Abstract
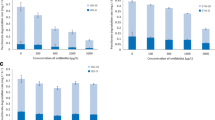
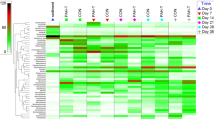
Extensive use of the fungicides azoxystrobin (AZ) and pyraclostrobin (PYR) can have negative effects on aquatic environments, but comprehensive studies on their effect on aquatic microbial communities are still lacking. We found that AZ and PYR could both inhibit the growth of Chlorella vulgaris, but PYR also inhibited Microcystis aeruginosa more strongly than did AZ. High-throughput sequencing analysis showed that AZ promoted the growth of Cyanobacteria in microcosms, and both PYR and AZ disturbed the ecological balance in the aquatic bacterial community and created distinct ecological risks. Our study suggests that the ecological risk of fungicides is complex, and fungicide use should be better managed to reduce potential risks to the environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balba H (2007) Review of strobilurin fungicide chemicals. J Environ Sci Health B 42:441–451
CCPIA (2017) Pesticides with sales of more than $300 million in 2016. China Crop Protection Industry Association. http://cn.agropages.com/News/NewsDetail—15141.htm. Accessed 5 Aug 2019
Dixit R, Wasiullah Malaviya D, Pandiyan K, Singh U, Sahu A, Shukla R, Singh B, Rai J, Sharma P, Lade H, Paul D (2015) Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: an overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustainability 7:2189–2212
Du B, Zhang Z, Liu W, Ye Y, Lu T, Zhou Z, Li Y, Fu Z, Qian H (2018) Acute toxicity of the fungicide azoxystrobin on the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:72–79
Gardestrom J, Ermold M, Goedkoop W, McKie BG (2016) Disturbance history influences stressor impacts: effects of a fungicide and nutrients on microbial diversity and litter decomposition. Freshwater Bio 61:2171–2184
Huisman J, Codd GA, Paerl HW, Ibelings BW, Verspagen JMH, Visser PM (2018) Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:471–483
Istvánovics V (2008) The role of biota in shaping the phosphorus cycle in lakes. Freshwater Rev 1:143–174
Jetten MS (2008) The microbial nitrogen cycle. Environ Microbiol 10:2903–2909
Li H, Cao F, Zhao F, Yang Y, Teng M, Wang C, Qiu L (2018) Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity induced by three strobilurins (pyraclostrobin, trifloxystrobin and picoxystrobin) in zebrafish embryos. Chemosphere 207:781–790
Liu L, Zhu B, Wang GX (2015) Azoxystrobin-induced excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and inhibition of photosynthesis in the unicellular green algae Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:7766–7775
Liu XX, Wang Y, Chen H, Zhang JL, Wang CJ, Li XF, Pang S (2018) Acute toxicity and associated mechanisms of four strobilurins in algae. Environ Toxicol Phar 60:12–16
Lu T, Zhu Y, Xu J, Ke M, Zhang M, Tan C, Fu Z, Qian H (2018a) Evaluation of the toxic response induced by azoxystrobin in the non-target green alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Environ Pollut 234:379–388
Lu T, Ke M, Lavoie M, Jin Y, Fan X, Zhang Z, Fu Z, Sun L, Gillings M, Penuelas J, Qian H, Zhu YG (2018b) Rhizosphere microorganisms can influence the timing of plant flowering. Microbiome 6:231
Lu T, Zhu Y, Ke M, Peijnenburg WJGM, Zhang M, Wang T, Chen J, Qian H (2019) Evaluation of the taxonomic and functional variation of freshwater plankton communities induced by trace amounts of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Environ Int 126:268–278
Morrison SA, McMurry ST, Smith LM, Belden JB (2013) Acute toxicity of pyraclostrobin and trifloxystrobin to Hyalella azteca. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:1516–1525
Nofiani R, de Mattos-Shipley K, Lebe KE, Han LC, Iqbal Z, Bailey AM, Willis CL, Simpson TJ, Cox RJ (2018) Strobilurin biosynthesis in Basidiomycete fungi. Nat Commun 9:3940
Ochoa-Acuna HG, Bialkowski W, Yale G, Hahn L (2009) Toxicity of soybean rust fungicides to freshwater algae and Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 18:440–446
Pesce S, Batisson I, Bardot C, Fajon C, Portelli C, Montuelle B, Bohatier J (2009) Response of spring and summer riverine microbial communities following glyphosate exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1905–1912
Reynaud I, Chanteperdrix V, Broux C, Pavese P, Croize J, Maurin M, Stahl JP, Jacquot C (2007) A severe form of Chryseobacterium indologenes pneumonia in an immunocompetent patient. Med Mal Infect 37:762–764
Rodrigues ET, Lopes I, Pardal MA (2013) Occurrence, fate and effects of azoxystrobin in aquatic ecosystems: a review. Environ Int 53:18–28
Song H, Lavoie M, Fan X, Tan H, Liu G, Xu P, Fu Z, Paerl HW, Qian H (2017) Allelopathic interactions of linoleic acid and nitric oxide increase the competitive ability of Microcystis aeruginosa. ISME J 11:1865–1876
Wu S, Lei L, Liu M, Song Y, Lu S, Li D, Shi H, Raley-Susman KM, He D (2018) Single and mixture toxicity of strobilurin and SDHI fungicides to Xenopus tropicalis embryos. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 153:8–15
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Syed JH, Cheng Z, Li J, Zhang G, Jones KC (2015) Current status of persistent organic pesticides residues in air, water, and soil, and their possible effect on neighboring countries: a comprehensive review of India. Sci Total Environ 511:123–137
Yang Z, Lu T, Zhu Y, Zhang Q, Zhou Z, Pan X, Qian H (2019) Aquatic ecotoxicity of an antidepressant, sertraline hydrochloride, on microbial communities. Sci Total Environ 654:129–134
Zhang Q, Qu Q, Lu T, Ke M, Zhu Y, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Du B, Pan X, Sun L, Qian H (2019) The fungicide azoxystrobin perturbs the gut microbiota community and enriches antibiotic resistance genes in Enchytraeus crypticus. Environ Int 131:104965
Zhu J, He Y, Zhu Y, Huang M, Zhang Y (2018) Biogeochemical sulfur cycling coupling with dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in freshwater sediments. Environ Rev 26:121–132
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21777144), One Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences to H.F. Qian, and Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region Talent Project to H.F. Qian.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, T., Zhou, Z., Zhang, Q. et al. Ecotoxicological Effects of Fungicides Azoxystrobin and Pyraclostrobin on Freshwater Aquatic Bacterial Communities. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103, 683–688 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02706-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02706-x