Abstract
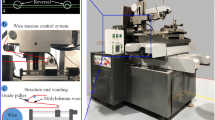
In order to improve the efficiency of micro electrical discharge machining (micro EDM), the rotational spindle is widely used at present. Since the EDM technology is invented, the relaxation-type pulse generator, transistor-type pulse generator, or their combinations have been generally used. However, with these pulse generators, it is difficult to supply electrical power to the tool electrode rotating at extremely high speed without causing the vibration and spindle wear due to the contact electric feeding using a brush. So the tool electrode rotating speed is less than thousands of revolutions per minute (rpm) usually. Based on the principle of electrostatic induction, the non-contact electric feeding can be realized in micro EDM. So the rotating speed of the tool electrode can reach high rotating speed. This paper studied the machining characteristics of micro EDM under the high spindle speed up to 60,000 rpm by the machining of micro rods and the micro holes. As a result, the minimum electrode of Φ 2 μm in diameter and 10 μm in length, and the micro rod of Φ 5 μm in diameter and 80 μm in length with a high aspect ratio of 16 were obtained by block electrical discharge grinding (BEDG) method. From the micro hole machining results, it was found that with the increase of the spindle speed, the material removal rate increases, while the electrode wear ratio decreases. Meanwhile, the higher aspect ratio and machining accuracy were realized and the surface roughness was also improved significantly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masuzawa T (2000) State of the art of micromachining. Annals of the CIRP 49(2):473–488
Masuzawa T (2001) Micro-EDM. Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium of Electromachining-ISEM XIII, Bilbao, Spain 3–19
Kunieda M, Yanatori K (1997) Study on debris movement in EDM gap. International Journal of Electrical Machining 2:43–49
Masuzawa T (2007) Application of EDM for micromachining. Journal of the Japan Society of Electrical Machining Engineers 41:148–151
Ozgedik A, Cogun C (2006) An experimental investigation of tool wear in electric discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27(5–6):488–500
Koenig W, Weill R, Wertheim R, Jutzler WI (1977) The flow fields in the working gap with electro-discharge-machining. Annals of the CIRP 25(1):71–76
Masuzawa T, Heuvelman CJ (1983) A self-flushing method with spark-erosion machining. Annals of the CIRP 32(1):109–111
Wang J, Han F (2014) Simulation model of debris and bubble movement in electrode jump of electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74(5–8):591–598
Huang H, Zhang H, Zhou L, Zheng HY (2003) Ultrasonic vibration assisted electro-discharge machining of micro holes in Nitinol. Journal of Micromechanics & Microengineering 13(5):693–700
Tong H, Li Y, Wang Y (2008) Experimental research on vibration assisted EDM of micro-structures with non-circular cross-section. J Mater Process Technol 208(1–3):289–298
Kunieda M, Hayasaka A, Yang XD, Sano S, Araie I (2007) Study on Nano EDM using capacity coupled pulse generator. Annals of the CIRP 56(1):213–216
Yang XD, Kimori M., Kunieda M, Araie I, Sano S (2007) Machining properties of micro EDM using electrostatic induction feeding. Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium of Electromashining-ISEM XV, Pittsburgh, USA 231–234
Yang XD, Kunieda M, Sano S (2008) Study on the influence of stray capacitance in micro EDM using electrostatic induction feeding. International Journal of Electrical Machining 13:35–40
Koyano T, Yahagi Y, Kunieda M, and Yang XD (2010) High spindle speed micro EDM using electrostatic induction feeding method. Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium of Electromashining-ISEM XVI, Shanghai, China 699–702
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, G.L., Yang, X.D. & Chi, G.X. Study on machining characteristics of micro EDM with high spindle speed using non-contact electric feeding method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 1979–1989 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0290-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0290-5