Abstract
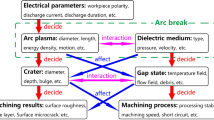
In electrical discharge machining (EDM), the arc plasma plays an important role in material removal and crater formation. However, the dynamic characteristics of arc plasma during the machining still have a lack of attention. In this study, a high-speed camera and an image processing method were applied to investigate the arc plasma movement behavior with respect to crater formation during single-pulse discharge. The results showed that when the tool electrode was copper and workpiece was steel, with different workpiece polarities, the arc plasma moving speed and moving range changed and thus different crater morphologies were generated. A larger discharge current and narrower gap distance caused more intense arc plasma movement, thus influencing the crater morphology. Changes in the electrode end shape could influence the arc plasma movement and shape, and the movement of arc plasma would be restricted when the discharge was conducted in oil compared with discharging in air.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunieda M, Lauwers B, Rajurkar KP, Schumacher BM (2005) Advancing EDM through fundamental insight into the process. CIRP Ann 54(2):64–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60020-1
Klink A, Holsten M, Hensgen L (2017) Crater morphology evaluation of contemporary advanced EDM generator technology. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 66(1):197–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2017.04.137
Maradia U, Filisetti E, Boccadoro M, Roten M, Dutoit JM, Hengsberger S (2018) Increasing the injection moulding productivity through EDM surface modulation. Procedia CIRP 68:58–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.022
Antar M, Hayward P, Dunleavey J, Butler-Smith P (2018) Surface integrity evaluation of modified EDM surface structure. Procedia CIRP 68:308–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.069
Zhang M, Zhang Q, Wang H, Liu G, Guo T (2015) Research on a single pulse discharge to discriminate EDM and EAM based on the plasma tunnel and crater geometry. J Mater Process Technol 219:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.12.016
Descoeudres A, Hollenstein C, WäLder G, Perez R (2005) Time-resolved imaging and spatially-resolved spectroscopy of electrical discharge machining plasma. J Phys D Appl Phys 38(22):4066–4073. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/38/22/009
Natsu W, Ojima S, Kobayashi T, Kunieda M (2004) Temperature distribution measurement in EDM arc plasma using spectroscopy. JSME Int J Ser C 47(1):384–390. https://doi.org/10.1299/jsmec.47.384
Koijma A, Natsu W, Kunieda M (2008) Spectroscopic measurement of arc plasma diameter in EDM. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 57(1):203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.097
Kitamura T, Kunieda M (2014) Clarification of EDM gap phenomena using transparent electrodes. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 63(1):213–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2014.03.059
Tang J, Yang X (2017) A novel thermo-hydraulic coupling model to investigate the crater formation in electrical discharge machining. J Phys D Appl Phys 50(36):365301. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa7bb7
Zhang F, Gu L, Hu J, Zhao W (2016) A new thermal model considering tie of the expanding spark for anode erosion process of EDM in water. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(1–4):573–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7389-3
Panda DK, Bhoi RK (2006) Electro-discharge machining-a qualitative approach. Mater Manuf Process 21(8):853–862. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602550600728208
Salonitis K, Stournaras A, Stavropoulos P, Chryssolouris G (2009) Thermal modeling of the material removal rate and surface roughness for die-sinking EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40(3–4):316–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1327-y
Peças P, Henriques E (2008) Effect of the powder concentration and dielectric flow in the surface morphology in electrical discharge machining with powder-mixed dielectric (PMD-EDM). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:1120–1132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1061-5
Amorim F, Dalcin V, Soares P, Mendes L (2017) Surface modification of tool steel by electrical discharge machining with molybdenum powder mixed in dielectric fluid. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9678-x
Shen Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Tan B, Ji R, Cai B, Zheng C (2014) Determining the energy distribution during electric discharge machining of Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(1–4):11–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5194-4
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Shen Y, Li Z, Ji R, Cai B (2014) A novel method of determining energy distribution and plasma diameter of EDM. Int J Heat Mass Transf 75:425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.03.082
Kunieda M, Xia H, Nishiwaki N, Kinoshita N (1992) Observation of arc column movement during monopulse discharge in EDM. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 41(1):227–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61191-3
Klocke F, Mohammadnejad M, Holsten M, Ehle L, Zeis M, Klink A (2018) A comparative study of polarity-related effects in single discharge EDM of titanium and iron alloys. Procedia CIRP 68:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.021
Wei D, Di S, Wang Y, Wang Z (2016) Analyzing of discharge wave oscillation mechanism in electrical discharge machining. Procedia CIRP 42:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.178
Weizhen P, Changning G, Yaowei Y (2015) Study on temperature distribution for single pulse discharge with moving center of plasma. Electromach Mould 3(8–11):15
Hayakawa S, Kusafuka Y, Itoigawa F, Nakamura T (2016) Observation of material removal from discharge spot in electrical discharge machining. Procedia CIRP 42:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.175
Tanabe R, Kusano H, Ito Y (2009) High-speed imaging system for observation of discharge phenomena 28th Int Cong High-Speed Imaging. Photonics 7126:71260–71269. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.822050
David LO (1993) ASM handbook, vol 6, 10th edn. ASM International, Materials Park, p 163
Xia H, Kunieda M, Nishiwaki N (1996) Removal amount difference between anode and cathode in EDM process. IJEM 1:45–52. https://doi.org/10.2526/ijem.1.45
Zhang M, Zhang Q, Zhu G, Liu Q, Zhang J (2016) Effects of some process parameters on the impulse force in single pulsed EDM. Procedia CIRP 42:627–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.260
Funding
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program, No. 51875133, 51575136) and the Key Laboratory of Micro-systems and Micro-structures Manufacturing of Ministry of Education, Harbin Institute of Technology (No. 2017KM002) for providing financial support for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Yang, X. Study on arc plasma movement and its effect on crater morphology during single-pulse discharge in EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106, 5033–5047 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04964-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04964-0