Abstract
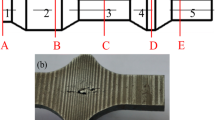
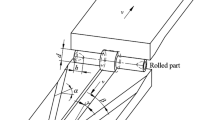
The formation of internal voids in workpieces during cross-wedge rolling affects die design and limits their widespread applications. This article investigated the formation of internal voids during the multi-wedge-multi-pass rolling production of connecting rods. A three-dimensional numerical simulation model of cross-wedge rolling (CWR) was established using the rigid-plastic finite element method, and a density change model of the porous material was developed to characterize the degree of internal void formation in the connecting rod during CWR. The optimal die parameters (forming angle, spreading angle, and distribution coefficient of area reduction) were determined by determining their relationship to the density. The stress and strain of characteristic points near the loose longitudinal sections were used to study the void formation mechanisms. The accuracy of the numerical simulations was verified by rolling experiments, which showed no void formation in the internal sections of the connecting rod after production, confirming the feasibility of using this scheme to prevent void formation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huo YM, Lin JG, Bai Q, Wang BY, Tang XF, Ji HC (2017) Prediction of microstructure and ductile damage of a high-speed railway axle steel during cross wedge rolling. J Mater Process Technol 239:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.09.001
Pater Z (2000) Theoretical and experimental analysis of cross wedge rolling process. Int J Mach Tool Manu 40(1):49–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(99)00047-4
Qiang YF, Song PB (2007) Analysis on temperature distribution in cross wedge rolling process with finite element method. J Mater Process Technol 187:392–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.11.193
Wang MT, Li XT, Du FS, Zheng YZ (2005) A coupled thermal-mechanical and microstructural simulation of the cross wedge rolling process and experimental verification. Mater Sci Eng A 391(1-2):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.08.080
Hu ZH, Wang BY, Zheng ZH (2018) Research and industrialization of near-net rolling technology used in shaft parts. Front Mech Eng 13(1):17–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-018-0480-3
Li Q, Lovell MR (2008) Cross wedge rolling failure mechanisms and industrial application. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:265–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-0979-y
Li JL, Wang BY, Qin Y, Fang S, Huang X, Chen P (2019) Investigating the effects of process parameters on the cross wedge rolling of TC6 alloy based on temperature and strain rate sensitivities. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103(5-8):2563–2577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03461-3
Jia Z, Zhou J, Ji JJ, Lei ZZ, Xiang D, Sun XT (2013) Influence analysis of area reduction for necking in twice-stage cross wedge rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 66(9-12):1407–1413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4418-3
Huang X, Wang BY, Zhou J, Ji HC, Mu YH, Li JL (2017) Comparative study of warm and hot cross-wedge rolling: numerical simulation and experimental trial. Int J Mach Tool Manu 92(9-12):3541–3551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0399-6
Li Q, Lovell MR, Slaughter W, Tagavi K (2002) Investigation of the morphology of internal defects in cross wedge rolling. J Mater Process Technol 125-126:248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00303-5
Yang CP, Dong HB, Hu ZH (2018) Micro-mechanism of central damage formation during cross wedge rolling. J Mater Process Technol 252:322–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.09.041
Urankar S, Lovell M, Morrow C, Li Q, Kawada K (2006) Establishment of failure conditions for the cross-wedge rolling of hollow shafts. J Mater Process Technol 177(1-3):545–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.04.052
Zhou J, Xiao C, Yu YY, Jia Z (2013) Influence of tool parameters on tool wear in two-roll cross-wedge rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65(5-8):745–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4213-1
Li Q, Lovell MR (2004) The establishment of a failure criterion in cross wedge rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 24(3-4):180–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-003-1607-0
Ma JW, Yang CP, Zheng ZH, Zhang KS, Ma WY (2016) Influence of process parameters on the microstructural evolution of a rear axle tube during cross wedge rolling. Int J Miner Metall Mater 23(11):1302–1314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1352-7
Pater Z (2006) Finite element analysis of cross wedge rolling. J Mater Process Technol 173(2):201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.11.027
Xiong Y, Sun S, Li Y, Zhao J, Lv Z, Zhao D, Zheng Y, Fu W (2006) Effect of warm cross-wedge rolling on microstructure and mechanical property of high carbon steel rods. Mater Sci Eng A 431(1-2):152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.148
Wei YL, Shu XD, Han ST, Tian DY, Wei J (2018) Analysis of microstructure evolution during different stages of closed-open cross wedge rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(5-8):1975–1988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1359-x
Li JL, Wang BY, Huang H, Fang S, Chen P, Shen JX (2018) Unified modelling of the flow behavior and softening mechanism of a TC6 titanium alloy during hot deformation. J Alloys Compd 748:1031–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.120
Li JL, Wang BY, Qin Y, Fang S, Huang X, Chen P (2019) Investigating the effects of process parameters on the cross wedge rolling of TC6 titanium alloy based on temperature and stain rate sensitivities. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103(5-8):2563–2577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03461-3
Huang X, Wang BY, Mu YH, Shen JX, Li JL, Zhou J (2019) Investigation on the effect of mandrels on hollow shafts in cross-wedge rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102(1-4):443–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-309
Pater Z, Weronski W, Kazanecki J, Gontarz A (1999) Study of the process stability of cross wedge rolling. J Mater Process Technol 92-93:458–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(99)00229-0
Wu ZJ, Peng WF, Shu XD (2016) Influence of rolling temperature on interface properties of the cross wedge rolling of 42CrMo/Q235 laminated shaft. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(1-4):517–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9734-6
Ji HC, Liu JP, Wang BY, Tang XF, Huo YM, Zhou J, Hu ZH (2016) Constitutive relational of 4Cr9Si2 and technological parameters on the inner bore of cross wedge rolling for preform hollow values. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(9-12):2621–2633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8360-7
Yang CP, Hu ZH (2016) Research on the ovality of hollow shafts in cross wedge rolling with mandrel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83(1-4):67–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7478-3
Zhou J, Yu YY, Zeng Q (2014) Analysis and experimental studies of internal voids in multi-wedge cross wedge rolling stepped shaft. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 72(9-12):1559–1566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5768-9
Huang HG, Du FS, Xu ZQ (2011) FEM analyses on compaction of porosity defects inside heavy forgings during hot forging process. Eng Mech 28(9):245–250. http://gclx.chinajournal.net.cn/WKE/WebPublication/kbDownload.aspx?fn=GCLX201109038
Li JL, Wang BY, Ji HC, Huang X, Tang XF, Ma WP (2017) Effect of the cross wedge rolling parameters on the formability of Ti-6Al-4 V alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92(5-8):2217–2229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0263-8
Li XT, Wang MT, Du FS (2006) The coupling thermal-mechanical and microstructural model for the FEM simulation of cross wedge rolling. J Mater Process Technol 172(2):202–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.10.011
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51665032), Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Gansu Province (Grant No. 18JR3RA134), and Lanzhou University of Technology Support plan for Excellent Young Scholars (Grant No. CGZH001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Z., Ji, J., Wang, Y. et al. Influence of die parameters on internal voids during multi-wedge-multi-pass cross-wedge rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 110, 1295–1304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05897-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05897-4