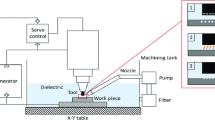
Abstract
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) with three-phase flow dielectric medium uses gas-liquid-powder mixture as the dielectric medium to improve the machining performance of the EDM. The appropriate selection of processing parameters makes for the improvement of machining properties for this EDM process. The material removal rate (MRR), tool wear rate (TWR), and surface roughness (SR) of EDM with three-phase flow dielectric medium are studied experimentally. The influence of process parameters, including peak current, pulse on time, pulse off time, flow rate, and concentration of powder particles, on these performance parameters, including MRR, TWR, and SR, are found out based on the orthogonal design experiment and the signal-to-noise ratio analysis. The reasons for these influences are analyzed. The optimal combination of process parameters to improve each single performance parameter is obtained. Verification tests are carried out. It is verified that the best combination of process parameters for MRR is powder concentration at the middle level, flow rate at the high level, pulse on time at the middle level, pulse off time at the low level, and peak current at the high level; the best for TWR is powder concentration at the low level, flow rate at the low level, pulse on time at the high level, pulse off time at the low level, and peak current at the low level; the best for Ra is powder concentration at the middle level, flow rate at the high level, pulse on time at the low level, pulse off time at the high level, and peak current at the low level, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu AY, Liu ZD, Li WP, Tian ZJ, Qiu MB (2014) Study of high-efficiency electrical discharge machining-induced ablation machining of titanium alloy TC4 using a multi-function electrode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 72(1–4):377–385
Aliakbari E, Baseri H (2012) Optimization of machining parameters in rotary EDM process by using the Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(9–12):1041–1053
Keskin Y, Halkacı H, Kizil M (2006) An experimental study for determination of the effects of machining parameters on surface roughness in electrical discharge machining (EDM). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28(11–12):1118–1121
Hadad M, Bui LQ, Nguyen CT (2017) Experimental investigation of the effects of tool initial surface roughness on the electrical discharge machining (EDM) performance. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1399-2
Lin JL, Wang KS, Yan BH, Tarng YS (2000) An investigation into improving worn electrode reliability in the electrical discharge machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 16(2):113–119
Shabgard MR, Gholipoor A, Baseri H (2016) A review on recent developments in machining methods based on electrical discharge phenomena. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(5–8):2081–2097
Amorim FL, Dalcin VA, Soares P, Mendes LA (2017) Surface modification of tool steel by electrical discharge machining with molybdenum powder mixed in dielectric fluid. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(1–4):341–350
Bhattacharya A, Batish A, Singh G, Singla VK (2012) Optimal parameter settings for rough and finish machining of die steels in powder-mixed EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61(5–8):537–548
Govindan P, Joshi SS (2010) Experimental characterization of material removal in dry electrical discharge drilling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(5):431–443
Saha SK, Choudhury SK (2009) Experimental investigation and empirical modeling of the dry electric discharge machining process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49(3–4):297–308
Shen Y, Liu YH, Dong H, Zhang K, Lv L, Zhang XZ, Wu XL, Zheng C, Ji RJ (2017) Surface integrity of Inconel 718 in high-speed electrical discharge machining milling using air dielectric. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90(1–4):691–698
Tanimura T, Isuzugawa K, Fujita I, Iwamoto A, Kamitani T (1989) Development of EDM in the mist. Proceedings of the 9th ISEM IX, Nagoya, Japan:313–316
Kao CC, Tao J, Shih AJ (2007) Near dry electrical discharge machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(15):2273–2281
Dhakar K, Dvivedi A, Dhiman A (2016) Experimental investigation on effects of dielectric mediums in near-dry electric discharge machining. J Mech Sci Technol 30(5):2179–2185
Tao J, Shih AJ, Ni J (2008) Experimental study of the dry and near-dry electrical discharge milling processes. J Manuf Sci Eng 130:011002-1-011002-9
Gu L, Zhao WS, Zhang ZH, Kang XM (2006) Mist-jetting-ED-milling and its mechanism. Electromachining Mould 2:1–4
Li L, Gu L, Xia YG, Zhao WS (2007) Experimental study of mist-jetting electric discharge milling. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ 41(10):1569–1572
Yang K, Gu L, Xue R, Zhang FW, Zhao WS (2012) Experimental study of mist-jetting electrical discharge milling. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ 46(7):1021–1025+1031
Zhang QH, Zhang JH, Ren SF, Deng JX, Ai X (2004) Study on technology of ultrasonic vibration aided electrical discharge machining in gas. J Mater Process Technol 149(1–3):640–644
Gao Q, Zhang QH, Zhang JH (2009) Experimental study of powder-mixed near dry electrical discharge machining. Chi J Mech Eng 45(11):169–175
Funding
The work is supported by a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (grant no. ZR2016EEB14) in China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 51075239).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X., Yang, T. & Zhang, Q. Experimental study on the electrical discharge machining with three-phase flow dielectric medium. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96, 2003–2011 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1747-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1747-x