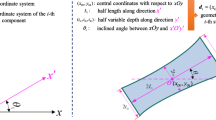
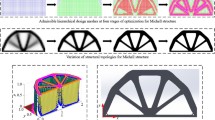
Abstract
In this paper, a new isogeometric topology optimization (ITO) method based on the moving iso-surface threshold (MIST) method is proposed, and the corresponding MATLAB code is provided. The same nonuniform rational B-splines (NURBS) basis functions are used to construct a geometrical model and evaluate the objective function for minimal compliance problems. In MIST-based ITO, the physical response function is calculated by using the same NURBS basis functions as the geometry model. First, the physical response function values of control points are calculated by using the NURBS basis function and the physical response function values of the Gauss points. Second, the physical response function values of the knots (the element nodes) are obtained by fitting the control points using NURBS basis functions. Finally, the physical response surface is formed by connecting its nodal values. The structure topology is iteratively updated by using an iso-surface with an appropriate threshold to cut the physical response surface. Compared to traditional MIST, MIST-based ITO can improve the computational accuracy and computational efficiency of high-order elements. Several numerical examples demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, verifying the validity of isogeometric topology optimization MATLAB codes in implementing MIST_based_ITO, which is provided in Online Appendix 1.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrianov IV, Bolshakov VI, Danishevs’kyy VV, Weichert D (2008) Higher order asymptotic homogenization and wave propagation in periodic composite materials. Proc R Soc A 464:1181–1201. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2007.0267
Belytschko T (2008) The finite element method: linear static and dynamic finite element analysis: Thomas J. R. Hughes. Comput-Aided Civil Infrastruct Eng 4:245–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8667.1989.tb00025.x
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71:197–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7825(88)90086-2
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech (Ingenieur Archiv) 69:635–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004190050248
Chen W, Tong L, Liu S (2017) Concurrent topology design of structure and material using a two-scale topology optimization. Comput Struct 178:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2016.10.013
Chen W, Tong L, Liu S (2018) Design of periodic unit cell in cellular materials with extreme properties using topology optimization. Proc Inst Mech Eng L 232:852–869. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420716652638
De Boor C (1972) On calculating with B-splines. J Approx Theory 6(1):50–62
Dedè L, Borden MJ, Hughes TJR (2012) Isogeometric analysis for topology optimization with a phase field model. Arch Comput Methods Eng 19:427–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-012-9075-z
Gao J, Xiao M, Zhang Y, Gao L (2020) A comprehensive review of isogeometric topology optimization: methods, applications and prospects. Chin J Mech Eng 33:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-020-00503-w
Gao J, Wang L, Luo Z, Gao L (2021) IgaTop: an implementation of topology optimization for structures using IGA in MATLAB. Struct Multidisc Optim 64:1669–1700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-02858-7
Gao J, Xiao M, Zhou M, Gao L (2022) Isogeometric topology and shape optimization for composite structures using level-sets and adaptive Gauss quadrature. Compos Struct 285:115263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115263
Ghasemi H, Park HS, Rabczuk T (2017) A level-set based IGA formulation for topology optimization of flexoelectric materials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 313:239–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2016.09.029
Guo X, Zhang W, Zhong W (2014) Doing topology optimization explicitly and geometrically—a new moving morphable components based framework. J Appl Mech 81:081009. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4027609
Hassani B, Khanzadi M, Tavakkoli SM (2012) An isogeometrical approach to structural topology optimization by optimality criteria. Struct Multidisc Optim 45:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-011-0680-5
Hou W, Gai Y, Zhu X, Wang X, Zhao C, Xu L, Jiang K, Hu P (2017) Explicit isogeometric topology optimization using moving morphable components. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 326:694–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2017.08.021
Hughes TJR, Cottrell JA, Bazilevs Y (2005) Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194:4135–4195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2004.10.008
Jahangiry HA, Tavakkoli SM (2017) An isogeometrical approach to structural level set topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 319:240–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2017.02.005
Jiang F, Chen L, Wang J, Miao X, Chen H (2022) Topology optimization of multimaterial distribution based on isogeometric boundary element and piecewise constant level set method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 390:114484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2021.114484
Luo Q, Tong L (2015) Design and testing for shape control of piezoelectric structures using topology optimization. Eng Struct 97:90–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.04.006
Luo Q, Tong L (2015) Structural topology optimization for maximum linear buckling loads by using a moving iso-surface threshold method. Struct Multidisc Optim 52:71–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1286-0
Masters IG, Evans KE (1996) Models for the elastic deformation of honeycombs. Compos Struct 35:403–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8223(96)00054-2
Nguyen C, Zhuang X, Chamoin L, Zhao X, Nguyen X, Rabczuk T (2020) Three-dimensional topology optimization of auxetic metamaterial using isogeometric analysis and model order reduction. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 371:113306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113306
Piegl LA, Tiller W (2012) The NURBS book. Springer, New York
Qiu W, Wang Q, Gao L, Xia Z (2022) Evolutionary topology optimization for continuum structures using isogeometric analysis. Struct Multidisc Optim 65:121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03215-y
Seo Y-D, Kim H-J, Youn S-K (2010) Isogeometric topology optimization using trimmed spline surfaces. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:3270–3296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2010.06.033
Sethian JA, Wiegmann A (2000) Structural boundary design via level set and immersed interface methods. J Comput Phys 163:489–528. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.2000.6581
Sigmund O (2001) A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct Multidisc Optim 21:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001580050176
Spink M, Claxton D, Falco C de, Vazquez R (2010) NURBS toolbox. Octave Forge. https://octave.sourceforge.io/nurbs/overview.html
Su X, Chen W, Liu S (2021) Multi-scale topology optimization for minimizing structural compliance of cellular composites with connectable graded microstructures. Struct Multidisc Optim 64:2609–2625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-03014-x
Tong L, Lin J (2011) Structural topology optimization with implicit design variable—optimality and algorithm. Finite Elem Anal Design 47:922–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2011.03.004
Vasista S, Tong L (2012) Design and testing of pressurized cellular planar morphing structures. AIAA J 50:1328–1338. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J051427
Vasista S, Tong L (2013) Topology-optimized design and testing of a pressure-driven morphing-aerofoil trailing-edge structure. AIAA J 51:1898–1907. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J052239
Vasista S, Tong L (2014) Topology optimisation via the moving iso-surface threshold method: implementation and application. Aeronaut J 118:315–342. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000009143
Wang Y, Benson DJ (2016) Isogeometric analysis for parameterized LSM-based structural topology optimization. Comput Mech 57:19–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-015-1219-1
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:227–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(02)00559-5
Wang YJ, Wang ZP, Xia ZH, Poh LH (2018) Structural design optimization using isogeometric analysis: a comprehensive review. Comput Model Eng Sci 117(3):455–507. https://doi.org/10.31614/cmes.2018.04603
Xia Z, Wang Y, Wang Q, Mei C (2017) GPU parallel strategy for parameterized LSM-based topology optimization using isogeometric analysis. Struct Multidisc Optim 56:413–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1672-x
Xie YM, Steven GP (1993) A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput Struct 49:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7949(93)90035-C
Xie X, Wang S, Xu M, Wang Y (2018) A new isogeometric topology optimization using moving morphable components based on R-functions and collocation schemes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 339:61–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.04.048
Yin L, Zhang F, Deng X, Wu P, Zeng H, Liu M (2019) Isogeometric bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization. IEEE Access 7:91134–91145. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2927820
Zhang W, Yuan J, Zhang J, Guo X (2016) A new topology optimization approach based on Moving Morphable Components (MMC) and the ersatz material model. Struct Multidisc Optim 53:1243–1260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1372-3
Zhang D, Wang S, Zheng L (2018) A comparative study on acoustic optimization and analysis of CLD/plate in a cavity using ESO and GA. Shock Vibration 2018:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7146580
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFB1708303), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1806215 and 12072058), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant DUT20LK02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Replication of results
The descriptions of the formulation, the numerical implementation, and the numerical results contain all the necessary information for reproducing the results of this article. A MATLAB code for the isogeomtric topology optimization method based on the moving iso-surface threshold method is presented in Online Appendix 1–5. Hence, we are confident that the results can be reproduced.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Graeme James Kennedy
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Su, X. & Liu, S. Algorithms of isogeometric analysis for MIST-based structural topology optimization in MATLAB. Struct Multidisc Optim 67, 43 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-024-03764-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-024-03764-4