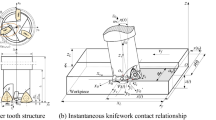
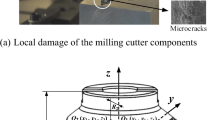
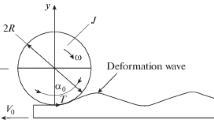
Abstract
Under the influence of a high-speed, interrupted-cutting impact load, a great difference is existed among the internal load propagation of a milling cutter. Furthermore, the cutter damage caused by partial particle severe vibration has restricted the improvement of a high-speed milling energy efficiency; thus, the essence of wave dynamics damage in milling cutter remains has yet to be revealed. In this paper, through the relation between the systematic whole vibration and the particle motion, the dynamic response of milling cutter’s particle to cutting force load can be solved by the particle motion differential equation which is constructed with a one-dimensional string dynamic system. A combination of Newton’s second law and the constitutive equation of milling cutter material establishes the wave dynamics equation of milling cutter components. An approach for solving the wave front position and wave velocity of milling cutter’s stress wave is proposed, and the propagation path of transient cutting force to the milling cutter is communicated. The attenuation model of stress wave reflection is established to provide a method for revealing the stress wave transmission and distribution in milling cutter. The constitutive relation of milling cutter components under the impact load is obtained by split Hopkinson pressure bar experiment. A force connection method is adopted to make the trans-scale correlation analysis between continuum medium mechanics and molecular dynamics, thereby revealing the wave dynamics damage characteristics of a high-speed milling cutter. The results show that the potential damage position and types of milling cutter can be distinguished by the above method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin G, Qi HJ, Cai YJ, Zhang QC (2016) Stability prediction for milling process with multiple delays using an improved semi-discretization method. Math Methods Appl Sci 39(4):949–958
Cui XB, Zhao B, Jiao F, Ming PM (2016) Formation characteristics of the chip and damage equivalent stress of the cutting tool in high-speed intermittent cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-016-9903-7
Liu AM, Shen H, Kruth JP (2008) Mechanism of the tool flank wear influenced by the vibration characteristics of the toolholder system in high-speed milling. Chin J Mech Eng 04:63–68
International Organization for Standardization (2002) ISO/T 15641–2001(E) Milling cutters for high-speed machining-Safety requirements.
Wang FZ, Zhao J, Li ZL, Li AH (2016) Coated carbide tool failure analysis in high-speed intermittent cutting process based on finite element method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83(5):805–813
Li C, Zhang JC, Wang XW (2013) Phase change and stress wave in picoseconds laser-material interaction with shock wave formation. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 112(3):677–687
Wang YW, Wang FC, Yu XD, Ma Z, Gao JB, Kang XP (2010) Effect of interlayer on stress wave propagation in CMC/RHA multi-layerd structure. Compos Sci Technol 70(12):1669–1673
Hu P, Zhu YG, Ying L (2016) Crystal plasticity extended models based on thermal mechanism and damage functions: application to muitiscale modeling of aiuminum alloy tensile behavior. Int J Plastcity 86:1–25
Makwana M, Antonakakis T, Maling B, Guenneau S, Craster RV (2016) Wave mechanics in media pinned at Bravais lattice points. SIAM J Appl Math 76(1):1–26
Barrett JA (2011) On the faithful interpretation of pure wave mechanics. Brit J Philos Sci 62(4):693–709
Li J, Ren XD (2011) Multi-scale based stochastic damage evolution. Eng Fail Anal 2:726–734
Kruch S, Chaboche J (2011) Multi-scale analysis in elasto-viscoplasticity coupled with damage. Int J Plast 12:2026–2039
Toribio J, Lorenzo M, Vergara D (2010) Influence of fatigue pre-loading level on hydrogen-assisted micro-damage in eutectoid steel. NACE International-Corrosion 2010 Conference and Expo 2010
Ghandeharium A, Kishawym HA, Umer U, Hussein HM (2016) Analysis of tool-particle interactions during cutting process of metal matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(1):143–152
Feng Y, Wang ML, Wang BS (2014) Research on cutting temperature of workpiece in milling process based on WPSO. J Mech Eng 50(19):205–212
Ying L, Shi DY, Hu P, Liu WQ (2016) Numerical prediction of formability during hot forming of high strength steel based on continuum damage mechanics. Chin J Mech Eng 52(4):36–44
Li J, Fang QH, Liu YW, Zhang LC (2015) Scratching of copper with rough surfaces conducted by diamond tip simulated using molecular dynamics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 7(5):1057–1070
Moussaoui K, Monies F, Mousseigne M, Gilles P, Rubio W (2016) Balancing the transverse cutting force during inclined milling and effect on tool wear: application to Ti6AL4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82:1859–1880
Jiang B, Zhang MH, Yao GS, Bai JX (2016) Trans-scale design method on safety of high-speed milling cutter. Chin J Mech Eng 52(5):202–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, B., He, T., Gu, Y. et al. Method for recognizing wave dynamics damage in high-speed milling cutter. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 139–150 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0128-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0128-1