Abstract
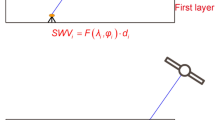
A near real-time troposphere tomography system (WATS-NRT) based on Global Positioning System (GPS) slant wet delays (SWD) was developed to reconstruct three-dimensional wet refractivity fields over a wide area. The NCEP Global Forecast System (GFS) short-range forecast products (GFS-FC) were taken as the tomography background to tackle the ill-condition issue, and the Adaptive Simultaneous Iterative Reconstruction Technique (ASIRT) was used for parameter estimation to avoid an inversion of a large sparse matrix. Experiments were set up for a 7-day period covering a severe storm event to evaluate the performance of the tomography system over an area with about 5000 tomographic nodes. Statistics of the computation time illustrate that WATS-NRT is efficient enough for providing 30 min interval tomography products in the studied area. Wet refractivity time series from the tomography product experience dramatic rises before the advent of heavy rain, which is not presented in the GFS-FC products. Comparisons also show general better agreements with the nearby radiosonde profiles in tomography products than GFS-FC, especially at the lower troposphere. In addition, average error RMS of SWD derived from tomography products is about 38 mm at an elevation of 15° and 9 mm in the zenith direction, compared to more than 70 and 16 mm for SWD from both GFS-FC and the reanalysis product ERA5, and compared to about 44 and 9 mm for ZWDINT method. These results suggest that WATS-NRT can be promising in some applications, such as monitoring extreme weather events, providing tropospheric delay estimates in geodetic data analysis and developing new mapping functions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
GPS data used in this study can be applied from Guangdong Institute of Land Resources Surveying and Mapping. Rain gauge data can be accessed at: https://data.cma.cn/. The radiosonde data can be downloaded from: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/data-access/weather-balloon/integrated-global-radiosonde-archive. The ERA5 products can be accessed at: https://climate.copernicus.eu/climate-reanalysis. The GFS products can be accessed at: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/data-access/model-data/model-datasets/global-forcast-system-gfs.
References
Bender M, Dick G, Ge M, Deng Z, Wickert J, Kahle H-G, Raabe A, Tetzlaff G (2011) Development of a GNSS water vapour tomography system using algebraic reconstruction techniques. Adv Space Res 47(10):1704–1720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2010.05.034
Benevides P, Nico G, Catalao J, Miranda P (2017) Analysis of Galileo and GPS integration for GNSS tomography. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(4):1936–1943. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2016.2631449
Bevis M, Businger S, Herring T, Rocken C, Anthes RA, Ware RH (1992) GPS meteorology: remote sensing of the atmospheric water vapor using the global positioning system. J Geophys Res 97:15787–15801. https://doi.org/10.1029/92JD01517
Boehm J, Kouba J, Schuh H (2009) Forecast Vienna Mapping Functions 1 for real-time analysis of space geodetic observations. J Geodesy 83:397–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0216-y
Boehm J, Möller G, Schindelegger M, Pain G, Weber R (2015) Development of an improved empirical model for slant delays in the troposphere (GPT2w). GPS Solut 19(3):433–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0403-7
Brenot H, Rohm W, Kacmarik M, Moller G, Sa A, Tondas D, Rapant L, Biondi R, Manning T, Champollion C (2018) Cross-validation of GPS tomography models and methodological improvements using CORS network. Atmos Meas Tech Discuss 1:1. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-2018-292
Buehner M, Morneau J, Charette C (2013) Four-dimensional ensemble-variational data assimilation for global deterministic weather prediction. Nonlin Process Geophy 20:669–682. https://doi.org/10.5194/npg-20-669-2013
Champollion C, Masson F, Bouin M, Walpersdorf A, Doerflinger E, Bock O, Van Baelen J (2005) GPS water vapour tomography: preliminary results from the ESCOMPTE field experiment. Atmos Res 74:253–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2004.04.003
Chen B, Liu Z (2016) Assessing the performance of troposphere tomographic modeling using multi-source water vapor data during Hong Kong’s rainy season from May to October 2013. Atmos Meas Tech 9:5249–5263. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-9-5249-2016
Dousa J, Dick G, Kacmarik M, Brozkova R, Zus F, Brenot H, Stoycheva A, Moller G, Kaplon J (2016) Benchmark campaign and case study episode in central Europe for development and assessment of advanced GNSS tropospheric models and products. Atmos Meas Tech 9:2989–3008
Flores A, Ruffini G, Rius A (2000) 4D tropospheric tomography using GPS slant wet de-lays. Ann Geophys 18(2):223–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00585-000-0223-7
Gilbert P (1972) Iterative methods for three-dimensional reconstruction of an object from its projections. J Theor Biol 36(1):105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(72)90180-4
Gordon R, Bender R, Herman G (1970) Algebraic reconstruction technique (ART) for three-dimensional electron microscopy and X-ray photography. J Theor Biol 29(3):471–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(70)90109-8
Hobier T, Ichikawa R, Takasu T, Koyama Y, Kondo T (2008) Ray-traced troposphere slant delays for precise point positioning. Earth, Planet and Space 60(5):e1–e4. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352809
Jarvinen H, Eresmaa R, Vedel H, Salonen K, Niemela S, de Vries J (2007) A variational data assimilation system for ground-based GPS slant delays. Q J R Meteorol Soc 133:969–980. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.79
Kacmarik M, Dousa J, Dick G, Zus F, Brenot H, Moeller G, Pottiaux E, Kaplon J, Hordyniec P, Vaclavovic P, Morel L (2017) Inter-technique validation of tropospheric slant total delays. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques 10(6):2183–2208. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-10-2183-2017
Kacmarik M, Dousa J, Zus F, Vaclavovic P, Balidakis K, Dick G, Wickert J (2019) Sensitivity of GNSS tropospheric gradients to processing options. Ann Geophys 37:429–446
Kawabata T, Shoji Y, Seko H, Saito K (2013) A Numerical Study on a Mesoscale Convective System over a Subtropical Island with 4D-Var Assimilation of GPS Slant Total Delays. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 91:705–721. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2013-510
Labbouz L, Van Baelen J, Tridon F, Reverdy M, Hagen M, Bender M, Dick G, Gorgas T, Planche C (2013) Precipitation on the lee side of the Vosges Mountains: multi-instrumental study of one case from the COPS campaign. Meteor Z 22:413–432. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2013/0413
Liu D, Nocedal J (1989) On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale minimization. Math Program 45:503–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01589116
Liu W, Lou Y, Zhang W, Huang J, Zhou Y, Zhang H (2019) On the study of influences of different factors on the rapid tropospheric tomography. Remote Sens 11:1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131545
Lou Y, Huang J, Zhang W, Liang H, Zheng F, Liu J (2018) A new zenith tropospheric delay grid product for real-time PPP applications over China. Sensor 18:65. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010065
Morales JL, Nocedal J (2002) Enriched methods for large scale unconstrained optimization. Comput Optim Appl 21:143–154. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013756631822
Notarpietro R, Cucca M, Gabella M, Venuti G, Perona G (2011) Tomographic reconstruction of wet and total refractivity fields from GNSS receiver networks. Adv Space Res 47:898–912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2010.12.025
Perler D, Geiger A, Hurter F (2011) 4D GPS water vapor tomography: new parameterized approaches. J Geodesy 85(8):539–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0454-2
Saastamoinen J (1972) Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. The use of artificial satellites for Geodesy. Geophys Monogr 15:247–251. https://doi.org/10.1029/GM015p0247
Seko H, Shimada S, Nakamura H, Kato T (2000) Three dimensional distribution of water vapor estimated from tropospheric delay of GPS data in a mesoscale precipitation system of the Baiu front. Earth Planets Sp 52:927–933. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352307
Shi C, Zhao Q, Geng J, Lou Y, Ge M, Liu J (2008) Recent development of PANDA software in GNSS data processing. In: Li D, Gong J, Wu H (eds) International conference on earth observation data processing and analysis (ICEODPA), International society for optical engineering (SPIE Proceedings, vol 7285). doi:10.1117/12.816261
Teke K, Boehm J, Nilsson T, Schuh H, Steigenberger P, Dach R, Heinkelmann R, Willis P, Haas R, García-Espada S, Hobiger T, Ichikawa R, Shimizu S (2011) Multi-technique comparison of troposphere zenith delays and gradients during CONT08. J Geod 85(7):395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0434-y
Troller M, Geiger A, Brockmann E, Kahle H (2006) Determination of the spatial and temporal variation of tropospheric water vapour using CGPS networks. Geophys J Int 167(2):509–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03101.x
Van Baelen J, Reverdy M, Tridon F, Labbouz L, Dick G, Bender M, Hagen M (2011) On the relationship between water vapour field evolution and the life cycle of precipitation systems. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:204–223. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.785
Wan X, Zhang F, Chu Q, Zhang K, Sun F, Yuan B, Liu Z (2011) Three-dimensional reconstruction using an adaptive simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique in electron tomography. J Struct Biol 175:277–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2011.06.002
Yao Y, Zhao Q, Zhang B (2016) A method to improve the utilization of GNSS observation for water vapor tomography. Ann Geophys 34:143–152. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-34-143-2016
Yao Y, Tang J, Zhang L, He C, Zhang S (2014) An adaptive simultaneous iteration reconstruction technique for three-dimensional ionospheric tomography. Chin J Geophys (in Chinese) 57(2):345–353. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg20140201
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102:5005–5017. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB03860
Zus F, Wickert J, Bauer HS, Schwitalla T (2011) Wulfmeyer V (2011) Experiments of GPS slant path data assimilation with an advanced MM5 4DVAR system. Meteorol Z 20:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2011/0232
Zus F, Dousa J, Kacmarik M, Vaclavovic P, Balidakis K, Dick G, Wickert J (2019) Improving GNSS zenith wet delay interpolation by utilizing tropospheric gradients: experiments with a dense station network in Central Europe in the Warm Season. Remote Sens 11:674
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41774036; 41804023; 41961144015), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2042020kf0020), the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University (17P01), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFB0503401). The authors would like to thank Guangdong Institute of Land Resources Surveying and Mapping for providing GPS data, CMA for providing rain gauge data, IGRA for providing radiosonde data, NOAA CISL for providing forecast products and ECMWF for providing ERA5 products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and WZ designed the research; JH and WL developed the software; WZ and WL performed the research. ZW, YZ, and HZ analyzed the data; and WZ wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Lou, Y., Liu, W. et al. Rapid troposphere tomography using adaptive simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique. J Geod 94, 76 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01386-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01386-4