Abstract
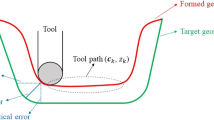
Incremental sheet forming (ISF) is a highly flexible sheet forming process, but it suffers from poor geometric accuracy. This paper presents a feedback control strategy using model predictive control (MPC) to obtain improved geometric accuracy in ISF. Based on the incremental deformation mechanism of ISF, a novel model for shape state prediction has been proposed. The step depth of the toolpath was optimised based on shape state feedback during the forming process. Two different cases were studied for experimental validation of the developed control strategy. Comparisons between formed parts in both controlled and uncontrolled ISF processes were implemented in terms of cross-sectional profiles, formed depth at the bottom area and global deviation distribution. Results show that the geometric accuracy in ISF with feedback control has been greatly improved at the bottom area of the formed parts compared with a standard ISF approach without control. Improved geometric accuracy has been achieved on the wall of the parts as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahloul R, Arfa H, BelHadjSalah H (2014) A study on optimal design of process parameters in single point incremental forming of sheet metal by combining Box–Behnken design of experiments, response surface methods and genetic algorithms. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74(1-4):163–185
Filice L, Ambrogio G, Gaudioso M (2013) Optimised tool-path design to reduce thinning in incremental sheet forming process. Int J Mater Form 6(1):173–178
Smith J et al. (2013) Deformation mechanics in single-point and accumulative double-sided incremental forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 1–17
Attanasio A et al (2008) Asymmetric two points incremental forming: Improving surface quality and geometric accuracy by tool path optimization. J Mater Process Technol 197(1-3):59–67
Leszak E (1967) Apparatus and process for incremental dieless forming. Google Patents
Rous P (1960) Machines for shaping sheet metal. Google Patents
Micari F, Ambrogio G, Filice L (2007) Shape and dimensional accuracy in single point incremental forming: state of the art and future trends. J Mater Process Technol 191(1-3):390–395
Al-Ghamdi K, Hussain G (2014) The pillowing tendency of materials in single-point incremental forming: experimental and finite element analyses. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Engineering Manuf
Wang H, Duncan S (2011) Optimization of tool trajectory for Incremental Sheet Forming using closed loop control. In IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE). 2011
Attanasio A, Ceretti E, Giardini C (2006) Optimization of tool path in two points incremental forming. J Mater Process Technol 177(1-3):409–412
Allwood JM, Braun D, Music O (2010) The effect of partially cut-out blanks on geometric accuracy in incremental sheet forming. J Mater Process Technol 210(11):1501–1510
Bambach M, Taleb Araghi B, Hirt G (2009) Strategies to improve the geometric accuracy in asymmetric single point incremental forming. Prod Eng 3(2):145–156
Ambrogio G, Napoli L, Filice L (2009) A novel approach based on multiple back-drawing incremental forming to reduce geometry deviation. Int J Mater Form 2(1):9–12
Ambrogio G et al (2004) Influence of some relevant process parameters on the dimensional accuracy in incremental forming: a numerical and experimental investigation. J Mater Process Technol 153–154:501–507
Hirt G et al (2004) Forming strategies and process modelling for CNC incremental sheet forming. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 53(1):203–206
Behera AK et al (2013) Tool path compensation strategies for single point incremental sheet forming using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Comput Aided Des 45(3):575–590
Fu ZM et al (2013) Tool path correction algorithm for single-point incremental forming of sheet metal. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(9-12):1239–1248
Allwood JM et al (2009) Closed-loop feedback control of product properties in flexible metal forming processes with mobile tools. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 58(1):287–290
Wang H, Duncan S (2011) Constrained model predictive control of an incremental sheet forming process. In IEEE International Conference on Control Applications (CCA). 2011
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2009) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Kearney, M., Li, Y. et al. Model predictive control of incremental sheet forming for geometric accuracy improvement. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82, 1781–1794 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7431-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7431-5