Abstract
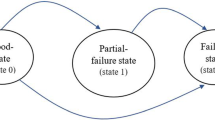
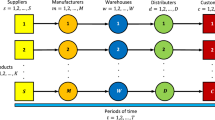
The buffer allocation problem (BAP) is one of the major optimization problems considered by production systems designers. The BAP is widely studied in the literature, since buffers have a great impact on improving the efficiency of production systems especially for mass production. Nevertheless, with all upcoming changes in world’s economy, industrial requirements and ecological awareness, the necessity of considering energy efficiency in manufacturing systems design becomes crucial. This paper introduces the first variant of energy-efficient buffer allocation problem (EE-BAP). It addresses a novel integrated analytical method to find the best buffer allocation that optimizes both throughput and energy consumption for serial production lines with unreliable machines. A large experimental study, based on different instances well established in the literature, is carried out to analyze the relevance of the proposed method. The obtained results show that considerable energy savings with low or almost no productivity loss are allowed. The energy-efficient BAP is a novel problem that considers the complex trade-off between throughput and energy efficiency performance and introduces new perspectives of research in the field of sustainable manufacturing systems design.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaouchiche Y, Ouazene Y, Yalaoui F (2020) Economic and energetic performance evaluation of unreliable production lines: an integrated analytical approach. IEEE Access 8:185330–185345
Alfieri A, Matta A, Pastore E (2020) The time buffer approximated buffer allocation problem: a row–column generation approach. Comput Oper Res 115:104835
Bajpai A, Fernandes KJ, Tiwari MK (2018) Modeling, analysis, and improvement of integrated productivity and energy consumption in a serial manufacturing system. J Clean Prod 199:296–304
Demir L, Diamantidis A, Eliiyi DT, O’Kelly ME, Papadopoulos CT, Tsadiras A, Tunalı S (2013) A comparison of three search algorithms for solving the buffer allocation problem in reliable production lines. IFAC Proceedings 46(9):1626–1631
Demir L, Tunali S, Eliiyi DT (2014) The state of the art on buffer allocation problem: a comprehensive survey. J Intell Manuf 25(3):371–392
Enginarlar E, Li J, Meerkov SM, Zhang RQ (2002) Buffer capacity for accommodating machine downtime in serial production lines. Int J Prod Res 40(3):601–624
Gershwin SB (1987) An efficient decomposition method for the approximate evaluation of tandem queues with finite storage space and blocking. Oper Res 35(2):291–305
Gershwin SB (2018) The future of manufacturing systems engineering. Int J Prod Res 56 (1-2):224–237
Gershwin SB, Schick IC (1983) Modeling and analysis of three-stage transfer lines with unreliable machines and finite buffers. Oper Res 31(2):354–380
Gershwin SB, Schor JE (2000) Efficient algorithms for buffer space allocation. Annals Oper Res 93(1-4):117–144
Koenigsberg E (1959) Production lines and internal storage—a review. Manag Sci 5(4):410–433
Kolb O, Göttlich S. (2015) A continuous buffer allocation model using stochastic processes. Eur J Oper Res 242(3):865–874
Levitin G, Meizin L (2001) Structure optimization for continuous production systems with buffers under reliability constraints. Int J Prod Econ 70(1):77–87
Li J, Meerkov SM (2008) Production systems engineering. Springer Science & Business Media, Germany
MacGregor Smith J, Cruz FR (2005) The buffer allocation problem for general finite buffer queueing networks. IIE Trans 37(4):343–365
Mohtashami A (2014) A new hybrid method for buffer sizing and machine allocation in unreliable production and assembly lines with general distribution time-dependent parameters. Int J Adv Manufact Technol 74(9-12):1577–1593
Motlagh MM, Azimi P, Amiri M, Madraki G (2019) An efficient simulation optimization methodology to solve a multi-objective problem in unreliable unbalanced production lines. Expert Syst Appl 138:112836
Nahas N (2017) Buffer allocation and preventive maintenance optimization in unreliable production lines. J Intell Manuf 28(1):85–93
Nahas N (2020) Buffer allocation, equipment selection and line balancing optimisation in unreliable production lines. European J Indust Eng 14(2):217–246
Nahas N, Nourelfath M (2018) Joint optimization of maintenance, buffers and machines in manufacturing lines. Eng Optim 50(1):37–54
Ouazene Y, Chehade H, Yalaoui A, Yalaoui F (2013) Equivalent machine method for approximate evaluation of buffered unreliable production lines. In: 2013 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Production and Logistics Systems (CIPLS). IEEE, pp 33–39
Ouazene Y, Yalaoui A, Yalaoui F, Chehade H (2014) Non-linear programming method for buffer allocation in unreliable production lines. In: International Conference on Analytical and Stochastic Modeling Techniques and Applications. Springer, pp 80–94
Papadopoulos H, Vidalis M (2001) A heuristic algorithm for the buffer allocation in unreliable unbalanced production lines. Comput Indust Eng 41(3):261–277
Pierreval H, Paris JL (2003) From ‘simulation optimization’ to ‘simulation configuration’ of systems. Simul Model Pract Theory 11(1):5–19
Renna P (2019) Adaptive policy of buffer allocation and preventive maintenance actions in unreliable production lines. J Indust Eng Int 15(3):411–421
Sabuncuoglu I, Erel E, Gocgun Y (2006) Analysis of serial production lines: characterisation study and a new heuristic procedure for optimal buffer allocation. Int J Prod Res 44(13):2499–2523
Seong D, Chang SY, Hong Y (1995) Heuristic algorithms for buffer allocation in a production line with unreliable machines. Int J Prod Res 33(7):1989–2005
Soyster AL, Schmidt J, Rohrer M (1979) Allocation of buffer capacities for a class of fixed cycle production lines. AIIE Trans 11(2):140–146
Su W, Xie X, Li J, Zheng L (2016) Improving energy efficiency in bernoulli serial lines: an integrated model. Int J Prod Res 54(11):3414–3428
Su W, Xie X, Li J, Zheng L, Feng SC (2017) Reducing energy consumption in serial production lines with bernoulli reliability machines. Int J Product Res 55(24):7356–7379
Weiss S, Schwarz JA, Stolletz R (2019) The buffer allocation problem in production lines: formulations, solution methods, and instances. IISE Trans 51(5):456–485
Weiss S, Stolletz R (2015) Buffer allocation in stochastic flow lines via sample-based optimization with initial bounds. OR Spectrum 37(4):869–902
Xi S, Chen Q, MacGregor Smith J, Mao N, Yu A, Zhang H (2019) A new method for solving buffer allocation problem in large unbalanced production lines. Int J Prod Res 1–22
Zhou BH, Liu YW, Yu JD, Tao D (2018) Optimization of buffer allocation in unreliable production lines based on availability evaluation. Opt Control Appl Methods 39(1):204–219
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the support from the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) and the Industrial Chair Connected-Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The article follows the guidelines of the Committee on Publication Ethics and involves no studies on human or animal subjects.
Consent to participate
Not applicable. The article involves no studies on humans.
Consent to publish
Not applicable. The article involves no studies on humans.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Authors’ contributions
The authors contributed equally to the different steps of this research.
Data availability
All the data have been presented in the manuscript. The codes developed for the current study are available from the corresponding author if requested.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alaouchiche, Y., Ouazene, Y. & Yalaoui, F. Energy-efficient buffer allocation problem in unreliable production lines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114, 2871–2885 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06971-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06971-1