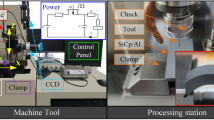
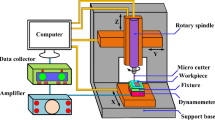
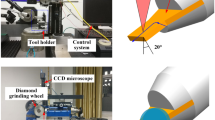
Abstract
Micro-stepped holes have been widely used in the fields of micro motor, precision mold, medical device, and so on. YG8 cemented carbide is widely used for machining micro-stepped hole because of its high hardness and good wear resistance. However, it is difficult to realize high-quality machining of micro-stepped holes on YG8 cemented carbide by turning and milling. Micro-EDM has no macroscopic cutting force and is not limited by material hardness, so it is the mainstream technology for machining microstructures on superhard materials. To address the above problems, the paper proposed to adopt micro-EDM to process the micro-stepped hole by using a micro milling cutter. Firstly, micro-EDM was carried out on YG8 cemented carbide with a high-speed rotating micro milling cutter to obtain the basic micro-hole structure. In the process of micro-EDM, the length of micro milling cutter was reduced due to wear. Secondly, micro-EDM was performed on the YG8 cemented carbide using the micro milling cutter with wear in length as the tool electrode, which was made to shake around the central axis of the basic micro-hole, so that a secondary basic micro-hole was machined on the basic micro-hole and a micro-stepped hole was formed. In the process of machining the secondary basic micro-hole, micro milling cutter with no wear would produce a secondary basic micro-hole with the same depth as the basic micro-hole, and no micro-stepped hole would be formed. In this paper, the wear of micro milling cutter in the length direction was transformed into a favorable factor. With the micro milling cutter shaking, a micro-stepped hole was obtained using the same micro milling cutter in different stages of EDM. Through a large number of machining experiments, the main process parameters were optimized and the experimental results were analyzed in this paper. Finally, the micro-EDM of YG8 cemented carbide was carried out with a micro milling cutter with a diameter of 400 µm at 2000 RPM rotational speed n, 90 V machining voltage V, and 0.5 duty ratio R, and a micro-stepped hole with good quality was obtained.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Hao TM, Du J, Su GS, Zhang PR, Sun YJ, Zhang JJ (2020) Mechanical and cutting performance of cemented carbide tools with Cr/x/DLC composite coatings. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106:5241–5254
Wang ZH, Sun N, Cao LY, Yin ZB, Wang YL, Yuan JT (2020) Cutting performance and wear mechanism of spark plasma-sintered silicon nitride ceramics tool in dry turning of 41Cr4 hardened steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107:3415–3424
Wu XL, Liu YH, Zhang XX, Dong H, Zheng C, Zhang F, Sun Q, Jin H, Ji RJ (2020) Sustainable and high-efficiency green electrical discharge machining milling method. J Clean Prod 274:123040
Kliuev M, Kutin A, Wegener K (2021) Electrode wear pattern during EDM milling of Inconel 718. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 117:2369–2375
Huang RN, Yi Y, Guo GL, Xiong XG (2020) Investigation of multielectrode multiloop with series capacitance pulse generator for EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109:143–154
Li Y, Deng J, Chai Y, Fan WL (2015) Surface textures on cemented carbide cutting tools by micro EDM assisted with high-frequency vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(9–12):2157–2165
Son S, Lim H, Kumar AS, Rahman M (2007) Influences of pulsed power condition on the machining properties in micro EDM. J Mater Process Technol 190(1–3):73–76
Jahan MP, Wong YS, Rahman M (2012) Experimental investigations into the influence of major operating parameters during micro-electro discharge drilling of cemented carbide. Mach Sci Technol 16(1):131–156
Wu YY, Huang TW, Sheu DY (2020) Desktop micro-EDM system for high-aspect ratio micro-hole drilling in tungsten cemented carbide by cut-side micro-tool. Micromachines (Basel) 11(7)
Abhilash PM, Chakradhar D (2021) Failure detection and control for wire EDM process using multiple sensors. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 33:315–326
Ozkavak HV, Sofu MM, Duman B, Duman B, Bacak S (2021) Estimating surface roughness for different EDM processing parameters on Inconel 718 using GEP and ANN. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 33:306–314
Dutta H, Debnath K, Sarma DK (2020) Multi-objective optimization of hole dilation at inlet and outlet during machining of CFRP by μEDM using assisting-electrode and rotating tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 110(9–10):2305–2322
Ming W, Shen F, Zhang Z, Huang H, Du JG, Wu J (2020) A comparative investigation on magnetic field–assisted EDM of magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109(3–4):1103–1116
Cao XJ, Wang KS, Han Y, Lin CC (2013) Press forging forming of stepped holes in thick sheet metal. Metal Adv Mat Res 706–708:234–237
Das S, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2016) Fabrication of stepped hole on zirconia bioceramics by ultrasonic machining. Mach Sci Technol 20(4):681–700
Yang X, Ran Y, Wang Z, Mu ZY, Zhang GB (2020) Early prediction method for assembly precision of mechanical system and assessment of precision reliability. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 112(1–2):203–220
Huang Y, Zhang Q, Xing Q, Yao Q, Li J (2019) Effects of electrode rotational speed on processing performances of AISI 304 in micro-electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105(1–4):1665–1674
Acknowledgements
The authors are also grateful to the colleagues for their essential contribution to the work.
Funding
This work is supported by the Science, Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality (Grant Nos. JSGG20201102145402008), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62003216), National Natural Science Foundation-Aerospace Joint Fund (Grant Nos.U2037205), and Shenzhen Stability Support Plan A (Grant Nos. 20200812104451001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bin Xu, Chun-yang Zhao, and Tao Feng designed all experiments included in this study and wrote and modified this manuscript. Xiao-yu Wu and Lian-yu Fu assisted in conducting the experiments. Jian-guo Lei and Hang Zhao made suggestions about this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The article follows the guidelines of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) and involves no studies on human or animal subjects.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to publish the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Feng, T., Xiao, Yc. et al. Micro-EDM of micro-stepped hole in YG8 cemented carbide by using micro milling cutter. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121, 1015–1026 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09268-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09268-z