Abstract
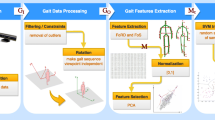
In this paper, we introduce a novel method for person identity recognition (identification) on skeleton animation/motion capture data representing persons performing various actions. The joints positions or orientation angles and the forward differences of these quantities are used to represent a motion capture sequence. First K-means clustering is applied on training data to discover the most representative patterns on joints positions or orientation angles (dynemes) and their forward differences (F-dynemes). Each frame is then assigned to one of these patterns and the frequency of occurrence histograms for each movement are constructed in a bag-of-words fashion. Person identity recognition is done through a nearest neighbor classifier. The proposed method is experimentally tested on a number of datasets of motion capture data, with very good results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa, I.B., Cristani, M., Del Bue, A., Bazzani, L., Murino, V.: Re-identification with rgb-d sensors. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV’12, vol. Part I, pp. 433–442. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2012)
Bashir, K., Xiang, T., Gong, S.: Gait recognition without subject cooperation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 31(13), 2052–2060 (2010)
Boulgouris, N., Hatzinakos, D., Plataniotis, K.: Gait recognition: a challenging signal processing technology for biometric identification. Signal Process. Mag. IEEE 22(6), 78–90 (2005)
Boyd, J.E.: Synchronization of oscillations for machine perception of gaits. Comput. Vision Image Underst. 96(1), 35–59 (2004)
Burdea, G., Coiffet, P.: Virtual reality technology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2003)
Gkalelis, N., Tefas, A., Pitas, I.: Combining fuzzy vector quantization with linear discriminant analysis for continuous human movement recognition. Circuits Syst Video Technol IEEE Trans 18(11), 1511–1521 (2008). doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2008.2005617
Gkalelis, N., Tefas, A., Pitas, I.: Human identification from human movements. In: Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP’09, pp. 2557–2560. IEEE Press, Piscataway (2009)
Gu, J., Ding, X., Wang, S., Wu, Y.: Action and gait recognition from recovered 3-D human joints. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 40(4), 1021–1033 (2010)
Han, J., Bhanu, B.: Individual recognition using gait energy image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(2), 316–322 (2006)
Iosifidis, A., Tefas, A., Pitas, I.: Activity-based person identification using fuzzy representation and discriminant learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 7(2), 530–542 (2012)
Iosifidis, A., Tefas, A., Pitas, I.: Dynamic action recognition based on dynemes and extreme learning machine. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 34(15), 1890–1898 (2013) (smart Approaches for Human Action Recognition)
Josiński, H., Świtoński, A., Jȩdrasiak, K., Kostrzewa, D.: Human identification based on gait motion capture data. In: Proceedings of the 2012 International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, IMECS’12 (2012)
Kapsouras, I., Nikolaidis, N.: Action recognition on motion capture data using a dynemes and forward differences representation. J. Vis. Commun. Image R 25, 1432–1445 (2014)
Lam, T.H.W., Lee, R.S.T.: A new representation for human gait recognition: motion silhouettes image (msi). In: Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Advances in Biometrics, ICB’06, pp. 612–618. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2006)
Lee, T., Belkhatir, M., Sanei, S.: A comprehensive review of past and present vision-based techniques for gait recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 72, 2833–2869 (2014)
Lin, Y.C., Yang, B.S., Lin, Y.T., Yang, Y.T.: Human recognition based on kinematics and kinetics of gait. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 31(4), 255–263 (2011)
Liu, F., Zhuang, Y., Wu, F., Pan, Y.: 3D motion retrieval with motion index tree. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 92(2–3), 265–284 (2003)
Liu, L.F., Jia, W., Zhu, Y.H.: Survey of gait recognition. In: Huang, D.S., Jo, K.H., Lee, H.H., Kang, H.J., Bevilacqua, V. (eds.) Emerging intelligent computing technology and applications. With aspects of artificial intelligence, lecture notes in computer science, vol. 5755, pp. 652–659. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2009)
Müller, M., Röder, T., Clausen, M., Eberhardt, B., Krüger, B., Weber, A.: Documentation mocap database HDM05. Tech. Rep. CG-2007-2. Universität Bonn (2007)
Munsell, B.C., Temlyakov, A., Qu, C., Wang, S.: Person identification using full-body motion and anthropometric biometrics from kinect videos. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on Computer Vision, ECCV’12, vol. Part III, pp. 91–100. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2012)
Nikolaidis, N., Pitas, I.: Nonlinear processing and analysis of angular signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 46(12), 3181–3194 (1998)
Nixon, M.S., Carter, J.N.: Advances in automatic gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the Sixth IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, FGR’04, pp. 139–144. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC (2004)
Ofli, F., Chaudhry, R., Kurillo, G., Vidal, R., Bajcsy, R.: Sequence of the most informative joints (smij): a new representation for human skeletal action recognition. J. Vis. Commun. Image Recogn. 25(1), 24–38 (2014) (visual Understanding and Applications with RGB-D Cameras)
Preis, J., Kessel, M., Werner, M., Linnhoff-Popien, C.: Gait recognition with kinect. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Kinect in Pervasive Computing (2012)
Sivapalan, S., Chen, D., Denman, S., Sridharan, S., Fookes, C.: Gait energy volumes and frontal gait recognition using depth images. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Joint Conference on Biometrics, IJCB ’11, pp. 1–6. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC (2011)
Tanawongsuwan, R., Bobick, A.: Gait recognition from time-normalized joint-angle trajectories in the walking plane. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. CVPR 2001., vol. 2, pp. II–726 (2001)
Wang, J., She, M., Nahavandi, S., Kouzani, A.: A review of vision-based gait recognition methods for human identification. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications, DICTA ’10, pp. 320–327. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC (2010)
Yam, C.Y., Nixon, M.S., Carter, J.N.: Extended model-based automatic gait recognition of walking and running. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Audio- and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication, AVBPA ’01, pp. 278–283. Springer, London (2001)
Zhang, Z., Hu, M., Wang, Y.: A survey of advances in biometric gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the 6th Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition, CCBR’11, pp 150–158. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapsouras, I., Nikolaidis, N. Person identity recognition on motion capture data using multiple actions. Machine Vision and Applications 26, 905–918 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-015-0704-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-015-0704-z