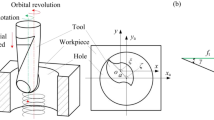
Abstract
Milling forces play an important role in the milling process and are generally calculated by the mechanistic or numerical methods; reliable model of cutting forces is very important for the simulation of milling process, which has big scientific significance to further improve machining quality. Ball helical milling technology is used to make holes based on the cutting principle of helical milling using ball end cutter, and due to the influence of spherical surface machining characteristic, the modeling of cutting force in ball helical milling is difficult. Therefore, the main purpose of this paper is to establish an analytical cutting force model in the ball helical milling process. Considering cutting characteristics in the axial feed, the kinematics of ball helical milling is first presented, then the chip thickness distribution in different directions along the cutting edges is predicted. Furthermore, based on the characteristics of helical milling technology and geometry shape of ball end cutter and the classical mechanical cutting force model, through the study on the ball-end milling mechanics, a new relatively accurate theoretical cutting force model is established. At the same time, cutting force coefficients are identified through instantaneous force method according to the Ti-alloy experimental research result. Finally, higher simulation precision of cutting force model in ball helical milling process is received.











Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- θ(°):
-
Rotational angle
- ϕ(°):
-
Orbital angle
- n(rpm):
-
Rotation speed
- n r(rpm):
-
Orbit speed
- s a(mm/t):
-
Axial feed rate per tooth
- s t(mm/t):
-
Feed rate per tooth at tool center
- a p (mm/rev):
-
Axial depth of cut per revolution
- N :
-
Number of cutting edges
- D t (R t)(mm):
-
Tool diameter (radius)
- D h (R h)(mm):
-
Hole-making diameter (radius)
- β(°):
-
Helix angle of tool
- R(mm):
-
Local cutter radius
- α(°):
-
Ramp angle
- z(mm):
-
Total cutting depth
- κ(°):
-
Axial position angle
- dF t, dF r, and dF a(N):
-
Micro cutting force in tangential, radial and axial directions
- h (mm):
-
Undeformed chip thickness
- db (mm):
-
Micro cutting width
- dz (mm):
-
Micro cutting depth
- dS (mm):
-
Length of the edge discrete element
- ψ(z)(°):
-
Radial lag angle
- e (mm):
-
Eccentricity
- H (mm):
-
Thickness of workpiece
- F x(N):
-
Cutting forces in the x direction
- F y(N):
-
Cutting forces in the y direction
- F z(N):
-
Cutting forces in the z direction
- K tc, K rc, and K ac(N/mm2):
-
Cutting force coefficients in tangential, radial and axial directions
- K te, K re and K ae(N/mm):
-
Rubbing force coefficients in tangential, radial and axial directions
- Kz(N/mm2):
-
Axial cutting coefficients
References
Wang HY, Qin XD (2016) A mechanistic model for cutting force in helical milling of carbon fiber-reinforced polymers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82:1485–1494
Wang HY, Qin XD, Ren CZ, Wang Q (2012) Prediction of cutting forces in helical milling process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58:849–859
Liu CY, Wang G, Dargusch MS (2012) Modelling, simulation and experimental investigation of cutting forces during helical milling operations. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 63:839–850
Ventura CEH, Hassui A (2013) Modeling of cutting forces in helical milling by analysis of tool contact angle and respective depths of cut. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68:2311–2319
Zhou L, Dong HY, Ke YL, Chen GL (2018) Modeling of non-linear cutting forces for dry orbital drilling process based on undeformed chip geometry. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94:203–216
Shang S, Qin XD, Li JH, Li SP, Huang T, Jin Y, Sun D (2018) Modelling of cutting forces and researching calibration method in helical milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94:2949–2960
Rey PA, LeDref J, Senatore J, Landon Y (2016) Modelling of cutting forces in orbital drilling of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 106:75–88
Li ZQ, Liu Q, Ming XZ, Wang X, Dong YF (2014) Cutting force prediction and analytical solution of regenerative chatter stability for helical milling operation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(1-4):433–442
Li ZL, Ding Y, Zhu LM (2017) Accurate cutting force prediction of helical milling operations considering the cutter runout effect. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:4133–4144
Araujo AC, Guillaume FG, Poulachon G (2013) Analytical and experimental investigations on thread milling forces in titanium alloy. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 67:28–34
Tanaka H, Ohta K, Takizawa R, Yanagi K (2012) Experimental study on tilted planetary motion drilling for CFRP. Procedia CIRP1:443-448.
Yucesan G, Altintas Y (1996) Prediction of ball end milling forces. J Eng Ind 118:95–103
Altintas Y, Lee P (1998) Mechanics and dynamics of ball end milling. J Manuf Sci E-T ASME 120:684–692
Jia ZY, Ge J, Ma JW, Gao YY, Liu Z (2016) A new cutting force prediction method in ball-end milling based on material properties for difficult to machine materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86:2807–2822
Wojciechowski S (2015) The estimation of cutting forces and specific force coefficients during finishing ball end milling of inclined surfaces. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 89:110–123
Lee P, Altintas Y (1996) Prediction of ball-end milling forces from orthogonal cutting data. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 36:1059–1072
Engin S, Altintas Y (2001) Mechanics and dynamics of general milling cutters. Part I: helical end mills. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41:2195–2212
Tlusty J, MacNeil P (1975) Dynamics of cutting forces in end milling. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 24(1):21–25
Altintas Y, Lee P (1996) A general mechanics and dynamics model for helical end mills. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 45(1): 59-64.
Dang JW, Zhang WH (2010) Cutting force modeling for flat end milling including bottom edge cutting effect. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50:986–997
Gradisek J, Kalveram M, Weinert K (2004) Mechanistic identification of specific force coefficients for a general end mill. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44:401–414
Wan M, Zhang WH, Dang JW, Yang Y (2010) A novel cutting force modelling method for cylindrical end mill. Appl Math Model 34:823–836
Funding
This project has received funding from the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China (Grant No. E2020501014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Tao, K. & Jin, T. Modeling and estimation of cutting forces in ball helical milling process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 117, 2807–2818 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07817-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07817-6