Abstract
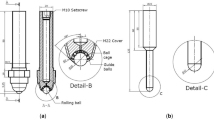
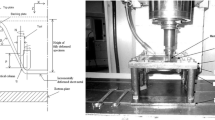
Single-point incremental forming (SPIF) is a rising technology used shaping sheet-metals. The emergence of this manufacturing process is due to its capability to produce parts with complex shape at lower cost. The present contribution is focused on the presentation of a new designed rolling ball forming tool that can improve (SPIF) operations. For that, the effects of process working parameters on a set of process qualification criteria when forming of AA1050 aluminum alloy sheets is presented. Deep analyses treating impacts of tool step down, tool rolling ball diameter, and tool feed rate on the process responses such as forming axial forces, surface roughness, and sheet thinning are made. The analysis is based on statistical methodologies which made it possible to establish, using the multiple regression method, predictive analytical models for the different responses.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- D:
-
Rolling ball diameter (mm)
- Df:
-
Degrees of freedom
- F:
-
Tool feed rate (mm/min)
- Favr :
-
Average axial forming force (N)
- Fmax :
-
Maximal axial forming force (N)
- Fz :
-
Axial Forming force (N)
- F-value:
-
Fisher test value
- ISF:
-
Incremental sheet forming
- MS:
-
Mean squares
- PC%:
-
Percentage of contribution (%)
- P value:
-
Value of significance
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- R2 :
-
Determination coefficient
- R2adjusted :
-
Adjusted determination coefficient
- R2predictif :
-
Predictive determination coefficient
- Ra :
-
Arithmetic mean roughness (μm)
- Rz :
-
Mean peak-to-valley height (μm)
- Rt :
-
Maximum profile height (μm)
- SPIF:
-
Single-point incremental forming
- SS:
-
Squared deviations
- SSD :
-
Sum of squared deviations
- SST :
-
Total sum of squared deviations
- ΔZ:
-
Vertical step down (mm)
- ϕ:
-
Wall angle (degree)
References
Leszak E (1967) Apparatus and process for incremental dieless forming, United States Patent Office. Patent [US 3342051]
Mason B, Appleton E (1984) Sheet metal forming for small batches using sacrificial tooling.. In: Proc 3rd Int. Conf. On rotary metalworking, Kyoto, Japan, pp. 495–511
Emmens WC, Sebastiani G, Boogaard AH (2010) The technology of incremental sheet forming – a brief review of the history. J Mater Process Technol 210:981–997
Iseki H, Kato K, Sakamoto S (1989) Flexible and incremental sheet metal forming using a spherical roller. Proceedings of 40th JJCTP41–44
Matsubara S (1994) Incremental backward bulge forming of a sheet metal with a hemispherical head tool. JJpn Soc Technol Plast 35(1994):1311–1316
Jeswiet J, Micari F, Hirt G, Bramley A, Duflou A, Allwood J (2005) Asymmetric single point incremental forming of sheet metal. CIRP Ann 54(2):623–649
Gunashekar G, Kishore K (2017) Modeling and manufacturing of an aerospace component by single point incremental forming process. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology 4(9): 600-603
Hussain G, Khan HR, Gao L, Hayat N (2013) Guidelines for tool-size selection for single-point incremental forming of an aerospace alloy. Mater Manuf Process 28(3):324–329
Boulila A, Ayadi M, Marzouki S, Slim B (2018) Contribution to a biomedical component production using incremental sheet forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95:2821
Wulf WA (2007) Changes in innovation ecology. Science 316:1253
Behera A K, Alves de Sousa R, Ingarao G, Oleksik V (2017) Single point incremental forming: an assessment of the progress and technology trends from 2005 to 2015. The Society of Manufacturing Engineers.1526–6125/2017
Li Y, Chen X, Liu Z, Sun J, Li F, Li J, Zhao GA Review on the recent development of incremental sheet-forming process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:2439–2462
Bahloul R, Arfa H, BelHadjSalah H (2014) A study on optimal design of process parameters in single point incremental forming of sheet metal by combining Box–Behnken design of experiments, response surface methods and genetic algorithms. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74:163–185
Gatea S, Ou H, McCartney G (2016) Review on the influence of process parameter in incremental sheet forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87:479–499
Cawley B, Adams D, Jeswiet J (2012) Examining tool shapes in single point incremental forming. Proc NAMRI/SME 13(17):163
Hussain G (2014) Experimental investigations on the role of tool size in causing and controlling defects in single point incremental forming process. Proc IMechE Part B 228:266–277
Siddiqi MUR, Corney JR, Sivaswamy G, Amir M, Bhattacharya R (2017) Design and validation of a fixture for positive incremental sheet forming. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 232(4):629–643
Do VC, Lee BH, Yang SH, Kim YS (2017) The forming characteristic in the single-point incremental forming of a complex shape. Int J Nanomanuf 13(1):33
Fernandez C, Trujillo A, Rivero A, Alvarez M, Puerta F J, Salguero J, Marcos M (2016) Implementing incremental sheet metal forming on a CNC machining centre. Proceedings of the 26th DAAAM International Symposium, pp.0926-0929, B
Li Y, Lu H, Daniel WJT, Meehan PA (2015) Investigation and optimization of deformation energy and geometric accuracy in the incremental sheet forming process using response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:2041–2055
Ambrogio G, Duflou J.R, Filice L, Aerens R (2007) Some considerations on force trends in Incremental Forming of different materials. 10th ESAFORM conference on material forming, AIP Conference Proceedings, vol 907, pp 193–198
Aerens R, Eyckens P, Van Bael A, Duflou JR (2010) Force prediction for single point incremental forming deduced from experimental and FEM observations. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 46:969–982
Dwivedy M, Kalluri V (2019) The effect of process parameters on forming forces in single point incremental forming. Procedia Manuf 29/120–128
Saidi B, Giraud-Moreau L, Boulila A, Cherouat A, Nasri R (2017) Experimental and numerical study on force reduction in SPIF by using response surface. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering, 835–844
Duflou JR, Tunçkol Y, Aerens R (2007) Force analysis for single point incremental forming. Key Eng Mater:344/543–344/550
Duflou J, Tunckol Y, Szekeres A, Vanherck P (2007) Experimental study on force measurements for single point incremental forming. J Mater Process Technol 189:65–72
Liu Z, Liu S, Li Y, Meehan PA (2014) Modeling and optimization of surface roughness in incremental sheet forming using a multi-objective function. Mater Manuf Process 29(7):808–818
Kurra S, Rahman NH, Regalla SP, Gupta AK (2018) Modeling and optimization of surface roughness in single point incremental forming process. J Mater Res Technol 4(3):304–313
Durante M, Formisano A, Langella A, Capece Minutolo FM (2009) The influence of tool rotation on an incremental forming process. J Mater Process Technol 209(9):4621–4626
Durante M, Formisano A, Langella A (2010) Comparison between analytical and experimental roughness values of components created by incremental forming. J Mater Process Technol 210(14):1934–1941
Salem E, Shin J, Nath M, Banu M, Taub A (2016) Investigation of thickness variation in single point incremental forming. Procedia Manuf:5/828–5/837
Li JC, Li C, Zhou TG (2012) Thickness distribution and mechanical property of sheet metal incremental forming based on numerical simulation. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 22(1):58–64
Iseki H, Kato K, Sakamoto S (1989) Flexible and incremental sheet metal forming using a spherical roller. Proceedings of 40th JJCTP41–44
Kim YH, Park JJ (2002) Effect of process parameters on formability in incremental forming of sheet metal. J Mater Process Technol 130-131:42–46
Shim MS, Park JJ (2001) The formability of aluminum sheet in incremental forming. J Mater Process Technol 113(1–3):654–658
Matsubara S (2001) Apparatus for dieless forming plate materials, United States Patent Office. Patent [US6216508B1]
Zhongyi C (2010) Rolling tool head for incremental forming, Chinese Patent Office. Patent [CN101758135A]
Lu B et al (2014) Mechanism investigation of friction-related effects in single point incremental forming using a developed oblique rollerball tool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 85:14–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilani, L., Mabrouki, T., Ayadi, M. et al. Effects of rolling ball tool parameters on roughness, sheet thinning, and forming force generated during SPIF process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106, 4123–4142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04918-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04918-1