Abstract
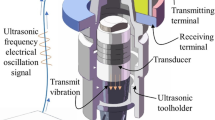
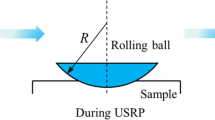
Surface texture technology is widely used in various friction pairs to obtain good lubrication. However, ever present researches are mainly focused on regular and simple texture shapes such as dimples and grooves. Few works on complex micro texture have been reported due to preparing difficulty. In this paper, two surfaces with complex micro texture, which are micro scale textured (MST) surface and micro furrow textured (MFT) surface, are prepared by ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling (UVAM) method. Also, their tribological behaviors under starved oil lubrication and reciprocating sliding condition are experimentally investigated with a smooth sample as comparison. Experimental results indicate that although the application of ultrasonic vibration leads to the increase of roughness of MST and MFT surfaces, both the two machined micro textures contribute to the improvement of lubricant film strength, and MFT surface has better tribological performance than that of MST surface. As a result, under test conditions, micro texture formed by UVAM method can greatly improve the tribological property of friction surface, especially for its bearing capacity and wear resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamilton DB, Walowit JA, Allen CM (1966) A theory of lubrication by micro irregularities. J Basic Eng 88(1):177–185
Etsion I, Burstein L (1996) A model for mechanical seals with regular micro surface structure. Tribol Trans 39(3):677–683
Brehl DE, Dow TA (2008) Review of vibration-assisted machining. Precis Eng 32:153–172
Wu Z, Deng JX, Zhang H, Lian YS, Zhao J (2012) Tribological behavior of textured cemented carbide filled with solid lubricants in dry sliding with titanium alloys. Wear 292–293:135–140
Peng Y, Liang Z, Wu Y, Guo Y, Wang C (2012) Effect of vibration on surface and tool wear in ultrasonic vibration-assisted scratching of brittle materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59(1–4):67–72
Hashemzadeh M, Voisey KT, Kazerooni M (2012) The effects of low-frequency workpiece vibration on low-power CO2 laser cutting of PMMA: an experimental investigation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 63(1–4):33–40
Pettersson U, Jacobson S (2004) Friction and wear properties of micro textured DLC coated surfaces in boundary lubricated sliding. Tribol Lett 17(3):553–559
Zhang XQ, Kumar AS, Rahman M, Nath C, Liu K (2013) Modeling of the effect of tool edge radius on surface generation in elliptical vibration cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65(1–4):35–42
Wang X, Kato K (2003) Improving the anti-seizure ability of SiC seal in water with RIE texturing. Tribol Lett 14(4):275–280
Uehara Y, Wakuda M, Yamauchi Y (2004) Tribology properties of dimpled silicon nitride under oil lubrication. J Eur Ceram Soc 24:369–373
Kortikar S, Stephens L, Hadinata P (2003) Manufacturing of micro asperities on thrust surfaces using ultraviolet photolithography. Proc ASPE 2003 Winter Top Meet 28:148–153
Etsion I (2004) Improving tribological performance of mechanical components by laser surface texturing. Tribol Lett 17(4):733–737
Shen XH, Zhang JH, Xing DL (2012) A study of surface roughness variation in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58(5–8):553–561
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, XH., Tao, GC. Tribological behaviors of two micro textured surfaces generated by vibrating milling under boundary lubricated sliding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79, 1995–2002 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6965-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6965-x