Abstract
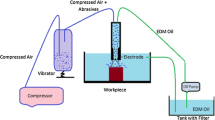
The purpose behind this work was the development of a hybrid methodology, which combines the electrical fischarge machining (EDM) with a high-pressure jet of dielectric fluid mixed with abrasive powder. The low MRR (material removal rate) observed on the EDM is, undoubtedly, one of the most important limitations of this process, especially today, where competitiveness among the enormous varieties of machining processes has attained an unbelievable level of speed and surface finishing. A special device was built in order to provide and apply the high-pressure abrasive jet. Cooper tube-shaped tools were used for the experiments and the machined material consisted of commercial high-speed steel (AISI M2). Kerosene, deionized water, and mineral-based oil were used as dielectric fluids and the abrasive was constituted of SiC (600 mesh), with jet pressures varying from zero to 100 bar, and abrasive concentration kept fixed at 30 g/l. The results show an eightfold increase in MRR when the EDM process is aided by abrasive particles. Furthermore, remarkable gains were obtained with kerosene and deionized water, both with enhanced surface finishing. Therefore, this new process, denominated as abrasive jet electrical discharge machining (AJEDM), proves to be efficient for increasing machining velocity while decreasing the surface roughness and its use has shown itself to be technically viable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajurkar KP, Zhu D, Mcgeough JA, Kozak J, De Silva A (1999) New developments in electro-chemical machining. CIRP Ann 48(2):569–579
Pajak PT, Silva AKM, Harrison DK, Mcgeough JA (2004) Modeling the aspects of precision and efficiency in laser-assisted jet electrochemical machining (LAJECM). J Mater Process Technol 149:512–518
Kozak J, Rajurkar KP (2001) Hybrid machining process evaluation and development. University or Nebraska, Lincoln
Mcgeough JA (1989) Advanced methods of machining. Chapman and Hall, London
Raslan AA, Arantes LJ (2009) Método de Usinagem Híbrida Combinando Descargas Elétricas e Erosão Abrasiva. Brasil, Patente PI0703468-7A2, 26p
Amorim FL (2002) Tecnologia de Eletroerosão por Penetração da Liga de Alumínio AMP 8000 e da Liga de Cobre CuBe para Ferramentas de Moldagem de Materiais Plásticos. Tese de Doutorado - Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis-SC, 134 p
Wong YS, Lim LC, Lee LC (1995) Effects of flushing on electro-discharge machining surfaces. J Mater Process Technol 48:299–305
Ming YQ, He LY (1995) Powder-suspension dielectric fluid for EDM. J Mater Process Technol 52:44–54
Fernandes AL (1999) Efeito da Adição de Pó de Carboneto de Silício nos Fluidos Dielétricos Sobre o Desempenho da Usinagem por Descargas Elétricas do Aço-Rápido AISI M2. Dissertação de Mestrado - Universidade Federal de Uberlândia, Uberlândia-MG, 72 p
Arantes LJ (2001) Avaliação de Fluidos Dielétricos no Processo de Usinagem por Descargas Elétricas. Dissertação de Mestrado, Universidade Federal de Uberlândia, Uberlândia-MG, 74 p
Yih-Fong T, Fu-Ghen C (2005) Investigation into some surface characteristics of electrical discharge machined SKD-11 using powder-suspension dielectric Oil. J Mater Process Technol 170:385–391
Zhao WS, Meng QG, Wang ZL (2002) The application of research on powder mixed EDM in rough machining. J Mater Process Technol 129:30–33
Lin YC, Chen YF, Wang AC, Sei WL (2012) Machining performance on hybrid process of abrasive jet machining and electrical discharge machining. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 2(supplement 3):775–780
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arantes, L.J., da Silva, E.R., dos Santos, R.F. et al. The electrical discharge machining process aided by abrasive jet. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87, 411–420 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8517-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8517-4