Abstract
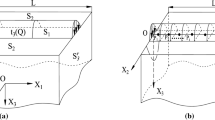
To investigate the edge drop control characteristics of the roll contour on the taper segment of a taper-work roll, a three-dimensional roll stack-strip-tension coupling model was established with the finite element method, and the simulation model was verified using experimental data. The effects of the taper-work roll shifting (T-WRS) for different contours on the edge drop, center crown, flatness, and nonuniformity of the rolling pressure field unevenness were studied. The results indicated that the thickness difference caused by the combination of the roll contour and the work roll shifting (WRS) effectively compensated for the edge drop caused by the elastic deformation of the roll was the main way for T-WRS to reduce edge drop. Increasing the height of the roll contour inserted into the strip could significantly improve the edge drop control ability. However, it would also lead to increasing the trend of M-mode waviness defects and increase the peak of rolling pressure and the unevenness of the contact pressure between the rolls. Therefore, a novel approach for the roll contour evaluation was proposed by constructing the multi-objective function of the taper-work roll shifting. With edge drop control as the primary goal, the optimal range and suitable range of the WRS for different roll contours were calculated for the first stand of the tandem cold mill.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Xia ZS, Kang YL, Wang QL (2008) Developments in the production of grain-oriented electrical steel. J Magn Magn Mater 320(23):3229–3233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.07.003
He HN, Shao J, Wang XC, Yang Q, Liu Y, Xu D, Sun YZ (2021) Research and application of approximate rectangular section control technology in hot strip mills. J Iron Steel Res Int 28(3):279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00558-6
Ma XB, Wang DC, Liu HM, Zhang S (2018) Influence of profile indicators of hot-rolled strip on transverse thickness difference of cold-rolled silicon steel. Metall Res Technol 116 (1) https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2018044
Yao CH, He AT, Shao J, Zhang YJ, Zhao HS (2018) Edge drop and high spot control of hot-rolled non-oriented electrical steel strip by taper roll shifting strategy. Ironmak Steelmak 47(2):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2018.1492660
Ma XB, Wang DC, Liu HM, Wen CC, Zhou Y (2016) Large concave roll technology for hot rolled silicon steel. Ironmak Steelmak 45(1):66–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2016.1240841
Cao JG, Wei GC, Zhang J, Xl C, Zhou YZ (2008) VCR and ASR technology for profile and flatness control in hot strip mills. J Cent South Univ Technol 15(2):264–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0049-0
Cao JG, Liu SJ, Zhang J, Song P, Yan TL, Zhou YZ (2011) ASR work roll shifting strategy for schedule-free rolling in hot wide strip mills. J Mater Process Technol 211(11):1768–1775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.05.025
He HN, Liu Y, Yang Q, Wang XC, Wang S, Wang Q (2019) Symmetry variable taper work roll technology for silicon steel profile control in hot strip mills. Ironmak Steelmak 47(6):587–595. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2019.1585098
Yasuda K-I, Narita K, Kobayashi K, Maeno I (1991) Shape controllability in new 6-high mill (UC-4 mill) with small diameter work rolls. ISIJ Int 31(6):594–598. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.31.594
Kobayashi K, Yasuda KMN (1988) Universal crown control mill (UC-mill) for higher shape control technology. Hitachi Rev 37(8):213–220
Kamada S (1996) Edge profile control using pair cross mill in cold rolling. Iron Steel Eng 73:20–25
Nishioka K, Hori Y, Ogawa S, Mizutani Y, Kojima A (1997) High reduction rolling technology on pair cross mill. Nippon Steel Tech Rep (Japan) (75):9–19
Kitamura K, Yarita I, Suganuma N, Nakanishi T, Toyoshima K (1992) Edge-drop control of hot and cold rolled strips by a tapered-crown work roll shifting mill. Kawasaki Steel Tech Rep (Japan) 27:5–12
Tateno J-I, KenmochiE K, Yarita I, Kaneko T, Yamada Y (1999) Controlling edge drop by tapered-crown work roll shifting mill and work roll crossing mill in cold strip rolling. Japan Soc Technol Plast 40:653–657
Hartung HG, Hollmann FW, Holz R, Richter HP (1998) A new way to reduce the edge drop. Steel Res 69(4–5):143–147
Hartung HG, Hollmann FW (1998) EDC—a new system for reduction of edge drop in cold rolling. Metall Plant Technol Int (Germany) 22(2):80–82
Wang XC, Yang Q, Hn He, Sun YZ, Xu D, Liu Y (2020) Effect of work roll shifting control on edge drop for 6-hi tandem cold mills based on finite element method model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107(5–6):2497–2511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05160-w
Cao JG, Jiang J, Qiu L, Li YL, He AR, Zhang YJ (2019) High precision integrated profile and flatness control for new-generation high-tech wide strip cold rolling mills. J Central South Univ (Sci Technol) 50(07):1584–1591. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.07.011
Feng XW, Wang XC, Sun JQ, Yang Q (2019) Analysis of tapered work roll shifting technique in 5-stand UCMW tandem cold rolling process. Aust J Mech Eng 1–9 https://doi.org/10.1080/14484846.2019.1606762
Wang DC, Liu HM, Liu J (2017) Research and development trend of shape control for cold rolling strip. Chin J Mech Eng 30(5):1248–1261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10033-017-0163-8
Peng Y, Niu S (2017) Review on assessment methods for shape control performance of strip rolling mills. J Mech Eng Sci 53(6):26–44. https://doi.org/10.3901/JME.2017.06.026
Zhang Y, Yang Q, Shao J, Du XZ, Wang XC (2009) Edge drop control using sinusoidal tapered work roll on a UCMW mill. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing 31(12):1611–1615. https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2009.12.015
Zhang QD, Bai J, Xu LJ, Gu HZ, Jin G (2009) Study and improvement of mill type of 1550 tandem cold mill in Baosteel. Iron and Steel 44(11):67–82
Sun WQ, Yang Q, Shao J, He AR, Li MX (2010) Edge drop control technique of silicon steel for UCM tandem cold rolling mills. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing 32(10):1340–1345
Cao JG, Chai XT, Yl Li, Kong N, Jia SH, Zeng W (2018) Integrated design of roll contours for strip edge drop and crown control in tandem cold rolling mills. J Mater Process Technol 252:432–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.09.038
He AR, Shao J, Sun WQ, Guan CL, Shen XY, Zhang JP (2011) Transverse thickness deviation control of non-oriented silicon steel during cold rolling. J Mech Eng Sci 47(10):25–30. https://doi.org/10.3901/JME.2011.10.025
Li GH (2018) EVC-Plus technique of transverse thickness deviation control of non-oriented silicon steel during cold rolling. Iron Steel 53(08):68–72+82. https://doi.org/10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20180174
Zhang JL, Chen W, Lu JD, Yue CX (2022) Design and application of work roll profile on UCM-mill. Iron Steel 57(08):123–131. https://doi.org/10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20220087
Ma XB, Wang DC, Liu HM (2017) Coupling mechanism of control on strip profile and flatness in single stand universal crown reversible rolling mill. Steel Res Int 88 (9) https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201600495
Zhang QD, Zhang XF, Wen J (2013) Theory and technology of transverse thickness deviation control for DI tinplate during tandem cold rolling. J Mech Eng Sci 49(24):30–38. https://doi.org/10.3901/JME.2013.24.030
Ren Z, Xiao H, Liu X, Yan Z (2018) An analysis of the metal transverse flow in the roll gap for ultra-thin strip rolling using the energy method. ISIJ Int 58(2):309–315. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2017-519
Shin JM, Han SL, Kim JS (2013) Development and experimental evaluation of strip shape prediction model for Sendzimir rolling mills. J Iron Steel Res Int 20(12):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1006-706x(13)60212-5
Zhou XM, Zhang QD, Wang CS, Wu P (2007) Edge drop and flatness decoupling control on UCMW cold mill. Iron Steel 42(5):55–57. https://doi.org/10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.2007.05.013
Moazeni B, Salimi M (2013) Investigations on formation of shape defects in square rolling of uniform thin flat sheet product. ISIJ Int 53(2):257–264. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.53.257
Shohet KN, Townsend N (1971) Flatness control in plate rolling. J Iron Steel Institule 209:769–775
Wang Q, Sun J, Li X, Wang Z, Wang P, Zhang D (2020) Analysis of lateral metal flow-induced flatness deviations of rolled steel strip: mathematical modeling and simulation experiments. Appl Math Modell 77:289–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.07.036
Zhao JW, Wang XC, Yang Q, Wang QN, Wang YY, Li WP (2021) Mechanism of lateral metal flow on residual stress distribution during hot strip rolling. J Mater Process Technol 288 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116838
Ataka M (2015) Rolling technology and theory for the last 100 years: the contribution of theory to innovation in strip rolling technology. ISIJ Int 55(1):89–102. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.55.89
Rout M, Pal SK, Singh SB (2016) Finite element simulation of a cross rolling process. J Manuf Processes 24:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.09.012
Zhang Y, Yang Q, Wang XC (2011) Control strategies of asymmetric strip shape in six-high cold rolling mill. J Iron Steel Res Int 18(9):27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1006-706x(12)60030-2
Wang QL, Sun J, Li X, Liu YM, Wang PF, Zhang DH (2018) Numerical and experimental analysis of strip cross-directional control and flatness prediction for UCM cold rolling mill. J Manuf Processes 34:637–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.07.008
Nam SY, Zamanian A, Shin TJ, Hwang SM (2020) A novel on-line model for the prediction of strip profile in cold rolling. ISIJ Int 60(2):308–317. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-233
Cao JG, Zhang Y, Yang GH, Meng XM, Cao LC, Zhou Xh, Wang ZK (2011) Intermediate roll contour of 6-hi UCM cold rolling mill. J Central South Univ (Sci Technol) 42(04):966–971
Zhang QD, Li B (2009) End contour of intermediate rolls for a UCMW cold tandem mill. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing 31(02):240–243. https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2009.02.011
Yang GH, Zhang J, Cao JG, Qi JB, Zeng W, Jia SH (2012) Roll configuration for edge drop control of wide strip on 4-hi tandem cold rolling mills. J Tianjin Univ 45 (12):1051-1056 0493-2137
Zhang QD, Bai J, Xu LJ, Wang KJ, Xu JY (2009) Improvement of mill type and development of flatness control capability for 1420 mm tandem cold mill. Iron Steel 44(04):42–45. https://doi.org/10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.2009.04.006
Yang Q, Chen XL, Xu YH, Xu LJ (1995) Applying VCL back-up roll to raise the control level of strip shape. Iron Steel 30(02):48–51
Li GL, Ma JJ, Wang LB, Zhao YP, Zhang GZ (2012) Optimization of control strategy for thickness difference in wide direction of UCMW mill. J Iron Steel Res 24(S1):52–56. https://doi.org/10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.2012.s1.019
Song CN, Cao JG, Wang LL, Xiao J, Zhao QF (2022) The prediction model for transverse thickness difference of electric steel in 6‐high cold rolling mills based on GA‐PSO‐SVR approach. Steel Res Int 2200302 https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.202200302
Song CN, Cao JG, Wang LL, Xiao J, Zhao QF (2022) Transverse thickness profile control of electrical steel in 6-high cold rolling mills based on the GA-PSO hybrid algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121(1–2):295–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09322-w
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52074085, 51774084, and 51634002), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFB0304100), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. N170708020 and N2004010), and Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1907065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhen Wei: methodology, data curation, visualization, investigation, and writing, original draft preparation.
Qinglong Wang: validation and writing, reviewing, and editing.
Jie Sun: conceptualization; methodology; supervision; writing, reviewing; editing; and resources.
Wen Peng: data curation and software.
Dianhua Zhang: conceptualization and resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Wang, Q., Sun, J. et al. Edge drop control characteristics of the taper-work roll contour for six-high cold mill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 126, 3615–3635 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11339-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11339-8