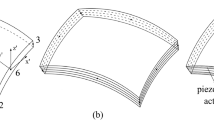
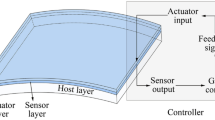
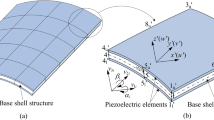
Abstract
Simultaneously optimizing the thickness of the base structure and the location of piezoelectric sensors/actuators as well as control gains is investigated for minimizing the sound radiation from the vibrating curved shell integrated with sensors/actuators under harmonic excitation. The finite element formulation of the piezoelectric curved shell structure is described. The piezoelectric element is coupled into the base shell element using nodal displacement constraint equations. The active control of structural vibration-acoustic radiation is formulated using the velocity feedback algorithm. Based on both passive and active control measures, an integrated optimization model of the vibro-acoustic problem is proposed, in which the sound power is taken as the objective function. The thickness of the base shell elements and the parameters of control system, including the location of sensors/actuators and control gains, are chosen as the design variables. In order to restrict the complexity of the control system, the number of sensors/actuators is considered as a constraint. A simulated annealing algorithm is extended to handle the vibro-acoustic optimization problem with the continuous and discrete variables co-existing. Numerical examples demonstrate the effectiveness of the optimization scheme and the correctness of the computation program.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann B, Kost B (2005) Structure assembling by stochastic topology optimization. Comput Struct 83:2175–2184
Belanger P, Berry A, Pasco Y, Robin O, St-Amant Y, Rajan S (2009) Multi-harmonic active structural acoustic control of a helicopter main transmission noise using the principal component analysis. Appl Acoust 70:153–164
Belegundu A, Salagame R, Koopmann G (1994) A general optimization strategy for sound power minimization. Struct Optimization 8:113–119
Chen T-Y, Su J-J (2002) Efficiency improvement of simulated annealing in optimal structural designs. Adv Eng Softw 33:675–680
Cheng W, Cheng C, Koopmann G (2011) A new design strategy for minimizing sound radiation of vibrating beam using dimples. J Vib Acoust 133:051008
Cheung Y, Li W, Tham L (1989) Free vibration analysis of singly curved shell by spline finite strip method. J Sound Vib 128:411–422
Choi S-B (2006) Active structural acoustic control of a smart plate featuring piezoelectric actuators. J Sound Vib 294:421–429
Cook RD, Malkus DS, Plesha ME (1989) Concepts and applications of finite element analysis, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Deaton JD, Grandhi RV (2014) A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49:1–38
Denli H, Sun J (2008) Optimization of boundary supports for sound radiation reduction of vibrating structures. J Vib Acoust 130:011007
Fuller C, Von Flotow A (1995) Active control of sound and vibration control systems. IEEE 15:9–19
Hasançebi O, Erbatur F (2002) Layout optimisation of trusses using simulated annealing. Adv Eng Softw 33:681–696. doi:10.1016/S0965-9978(02)00049-2
Holland KR, Fahy FJ (1997) An investigation into spatial sampling criteria for use in vibroacoustic reciprocity. Noise Control Eng J 45:217–221(215)
Jeon J-Y, Okuma M (2004) Acoustic radiation optimization using the particle swarm optimization algorithm. JSME Int J, Ser C 47:560–567
Joshi P, Mulani SB, Gurav SP, Kapania RK (2010) Design optimization for minimum sound radiation from point-excited curvilinearly stiffened panel. J Aircr 47:1100–1110
Kane C, Schoenauer M (1996) Topological optimum design using genetic algorithms. Control Cybern 25(5):1059–1087
Kaneda S, Yu Q, Shiratori M, Motoyama K (2002) Optimization approach for reducing sound power from a vibrating plate by its curvature design. JSME Int J, Ser C 45:87–98
Kaneda S, Yu Q, Shiratori M, Motoyama K (2003) Structural design optimization for reducing sound radiation from a vibrating plate using a genetic algorithm. JSME Int J, Ser C 46:1000–1009
Kim J, Ko B (1998) Optimal design of a piezoelectric smart structure for noise control. Smart Mater Struct 7:801
Kuo SM, Morgan DR (1999) Active noise control: a tutorial review. Proc IEEE 87:943–973
Li S, Zhao D (2004) Numerical simulation of active control of structural vibration and acoustic radiation of a fluid-loaded laminated plate. J Sound Vib 272:109–124. doi:10.1016/s0022-460x(03)00321-3
Li DS, Cheng L, Gosselin CM (2004) Optimal design of PZT actuators in active structural acoustic control of a cylindrical shell with a floor partition. J Sound Vib 269:569–588
Liew K, Bergman L, Ng T, Lam K (2000) Three-dimensional vibration of cylindrical shell panels–solution by continuum and discrete approaches. Comput Mech 26:208–221
Liew KM, He XQ, Kitipornchai S (2004) Finite element method for the feedback control of FGM shells in the frequency domain via piezoelectric sensors and actuators. Comput Method Appl M 193:257–273. doi:10.1016/j.crna.2003.09.009
Oude Nijhuis MHH, Boer Ad (2003) Optimization strategy for actuator and sensor placement in active structural acoustic control. Paper presented at the International Forum on Aeroelasticity and. Structural Dynamics, IFASD, Amsterdam
Petyt M (1971) Vibration of curved plates. J Sound Vib 15:381–395
Ruckman CE, Fuller CR (1995) Optimizing actuator locations in active noise control systems using subset selection. J Sound Vib 186:395–406. doi:10.1006/jsvi.1995.0458
Shim PY, Manoochehri S (1997) Generating optimal configurations in structural design using simulated annealing. Int J Numer Methods Eng 40:1053–1069
Sigmund O (2011) On the usefulness of non-gradient approaches in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43:589–596
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48:1031–1055
Sors T, Elliott S (2002) Volume velocity estimation with accelerometer arrays for active structural acoustic control. J Sound Vib 258:867–883
Tinnsten M, Carlsson P, Jonsson M (2002) Stochastic optimization of acoustic response–a numerical and experimental comparison. Struct Multidiscip O 23:405–411
Wang B-T, Burdisso RA, Fuller CR (1994) Optimal placement of piezoelectric actuators for active structural acoustic control. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 5:67–77
Wang J, Zhao GZ, Zhang HW (2009) Optimal placement of piezoelectric curve beams in structural shape control. SMART STRUCT SYST 5:241–260
Xu Z, Huang Q, Zhao Z (2011) Topology optimization of composite material plate with respect to sound radiation. Eng Anal Bound Elem 35:61–67
Yang R, Du J (2013) Microstructural topology optimization with respect to sound power radiation. Struct Multidiscip O 47:191–206
Yang J, Shen H-S (2003) Free vibration and parametric resonance of shear deformable functionally graded cylindrical panels. J Sound Vib 261:871–893. doi:10.1016/S0022-460X(02)01015-5
Yuksel E, Kamci G, Basdogan I (2012) Vibro-acoustic design optimization study to improve the sound pressure level inside the passenger cabin. J Vib Acoust 134:061017
Zhang X, Kang Z (2013) Topology optimization of damping layers for minimizing sound radiation of shell structures. J Sound Vib 332:2500–2519
Zhang C, Wang H-P (1993) Mixed-discrete nonlinear optimization with simulated annealing. Eng Optim 21:277–291
Zhang Z, Chen Y, Li H, Hua H (2011) Simulation and experimental study on vibration and sound radiation control with piezoelectric actuators. Shock Vib 18:343–354
Zhang X, Kang Z, Li M (2014) Topology optimization of electrode coverage of piezoelectric thin-walled structures with CGVF control for minimizing sound radiation. Struct Multidiscip O 50:799–814
Zhu JH, Zhang WH (2010) Integrated layout design of supports and structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:557–569
Zhu J, Zhang W, Beckers P (2009) Integrated layout design of multi-component system. Int J Numer Methods Eng 78:631–651
Zhu J-H, Zhang W-H, Xia L (2016) Topology optimization in aircraft and aerospace structures design. Arch Comput Meth Eng 23:595–622. doi:10.1007/s11831-015-9151-2
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11072049, U1508209), and the Key Project of Chinese National Programs for Fundamental Research and Development (2015CB057306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, J., Zhao, G. & Shang, L. Integrated design optimization of structural size and control system of piezoelectric curved shells with respect to sound radiation. Struct Multidisc Optim 56, 1287–1304 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1721-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1721-5