\), i.e., all except for NEQ. The formal errors are ordered by the length of the observation periods for their corresponding antennas. The absolute changes in formal errors are largest for antennas with short observation periods, mainly because the relative changes are more or less constant, and the errors are largest for these antennas in the reference scenario in the first place. The same behavior is also observed for the formal errors of the other estimated parameters.
4.3 Estimated antenna motions
The estimated offsets and horizontal velocities of the scenario with all NTL components reduced at the observation level (SUM) are shown in Fig. 3. The differences between the estimated linear motions of the distinct scenarios are hardly visible on such world maps, so the changes w.r.t. the reference scenario are plotted in topocentric coordinates in Fig. 4. There, the antennas are still ordered by the length of their observation periods. When reducing NTL, the position offsets can change by a few millimeters, but mostly for antennas with short observation periods. The largest vertical velo-city change is about \(6\) mm/year for the antenna RAEGYEB, Spain, which has the shortest observation period of less than \(1\) year. According to Blewitt and Lavallée (2002), at least \(2.5\) years of observations are necessary to estimate a reliable velocity (in the presence of annual signals). However, if we reduce residual signals like NTL, we expect the velocity estimates to be improved for the short periods. As Fig. 4 suggests, the impact of NTL is basically negligible for observation periods longer than 15 years, since the nonlinear signals are almost completely averaged out. Soja et al. (2016) emphasize that the period length itself is not the main criterion, but an antenna also needs to participate in a sufficiently large number of sessions. If there are only few sessions available for particular antennas, this is also reflected in large formal errors of the estimated position parameters. The impact of the reduction of NTL is seldom exceeding these formal errors, which are represented by the error bars in Fig. 4.
Another conclusion from this figure is the minor relevance of the NTL reduction level for the linear antenna motions. The differences in estimates for scenarios SUM and NEQ w.r.t. the reference scenario are very similar, so the potential sources for deviations listed in Sect. 3.3 do not take much effect. Regarding the antenna positions, reducing NTL at the normal equation level hence is a suitable approximation for the reduction at the observation level.
Changes in estimated topocentric coordinate offsets (left column) and velocities (right column) between the reference scenario REF and the scenarios ATM (blue), SUM (red), and NEQ (yellow). The corresponding antennas are ordered by the length of their observation periods (x-axes), and the error bars reflect the formal errors of the respective parameters in the NTL scenarios. Top: North, middle: East, bottom: up direction
An important open question is whether the new antenna motions are beneficial. When comparing our VLBI-only secular TRFs to the VLBI single-technique solution of the ITRF2020, we found a very good agreement for antennas with an observation period longer than 15 years (independent of the scenario). However, for many of the antennas with a less long or dense observation history, the discrepancies in estimated velocities already were much larger than the impact of any NTL in our study. The ITRF2020 is combined at the solution level, and semi-annual and annual signals are fitted to the position time series, so the methodologies are quite different in the first place. For this reason, maybe, we could not show that our velocities approach those of the ITRF2020 when we reduce NTL, either.
Another validation procedure would be to check for an improvement of local ties of co-located stations, as done by Collilieux et al. (2009) and Seitz et al. (2022). However, since we are only using the VLBI-technique, we do not have that possibility here. This analysis could be caught up with the DTRF2020.
Estimated velocities (y-axes) for solutions A01 (black, all three series almost identical) and A02 (colored) for different lengths \(T_2\) of the observation periods for solutions A02 (x-axes). The period lengths for solutions A01 are equal to \(T-T_2\), with \(T\) being the original total observation period length. The scenarios REF (blue), SUM (red), and NEQ (yellow) are considered for the sample antennas WETTZELL (left, \(T = 37.1\) years) and SESHAN25 (right, \(T = 32.6\) years). Top: x, middle: y, bottom: z direction
Instead, we use an indirect approach: We artificially introduce discontinuities and divide the observation periods of various antennas into a long part, solution A01, and a short part, A02. Thereby, the short parts have lengths of \(0.5\) to \(3\) years (with a step size of \(0.5\) years), and for each case we compare the antenna velocities estimated for A01 and A02 with and without reducing NTL. Ideally, the velocity of A02 would agree more with that of A01 (which is supposed to be the true velocity) when NTL is considered. The estimated velocities in x, y, and z directions for the distinct solutions of the antennas WETTZELL, Germany, and SESHAN25, China, are shown in Fig. 5. The black lines refer to the solutions A01 with the long observation periods, and we find that the velocities basically agree independent of the reduction of NTL. Beside the maximum period lengths (37.1 years and 32.6 years, respectively), the main difference between WETTZELL and SESHAN25 is the number of their appearances in the VLBI sessions. WETTZELL takes part much more often (in about 96 sessions per year on average versus about 13 sessions), and so the signals in the NTL displacement series can also be reflected more densely in the position time series of this antenna.
In particular for SESHAN25, there is no continuous convergence of the velocities for solutions A02 toward those for solutions A01. This is in line with the results of Blewitt and Lavallée (2002), who report an alternating velocity bias (induced by annual signals) depending on the observation time span. Furthermore, even for observation periods of \(3\) years and with the reduction of NTL, the velocities estimated for solutions A01 and A02 still do not completely agree in most cases. But this is not necessarily erroneous, because the time series of antenna positions might contain some long-period signals that still affect the distinct velocity estimates. (And the site displacements have been detrended.) We see, however, that the impact of NTL is particularly strong for periods shorter than \(2\) years in both examples, and the velocities estimated for A02 with the reduction of NTL are often closer to those estimated for A01. For WETTZELL, the velocities of A02 for REF, SUM, and NEQ already agree well after \(2\) years, while it takes \(3\) years for SESHAN25 to get independent of the reduction of NTL at any level. This is probably related to the average session appearances, but the concrete locations (i.e., time series phases) of the extracted observation periods are also relevant. The mismatch for the period length of \(2.5\) years (the proposed minimum time series length for reliable velocity estimates, compare above) with SESHAN25 might be explained by the fact that the NTL data contain more than just annual and semi-annual signals.
To conclude, the ability to improve the velocity estimates for antennas with short observation periods (and hence to include them in a secular TRF computation) by considering NTL depends on the particular antennas and their observation history. Notably, the agreement of the displacement series and the corresponding time series of antenna position resi-duals (w.r.t. their estimated linear motions) is important, i.e., the agreement of the amplitudes and phases of their respective spectra (see the comparisons for GNSS stations by Glomsda et al. 2022).
4.4 Helmert transformations
We perform 14-parameter Helmert transformations at epoch 2010.0 between the secular TRFs from scenario REF and each of the NTL scenarios. That is, we estimate three translations, three rotations, a scale parameter, and their rates in an unweighted least-squares adjustment. All estimated parameters, their formal errors, and the root-mean-square (RMS) values of the offset and velocity residuals can be found in Table 3. Although the parameter values are mostly statistically significant, they are all below \(1\) mm, just like the RMS values. Even when extrapolating the values with their rates over three decades, hardly more than \(0.5\) mm are added. Hence, there is no major change in the datum or the mean deformation of the networks induced by the reduction of NTL, which is similarly reported by Collilieux et al. (2009). Since the corresponding parameters for the scena-rios SUM and NEQ are very close, we have further evidence for the good agreement of the application levels. The site displacements generated from the NTL models are largest in the vertical direction, so the scale is the most interesting transformation parameter here, also because the scale is the datum parameter which can actually be realized by VLBI. As expected, its values are greater when reducing all NTL components instead of the non-tidal atmospheric loading only.
4.5 Earth orientation parameters
To analyze the impact of the reduction of NTL on the EOPs, we also use our estimated secular TRFs as a priori reference frames to compute single-session solutions. That is, we take the datum-free normal equations for scenarios REF, ATM, SUM, and NEQ and transform the a priori antenna positions to the values picked from the respective secular TRFs (compare Bloßfeld 2015). During the solution of the session-wise equation systems, the NNT and NNR constraints hence align the estimated antenna positions to our new secular TRFs instead of the ITRF2020. As we have seen in Sect. 4.3, the effect of NTL on the estimated antenna motions in the secular TRF is rather small, and there are hardly any discrepancies between the application levels. Maybe this situation changes for the EOPs, which are still estimated per session epoch.
If we pick a scenario from Table 1 and compare the EOPs from the single-session and the secular TRF solutions, the differences are significantly larger than the differences between two scenarios for the same solution type. As an example, we show the differences for \(dy_\textrm{pol}\) in Fig. 6. The peak-to-peak variation for scenario REF between the single-session and the secular TRF values for \(dy_\textrm{pol}\) is about \(0.2\) mas. The variation between the single-session values for scenarios REF and SUM, on the other hand, is only half as large. And the variation between the secular TRF values for scenarios REF and SUM is still smaller. Hence, the nature of the EOPs estimated in a secular TRF deviates from that of EOPs estimated in single-session solutions.
Since their positions are moving only linearly with time, the antenna networks are more stable in a secular TRF. With a fixed celestial reference frame as in our solutions, we might expect the same for the EOPs, at least for the ERPs (\(dx_\textrm{pol}\), \(dy_\textrm{pol}\), \(\varDelta \textrm{UT}1\)), which are responsible for the terrestrial part of Earth rotation. When determining the correlation matrix from the covariance matrix of the estimated parameters in Eq. (22), we indeed observe that the correlations between the antenna parameters and the ERP offsets (as opposed to their rates in a discontinuous piecewise linear representation) are the largest among the EOPs (see Fig. 7). We conclude that the ERP offsets will probably show less variability in secular TRF solutions than in single-session solutions.
Correlation matrix of the estimated antenna parameters and EOPs for a version of the reference scenario REF where all EOPs are reduced except for the years 2000–2002. The scale of the color map is capped to highlight the correlations which are significantly different from zero. The order of the estimated parameters is: \(DX_\textrm{CIP}\) (1–430), \(DY_\textrm{CIP}\) (431–860), (LOD) (861–1290), \(\varDelta \textrm{UT}1\) (1291–1720), \(dx_\textrm{pol}\) rates (1721–2150), \(dx_\textrm{pol}\) (2151–2580), \(dy_\textrm{pol}\) rates (2581–3010), \(dy_\textrm{pol}\) (3011–3440), antenna offsets and velocities (3441–4154)
The correlation values of the estimated parameters are mostly small, especially for the ERP rates and the celestial pole offsets. The latter are mainly correlated with their counterparts at the same epoch, which is indicated by the diagonals in Fig. 7. The ERP offsets and the antenna para-meters, however, are also correlated with the EOPs at other epochs, including the rates and the celestial pole offsets. Hence, the EOPs in a secular TRF are not as independent as the ones from the single-session solutions. In Table 4, we show the weighted RMS (WRMS) values of the differences between the respective EOPs estimated in the two solution types. The values are given for the reference scenario and the two scenarios with the total NTL applied. The results for both application levels are again very close, and we observe that the discrepancies between the EOPs of the two solution types are systematically decreased by about 3–4% when NTL is reduced.
The application of NTL has yet another effect on the ERP offsets. Figure 6 reveals an annual signal for the differences between \(dy_\textrm{pol}\) estimated with and without considering NTL, both in the secular TRF and the single-session solutions. This annual signal w.r.t. scenario REF appears for the scenarios ATM, SUM, and NEQ, and the corresponding amplitudes for the secular TRF solutions are listed in Table 5. Generally, the annual signal in the differences is larger when the total NTL is applied than when only the non-tidal atmospheric loading is applied, and the application level is little relevant. The amplitude of the signal is about half of the WRMS values of the differences, compare Fig. 8.
When comparing our EOPs with external data, i.e., the 14 C04 (Bizouard et al. 2019) and IAU2000 finals series of the IERS, we find that the differences (again expressed as WRMS values) for the ERP offsets are smaller for the secular TRF solutions (see Table 6). For the celestial pole offsets (\(DX_\textrm{CIP}\) and \(DY_\textrm{CIP}\)) and the length of day (LOD, the negative rate of \(\varDelta \textrm{UT}1\)), this is also mostly the case, but the percentage changes are less significant (at least compared to the polar motion offsets). This might confirm that the ERP offsets actually are more stable in a secular TRF, since the external series have been derived from the combination of various single-technique series and thus should be quite robust, too.
The deviations between scenario REF and the NTL scenarios are all significantly smaller than the deviations to the reference series (i.e., the current precision level), which was also reported by, e.g., Petrov and Boy (2004), or Collilieux et al. (2009). In Fig. 8, we show the corresponding WRMS values for both single-session and secular TRF solutions. First, we observe that the ERP offsets do not behave like their rates and the celestial pole offsets. The ERPs are parameterized as discontinuous piecewise linear functions per session. If constant site displacements are applied in a single session, as with scenario NEQ, then mainly an ERP’s offset will be shifted, while only a minor impact on its rate is expected. If, on the other hand, the site displacements have a large intra-session variation, then also an ERP’s rate will probably change more strongly, while its offset might only reflect the average level of the displacements. This is potentially the case in scenario SUM. As a consequence, we expect a significant deviation between the results for the two application levels for the ERP rates rather than the ERP offsets. This is exactly what we see in Fig. 8, and what Glomsda et al. (2020) have found in the VLBI single-session analysis before.
We also observe different properties for the secular TRF and the single-session solutions again. Earlier, we claimed that the EOPs between the distinct session epochs are correlated in a secular TRF solution, and that their time series will be less noisy than for the single-session solutions. The first assumption is reflected by the fact that the impact of NTL at the normal equation level on the ERP rates is significantly larger in the secular TRF solution. The second assumption might be supported by the fact that the influence of NTL on the ERP offsets is smaller in the secular TRF solution for both application levels. Together, we note that the impact of NTL is more distributed between ERP offsets and rates in secular TRF than in single-session solutions for both levels. Finally, we find that the celestial pole offsets behave like the ERP rates. Their connection with terrestrial site displacements is rather weak, and their correlation structure resembles that of the rates, too (compare Fig. 7 again).
In absolute numbers, the impact of NTL on the ERP offsets did not increase compared to previous VLBI studies. Petrov and Boy (2004) report RMS values of \(100\) prad for polar motion (\(\approx 0.02\) mas) and \(\varDelta \textrm{UT}1\) (\(\approx 0.001\) ms) when applying the horizontal component of atmospheric loading. When reducing all components of NTL, Roggenbuck et al. (2015) and Männel et al. (2019) obtain changes in polar motion and \(\varDelta \textrm{UT}1\) usually below \(0.1\) mas and \(0.003\) ms, respectively, which will provide (W)RMS values close to those of ours and Petrov and Boy (2004). Only Collilieux et al. (2009) find larger WRMS values of \(0.062-0.068\) mas for polar motion, while the value of \(0.002\) ms for \(\varDelta \textrm{UT}1\) is again similar to that of the other studies. However, the latter authors apply a combination at solution level.
Since the effect of NTL is concealed by the differences to the reference EOP series, we cannot tell whether the annual signals of Fig. 6 and Table 5 imply a decrease of residual annual signals in the ERP estimates. However, we have good reason to assume this, because the reduction of the total NTL also lessens the annual signals in antenna heights and the scale parameter in Helmert transformations of VLBI single-session solutions (e.g., Glomsda et al. 2020).
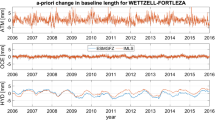
4.6 Baseline length repeatabilities
Finally, we use the single-session solutions with their corresponding a priori TRFs to compute the baseline length repeatabilities (BLRs) for the scenarios REF, ATM, SUM, and NEQ. The BLR equals the WRMS value of the estimated session-wise baseline lengths w.r.t. their long-term linear approximation. In the middle and bottom panels of Fig. 9, we plot the absolute and relative changes in the BLRs when reducing NTL in the distinct scenarios, respectively. We observe that the BLRs systematically improve by up to \(20\)% when the total NTL is applied at either the observation or the normal equation level. For the non-tidal atmospheric loading, the general decrease is smaller and some BLRs even increase slightly.
The improvement is driven by the application of site displacements in the observation or normal equations of the single-session solutions. That is, the BLRs would equally decrease if the a priori TRFs were not reduced by the total NTL (compare Glomsda et al. 2020). However, the secular TRFs computed from such reduced single-session solutions (like those in this study) will clearly benefit from the smaller BLRs, which reflect the mitigation of systematic effects that distort the estimation of the linear antenna motions.
5 Conclusion
We have generated various VLBI-only secular TRFs with and without the reduction of NTL. The latter has been applied in the form of antenna site displacements at the observation (i.e., within the theoretical delay model) or the normal equation level of the geodetic parameter estimation process. Linear trends in the displacement time series are removed to not distort the estimated linear antenna positions (and to a minor extent also the consistently estimated ERPs) and the realized geodetic datum, i.e., the scale in the case of VLBI.
Although both the VLBI analysis and the geophysical models for NTL have improved during the last years, the impact of NTL is still quite small. In particular for secular TRFs, where long-term linear positions are estimated, the nonlinear effects of NTL are averaged out for antennas with a sufficiently long and dense observation history. The overall statistics and the formal errors of the estimation process hardly change. Nevertheless, for antennas with only short observation histories or sparse data, the reduction of NTL will be relevant and beneficial. The application of site displacements at the normal equation level is a suitable approximation for the application at the observation level, since the results for the linear antenna motions agree very well for both approaches.
The effect of NTL is more striking for the epoch-wise estimated EOPs. While the absolute changes are small as well, we observe quite different behaviors for the ERP offsets compared to those of their rates and the celestial pole offsets. The former have a larger correlation with the estimated antenna positions in the secular TRF than the latter, while all EOPs are mathematically uncorrelated between the single-session solutions. As a consequence, the variability and the dependence on NTL of the EOPs is also different between secular TRF and single-session solutions. The ERP rates are more affected by the sub-diurnal variation of the site displacements, and thus the choice of the application level is especially relevant for them. Finally, there is an annual signal in the differences between the ERP offsets estimated with and without the reduction of (the total) NTL.
After all, it appears that the precision of VLBI results (both secular TRF and single-session solutions) is still suffering from the sparse antenna network and/or the network variations between the distinct sessions. Furthermore, unmodeled errors such as radio source structure (e.g., Anderson and Xu 2018) might impair a larger impact of the reduction of NTL. Maybe the increased precision of the next-generation system, the VLBI Global Observing System (VGOS, e.g., Niell et al. 2018), will also increase the significance of NTL. Ne-vertheless, as confirmed by the improvement of the baseline length repeatabilities or the mitigation of the annual signal in the scale time series (e.g., Glomsda et al. 2020), for example, the benefits are already systematic for the legacy system, so the total NTL should generally be reduced in routine VLBI analyses.
Data availability statement
The VLBI observation data can be found at ftp://cddis.nasa.gov/vlbi/ivsdata/vgosdb/, and the contribution of the GGFC to the ITRS 2020 realization at http://loading.u-strasbg.fr/ITRF2020/. Other data sets generated and analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbondanza C, Chin TM, Gross RS, Heflin MB, Parker JW, Soja BS, van Dam T, Wu X (2017) JTRF2014, the JPL Kalman filter and smoother realization of the International Terrestrial Reference System. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 122(10):8474–8510. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB014360
Altamimi Z, Rebischung P, Metivier L, Collilieux X (2016) ITRF2014: a new release of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame modeling nonlinear station motions. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JB013098
Altamimi Z, Rebischung P, Collilieux X et al (2023) ITRF2020: an augmented reference frame refining the modeling of nonlinear station motions. J Geod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-023-01738-w
Anderson JM, Xu MH (2018) Source structure and measurement noise are as important as all other residual sources in geodetic VLBI combined. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 123:10162–10190. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JB015550
Angermann D, Drewes H, Krügel M, Meisel B, Gerstl M, Kelm R, Müller H, Seemüller W, Tesmer V (2004) ITRS combination center at DGFI: a Terrestrial Reference Frame Realization 2003. Deutsche Geodätische Kommission, Reihe B, München
Bizouard C, Lambert S, Gattano C, Becker O, Richard JY (2019) The IERS EOP 14C04 solution for Earth orientation parameters consistent with ITRF 2014. J Geod 93:621–633
Blewitt G, Lavallée D (2002) Effects of annual signals on geodetic velocity. J Geophys Res 107(B7):2145. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000570
Bloßfeld M (2015) The key role of satellite laser ranging towards the integrated estimation of geometry, rotation and gravitational field of the Earth. PhD thesis, Technische Universität München, Reihe C der Deutschen Geodätischen Kommission. ISBN: 978-3-7696-5157-7
Böhm J, Heinkelmann R, Mendes Cerveira PJ et al (2009) Atmospheric loading corrections at the observation level in VLBI analysis. J Geod 83:1107–1113
Boy J-P (2021) GGFC contribution to the ITRS 2020 realization. http://loading.u-strasbg.fr/ITRF2020/ggfc.pdf. Accessed 16 Dec 2021
Carrère L, Lyard F (2003) Modeling the barotropic response of the global ocean to atmospheric wind and pressure forcing—comparisons with observations. Geophys Res Lett 30:1275. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GL016473
Charlot P, Jacobs CS, Gordon D et al (2020) The third realization of the International Celestial Reference Frame by very long baseline interferometry. Astron Astrophys. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202038368
Collilieux X, Altamimi Z, Coulot D, van Dam T, Ray J (2009) Impact of loading effects on determination of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame. Adv Space Res 45:144–154
Dach R, Böhm J, Lutz S, Steigenberger P, Beutler G (2010) Evaluation of the impact of atmospheric pressure loading modelling on GNSS data analysis. J Geod 85:75–91
Dong D, Yunck T, Heflin M (2003) Origin of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame. J Geophys Res 108(B4):2200. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JB002035
Eriksson D, MacMillan DS (2014) Continental hydrology loading observed by VLBI measurements. J Geod 88:675–690
Farrell WE (1972) Deformation of the earth by surface loads. Rev Geophys Space Phys 10(3):761–797
Gerstl M, Kelm R, Müller H, Ehrnsperger W (2000) DOGS-CS - Kombination und Lösung großer Gleichungssysteme, Internal Report. DGFI-TUM, München
Glomsda M, Bloßfeld M, Seitz M, Seitz F (2020) Benefits of non-tidal loading applied at distinct levels in VLBI analysis. J Geod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01418-z
Glomsda M, Bloßfeld M, Seitz M, Seitz F (2021) Correcting for site displacements at different levels of the Gauss–Markov model—a case study for geodetic VLBI. Adv Space Res 68(4):1645–1662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.04.006
Glomsda M, Bloßfeld M, Seitz M, Angermann D, Seitz F (2022) Comparison of non-tidal loading data for application in a secular terrestrial reference frame. Earth Planets Space 74:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-022-01634-1
Hart-Davis M, Piccioni G, Dettmering D, Schwatke C, Passaro M, Seitz F (2021) EOT20—a global Empirical Ocean Tide model from multi-mission satellite altimetry. SEANOE. https://doi.org/10.17882/79489
Hellmers H, Modiri S, Bachmann S, Thaller D, Bloßfeld M, Seitz M, Gipson J (2022) Combined IVS contribution to the ITRF2020, IAG symposium series
Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P et al (2020) The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 146:1999–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803
Johnston G, Riddell A, Hausler G (2017) The International GNSS Service. In: Teunissen PJG, Montenbruck O (eds) Springer handbook of global navigation satellite systems, 1st edn. Springer, Cham, pp 967–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42928-1
Kierulf HP, Kohler J, Boy J-P et al (2022) Time-varying uplift in Svalbard—an effect of glacial changes. Geophys J Int 231(3):1518–1534. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggac264
Koch K-R (1999) Parameter estimation and hypothesis testing in linear models, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (original German edition published by Dümmlers, Bonn)
Kwak Y, Gerstl M, Bloßfeld M, Angermann D, Schmid R, Seitz M, DOGS-RI: new VLBI analysis software at DGFI-TUM. In: Proceedings of the 23rd EVGA meeting (2017)
MacMillan DS, Gipson JM (1994) Atmospheric pressure loading parameters from very long baseline interferometry observations. J Geophys Res 99:18081–18087
MacMillan DS, Fey A, Gipson J et al (2019) Galactocentric acceleration in VLBI analysis: findings of IVS WG8. Astron Astrophys. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201935379
Männel B, Dobslaw H, Dill R, Glaser S, Balidakis K, Thomas M, Schuh H (2019) Correcting surface loading at the observation level: impact on global GNSS and VLBI station networks. J Geod 93(10):2003–2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01298-y
Mémin A, Boy J-P, Santamaria-Gómez A (2020) Correcting GPS measurements for non-tidal loading. GPS Solut 24:45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-0959-3
Niell A, Barrett J, Burns A et al (2018) Demonstration of a broadband very long baseline interferometer system: a new instrument for high-precision space geodesy. Radio Sci 53:1269–1291
Nothnagel A, Springer A, Heinz E, Artz T, de Vicente P (2014) Gravitational deformation effects. The YEBES40M Case, IVS 2014 general meeting proceedings
Nothnagel A, Artz T, Behrend D, Malkin Z (2017) International VLBI service for geodesy and astrometry—delivering high-quality products and embarking on observations of the next generation. J Geod 91(7):711–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-016-0950-5
Pavlis E, Luceri V, Basoni A, Sarrocco D, Kuzmicz-Cieslak M, Evans K, Bianco G (2021) ITRF2020: the international laser ranging service (ILRS) contribution, presented at AGU fall meeting, December 13–17, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/essoar.10509208.1
Petit G, Luzum B (eds) (2010) IERS conventions (V. 1.3.0), IERS Technical Note 36, Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt am Main
Petrov L, Boy J-P (2004) Study of the atmospheric pressure loading signal in very long baseline interferometry observations. J Geophys Res 109:B03405. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JB002500
Rabbel W, Zschau J (1985) Static deformations and gravity changes at Earth’s surface due to atmospheric loading. J Geophys 56:81–89
Roggenbuck O, Thaller D, Engelhardt G, Franke S, Dach R, Steigenberger P (2015) Loading-induced deformation due to atmosphere, ocean and hydrology: model comparisons and the impact on global SLR, VLBI and GNSS solutions. In: van Dam T (ed) REFAG 2014, International Association of Geodesy Symposia, vol 146. Springer, Cham
Seitz M, Bloßfeld M, Angermann D, Seitz F (2022) DTRF2014: DGFI-TUM’s ITRS realization 2014. Adv Space Res 69(6):2391–2420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.12.037
Soja B, Nilsson T, Balidakis K et al (2016) Determination of a terrestrial reference frame via Kalman filtering of very long baseline interferometry data. J Geod 90:1311–1327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-016-0924-7
Tregoning P, van Dam T (2005) Effects of atmospheric pressure loading and seven-parameter transformations on estimates of geocenter motion and station heights from space geodetic observations. J Geophys Res 110:B03408. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003334
Tregoning P, van Dam T (2005) Atmospheric pressure loading corrections applied to GPS data at the observation level. Geophys Res Lett 32:L22310. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL024104
van Dam TM, Wahr J (1987) Displacements of the Earth’s surface due to atmospheric loading: effects on gravity and baseline measurements. J Geophys Res 92:1281–1286
van Dam T, Wahr J, Milly P, Shmakin A, Blewitt G, Lavallee D, Larson K et al (2001) Crustal displacements due to continental water loading. Geophys Res Lett 28:651–654. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL012120
van Dam T, Collilieux X, Wuite J et al (2012) Nontidal ocean loading: amplitudes and potential effects in GPS height time series. J Geod 86(11):1043–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-012-0564-5
Williams SDP, Penna NT (2011) Non-tidal ocean loading effects on geodetic GPS heights. Geophys Res Lett 38:L09314. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL046940
Willis P, Fagard H, Ferrage P, Lemoine FG, Noll CE, Noomen R, Otten M, Ries JC, Rothacher M, Soudarin L, Tavernier G, Valette J-J (2010) The International DORIS Service (IDS): toward maturity. Adv Space Res 45(12):1408–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2009.11.018
Acknowledgements
We thank the IVS and its member institutions for generating and sharing the VLBI observation data. We are also grateful for the GGFC providing the NTL data for the ITRS 2020 realizations. Without both of them, this study would not have been possible. We further thank Daniel Scherer (DGFI-TUM) for creating Fig. 3. Last but not least, we express our gratitude to the three anonymous reviewers and the journal editors. Their valuable comments and feedback significantly improved our manuscript.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG and MS conceptualized the study. MG prepared most of the non-tidal loading and all the VLBI data. He performed the calculations and analyses, compiled all but one figure, and wrote the majority of the manuscript. MS provided the expertise and scripts for computing the secular TRFs. MB prepared the final format of the non-tidal loading data. MG, MS, and MB discussed the results and the validation strategy. FS supervised the study and provided the basic resources. All authors read and improved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Glomsda, M., Seitz, M., Bloßfeld, M. et al. Effects of non-tidal loading applied in VLBI-only terrestrial reference frames. J Geod 97, 76 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-023-01766-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-023-01766-6