Abstract
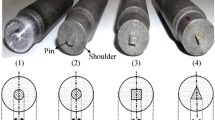
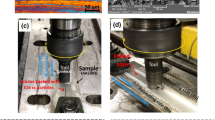
The aim of this work is to produce a surface composite by incorporating B4C particles on the surface of AA7075 alloy through friction stir processing (FSP) using both a pinless and a cone pin tool. The influence of friction stir processing parameters on the microstructure, hardness, and wear properties of the processed surface composites was investigated. The studied parameters include rotational tool speed (400 and 600 rpm) and number of passes (1, 2, 3, and 4 passes). Microstructural analysis and microhardness profiles were performed on cross sections of FSPed samples at different depths. Wear behavior of the processed samples was evaluated by means of dry sliding tests. The results indicate that (i) increasing the number of passes results in improving the distribution of B4C reinforcing particles, (ii) samples processed with the pinless tool displayed a more homogeneous distribution of the reinforcement in the outer layer of the material with respect to the samples processed with the cone pin, (iii) the addition of B4C particles improved the wear resistance of the AA7075 alloy even if it led to a raise in the coefficient of friction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora HS, Singh H, Dhindaw BK (2012) Composite fabrication using friction stir processing - a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61:1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3758-8
Węglowski MS (2018) Friction stir processing – state of the art. Arch Civ Mech Eng 18:114–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2017.06.002
Mishra RS, Ma ZY, Charit I (2003) Friction stir processing: a novel technique for fabrication of surface composite. Mater Sci Eng A 341:307–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00199-5
Mishra RS, Ma ZY (2005) Friction stir welding and processing. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 50:1–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2005.07.001
Ma ZY (2008) Friction stir processing technology: a review. Metall Mater Trans A 39:642–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9459-0
Mishra R, Sarathi De P, Kumar N (2014) Friction stir welding and processing, 1st ed. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07043-8.
Park SHC, Sato YS, Kokawa H (2003) In: David SA, DebRoy T, Lippold JC, Smaett HB, Vitek JM (eds) Proc. Sixth Int. Conf. Trends Weld. Res. ASM International, Pine Mountain, p 267
Lee WB, Yeon YM, Kim DU, Jung SB (2003) Effect of friction welding parameters on mechanical and metallurgical properties of aluminium alloy 5052–A36 steel joint. Mater Sci Technol 19:773–778. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708303225001876
Bauri R, Yadav D, Suhas G (2011) Effect of friction stir processing (FSP) on microstructure and properties of Al-TiC in situ composite. Mater Sci Eng A 528:4732–4739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.085
Maurya R, Kumar B, Ariharan S, Ramkumar J, Balani K (2016) Effect of carbonaceous reinforcements on the mechanical and tribological properties of friction stir processed Al6061 alloy. Mater Des 98:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.03.021
Shyam Kumar CN, Bauri R, Yadav D (2016) Wear properties of 5083 Al-W surface composite fabricated by friction stir processing. Tribol Int 101:284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.04.033
Dolatkhah A, Golbabaei P, Besharati Givi MK, Molaiekiya F (2012) Investigating effects of process parameters on microstructural and mechanical properties of Al5052/SiC metal matrix composite fabricated via friction stir processing. Mater Des 37:458–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.09.035
Raaft M, Mahmoud TS, Zakaria HM, Khalifa TA (2011) Microstructural, mechanical and wear behavior of A390/graphite and A390/Al2O3 surface composites fabricated using FSP. Mater Sci Eng A 528:5741–5746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.03.097
Dinaharan I, Nelson R, Vijay SJ, Akinlabi ET (2016) Microstructure and wear characterization of aluminum matrix composites reinforced with industrial waste fly ash particulates synthesized by friction stir processing. Mater Charact 118:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2016.05.017
Barenji RV, Khojastehnezhad VM (2015) Wear properties of Al–Al2O3/TiB2 surface hybrid composite layer prepared by friction stir process. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998315592007.
Elangovan K, Balasubramanian V, Valliappan M (2008) Influences of tool pin profile and axial force on the formation of friction stir processing zone in AA6061 aluminium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 38:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1100-2
Palanivel R, Dinaharan I, Laubscher RF, Davim JP (2016) Influence of boron nitride nanoparticles on microstructure and wear behavior of AA6082/TiB2 hybrid aluminum composites synthesized by friction stir processing. Mater Des 106:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.127
Thévenot F (1990) Boron carbide—a comprehensive review. J Eur Ceram Soc 6:205–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/0955-2219(90)90048-K
N. Eustathopoulos, A. Mortensen (1993) Chapter 3—capillary phenomena, interfacial bonding, and reactivity. In: Fundam. Met. Compos., Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp. 42–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-052371-2.50007-9
Canakci A, Arslan F, Varol T (2013) Effect of volume fraction and size of B4C particles on production and microstructure properties of B4C reinforced aluminium alloy composites. Mater Sci Technol 29:954–960. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284713Y.0000000232
Baradeswaran A, Elaya Perumal A (2013) Influence of B4C on the tribological and mechanical properties of Al 7075-B4C composites. Compos Part B Eng 54:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.05.012
Pang JJ, Liu FC, Liu J, Tan MJ, Blackwood DJ (2015) Friction stir processing of aluminium alloy AA7075: microstructure, surface chemistry and corrosion resistance. Corros Sci 106:217–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2016.02.006.
Rana H, Badheka V, Kumar A, Satyaprasad A (2018) Strategical parametric investigation on manufacturing of Al–Mg–Zn–Cu alloy surface composites using FSP. Mater Manuf Process 33:534–545. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1364752
Ahmed MMZ, Ahmed E, Hamada AS, Khodir SA, El-Sayed Seleman MM, Wynne BP (2016) Microstructure and mechanical properties evolution of friction stir spot welded high-Mn twinning-induced plasticity steel. Mater Des 91:378–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.12.001
Hoziefa W, Toschi S, Ahmed MMZ, Morri A, Mahdy AA, El-Sayed Seleman MM, El-Mahallawi I, Ceschini L, Atlam A (2016) Influence of friction stir processing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a compocast AA2024-Al2O3 nanocomposite. Mater Des 106:273–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.114
Refat M, Elashery A, Toschi S, Ahmed MMZ, Morri A, El-Mahallawi I, Ceschini L (2016) Microstructure, hardness and impact toughness of heat-treated nanodispersed surface and friction stir-processed aluminum alloy AA7075. J Mater Eng Perform 25:5087–5101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2346-3
Zhu Y, Sun K, Frankel GS (2018) Intermetallic phases in aluminum alloys and their roles in localized corrosion. J Electrochem Soc 165:807–820. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0931811jes
Kumar PV, Reddy GM, Rao KS (2015) Microstructure , mechanical and corrosion behavior of high strength AA7075 aluminium alloy friction stir welds - effect of post weld heat treatment. Def Technol 11:362–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2015.04.003
Vander Voort GF (2004) ASM handbook volume 9 - metallography and microstructures. ASM Interbational. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v09.9781627081771
Narimani M, Lotfi B, Sadeghian Z (2015) Investigating the effect of tool dimension and rotational speed on microstructure of Al-B4C surface composite layer produced by friction stir processing (FSP). J Adv Mate Proc 3(2):61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.09.009
Deuis RL, Subramanian C, Yellupb JM (1997) Dry sliding wear of aluminium composites-a review. Compos Sci Technol 57:415–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(96)00167-4.
Singh J, Chauhan A (2016) Overview of wear performance of aluminium matrix composites reinforced with ceramic materials under the influence of controllable variables. Ceram Int 42:56–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.150
Ceschini L, Toschi S (2017) Friction and wear of aluminum alloys and composites. In: ASM handb. Vol.18 - Frict. Lubr. Wear Technol., ASM international, pp. 509–532. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v18.a0006388
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF)—Egypt for the support with grant no. 3926. The activity is also part of the Mobility Project Italy-Egypt M02115 entitled “Modification of the aluminium pistons’ crown by means of nanoparticle addition and friction stir processing.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tonelli, L., Morri, A., Toschi, S. et al. Effect of FSP parameters and tool geometry on microstructure, hardness, and wear properties of AA7075 with and without reinforcing B4C ceramic particles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102, 3945–3961 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03442-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03442-6