Abstract
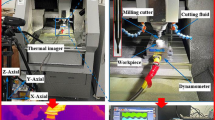
The ability to manufacture a product is assessed by factors such as surface quality and features tolerances. The main goal of the present investigation is to carry out an experimental study on the accuracy of holes produced through a novel helical milling process on AISI 4340 alloy steel. This process is referred to as production of holes through mobile milling on a helical path. Taguchi experimental design method was used in order to investigate the effect of the main parameters including feed rate, cutting speed, axial depth of cut, and workpiece hardness on the hole surface roughness and geometrical and dimensional tolerances. In addition, the impact of using two methods of minimum quantity lubrication and dry milling was discussed. The results showed that the helical milling method can be a suitable alternative for conventional drilling. Lubrication method was the most effective parameter on surface roughness and nominal diameter with contribution of 43 and 41%, respectively. In addition, cutting speed had the most impact on circularity and cylindricity with contribution of 44 and 41%, respectively. Furthermore, the most precise hole was obtained at cutting speed of 70 m/min and feed rate of 0.01 mm/tooth in presence of minimum quantity lubrication system using vegetable oil, while using mineral oil led to making a hole with highest surface quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tönshoff H, Spintig W, König W, Neises A (1994) Machining of holes developments in drilling technology. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 43(2):551–561
Byrne G, Dornfeld D, Denkena B (2003) Advancing cutting technology. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 52(2):483–507
Denkena B, Boehnke D, Dege J (2008) Helical milling of CFRP–titanium layer compounds. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 1(2):64–69
Shan Y, He N, Li L, Zhao W, Qin X (2011) Orbital milling hole of aerospace Al-alloy with big pitch. Trans Tianjin Univ 17:329–335
Lawal S, Choudhury I, Nukman Y (2012) Application of vegetable oil-based metalworking fluids in machining ferrous metals—a review. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 52(1):1–12
Sadeghi M, Haddad M, Tawakoli T, Emami M (2009) Minimal quantity lubrication-MQL in grinding of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(5–6):487–500
Iyer R, Koshy P, Ng E (2007) Helical milling: an enabling technology for hard machining precision holes in AISI D2 tool steel. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(2):205–210
Sasahara H, Kawasaki M, Tsutsumi M (2008) Helical feed milling with MQL for boring of aluminum alloy. J Adv Mech Des, Syst Manuf 2(6):1030–1040
Li H, He G, Qin X, Wang G, Lu C, Gui L (2014) Tool wear and hole quality investigation in dry helical milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(5–8):1511–1523
Olvera D, de Lacalle LNL, Urbikain G, Lamikiz A, Rodal P, Zamakona I (2012) Hole making using ball helical milling on titanium alloys. Mach Sci Technol 16(2):173–188
Ribeiro JLS, Diniz SB, Rubio JCC, Abrão AM (2012) Dimensional and geometric deviations induced by milling of annealed and hardened AISI H13 tool steel. Am J Mater Sci 2(1):14–21
Li Z, Liu Q (2013) Surface topography and roughness in hole-making by helical milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 66(9–12):1415–1425
Kilickap E, Huseyinoglu M, Yardimeden A (2011) Optimization of drilling parameters on surface roughness in drilling of AISI 1045 using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 52(1–4):79–88
Tasdelen B, Wikblom T, Ekered S (2008) Studies on minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) and air cooling at drilling. J Mater Process Technol 200(1):339–346
Tönshoff HK, Friemuth T, Andrae P, Groppe M (2001) High efficient circular milling: a solution for economical machining of bore holes in composite materials. In proceedings of the third international conference on high speed machining, Metz, France: 287–296
Brinksmeier E, Fangmann S, Meyer I (2008) Orbital drilling kinematics. Prod Eng 2(3):277–283
Abrao AM, Ribeiro JLS, Davim JP (2011) Surface Integrity, Machining of Hard Materials. Springer: 115–141
Rey P, LeDref J, Senatore J, Landon Y (2016) Modelling of cutting forces in orbital drilling of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 106:75–88
Abdalla H, Patel S (2006) The performance and oxidation stability of sustainable metalworking fluid derived from vegetable extracts. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 220(12):2027–2040
Yallese MA, Chaoui K, Zeghib N, Boulanouar L, Rigal J-F (2009) Hard machining of hardened bearing steel using cubic boron nitride tool. J Mater Process Technol 209(2):1092–1104
Cui X, Zhao J, Jia C, Zhou Y (2012) Surface roughness and chip formation in high-speed face milling AISI H13 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61(1–4):1–13
Vivancos J, Luis C, Ortiz J, González H (2005) Analysis of factors affecting the high-speed side milling of hardened die steels. J Mater Process Technol 162:696–701
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saadatbakhsh, M.H., Imani, H., Sadeghi, M.H. et al. Experimental study of surface roughness and geometrical and dimensional tolerances in helical milling of AISI 4340 alloy steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93, 4063–4074 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0782-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0782-3