Abstract
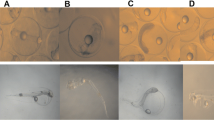
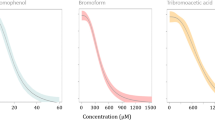
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are ubiquitous and coexisted in the aquatic environment. Individual and combined toxic effects of benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) and 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) on embryogenesis, and larval survival of the Pacific oyster were investigated. The EC50 values of BaP, BDE-47 and their mixture on embryogenesis were 18.4, 203.3 and 72.0 µg/L respectively, while the LC50 values for 96 h larval mortality were 26.8, 244.5 and 108.9 µg/L respectively. The Marking-Dawson additive toxicity indices were −0.02 and −0.19, indicating an additive effect with a trend to antagonism. In addition, DNA strand breaks were also observed in oyster embryos after exposure. Our study suggests that BaP and BDE-47 exposure can cause developmental abnormalities, DNA damage and larval mortality. Furthermore, the toxicity of the mixture is slightly lower than individual pollutant. These data will be helpful to predict the toxicity of organic pollutants, and provide criteria for marine water quality standards.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcha F, Hubert FV, Pfhol-Leszkowicz A (2003) Potential value of the comet assay and DNA adduct measurement in dab (Limanda limanda) for assessment of in situ exposure to genotoxic compounds. Mutation Res-Gen Tox En 534:21–32
Akcha F, Spagnol C, Rouxel J (2012) Genotoxicity of diuron and glyphosate in oyster spermatozoa and embryos. Aquat Toxicol 106–107:104–113
Beiras R, Albentosa M (2004) Inhibition of embryo development of the commercial bivalves Ruditapes decussatus and Mytilus galloprovincialis by trace metals; implications for the implementation of seawater quality criteria. Aquaculture 230:205–213
Binelli A, Riva C, Cogni D, Provini A (2008) Assessment of the genotoxic potential of benzo(a) pyrene and pp’-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene in Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Mutat Res 649:135–145
Braekevelt E, Tittlemier SA, Tomy GT (2003) Direct measurement of octanol–water partition coefficients of some environmentally relevant brominated diphenyl ether congeners. Chemosphere 51:563–567
Chan WK, Chan KM (2012) Disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in zebrafish embryo–larvae following waterborne exposure to BDE-47, TBBPA and BPA. Aquat Toxicol 108:106–111
Dabestani RT, Ivanov IN (1999) A compilation of physical, spectroscopic, a photophysical properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Photochem Photobiol 70:10–34
Deng X, Pan L, Miao J, Cai Y, Hu F (2014) Digital gene expression analysis of reproductive toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene in male scallop Chlamys farreri. Ecotox Environ Safe 110:190–196
Elliott JE, Wilson LK, Wakeford B (2005) Polybrominated diphenyl ether trends in eggs of marine and freshwater birds from British Columbia, Canada, 1979–2002. Environ Sci Technol 39:5584–5590
Han J, Won EJ, Lee MC, Seo JS, Lee SJ, Lee JS (2015) Developmental retardation, reduced fecundity, and modulated expression of the defensome in the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus exposed to BDE-47 and PFOS. Aquat Toxicol 165:136–143
Hannam ML, Bamber SD, Galloway TS, John Moody A, Jones MB (2010) Effects of the model PAH phenanthrene on immune function and oxidative stress in the haemolymph of the temperate scallop Pecten maximus. Chemosphere 78(7):779–784
His E, Seaman MNL, Beiras R (1997) A simplification the bivalve embryogenesis and larval development bioassay method for water quality assessment. Water Res 31:351–355
His E, Beiras R, Seaman MN (1999) The assessment of marine pollution-bioassays with bivalve embryos and larvae. Adv Mar Biol 37:1–178
Hylland K (2006) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) ecotoxicology in marine ecosystems. J Toxicol Environ Health A 69:109–123
Jiang X, Qiu L, Zhao H, Song Q, Zhou H, Han Q (2016) Transcriptomic responses of Perna viridis embryo to benzo(a)pyrene exposure elucidated by RNA sequencing. Chemosphere 163:125–132
Jiang Y, Tang X, Sun T, Wang Y (2017) BDE-47 exposure changed the immune function of haemocytes in Mytilus edulis: an explanation based on ROS-mediated pathway. Aquat Toxicol 182:58–66
Li J, Dong H, Zhang D, Han B, Zhu C, Liu S (2015) Sources and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in surface sediments from Bohai Sea and northern part of the Yellow Sea, China. Mar Pollut Bull 96:485–490
Lyons BP, Pascoe CK, Mcfadzen IR (2002) Phototoxicity of pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene to embryo-larval stages of the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Mar Environ Res 54:627–631
Mai H, Cachot J, Brune J, Geffard O, Belles A, Budzinski H, Morin B (2012) Embryotoxic and genotoxic effects of heavy metals and pesticides on early life stages of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Mar Pollut Bull 64:2663–2670
Marking LL, Dawson VK (1975) Method for assessment of toxicity or efficacy of mixtures of chemicals. In: Investigations in fish control, no. 67. U.S. Department of Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, DC
Newman MC (1995) Quantitative methods in aquatic ecotoxicology. Lewis Publishers, CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 426
Pan X, Tang J, Li J, Guo Z, Zhang G (2010) Levels and distributions of PBDEs and PCBs in sediments of the Bohai Sea, North China. J Environ Monit 12:1234–1241
Paredes E, Bellas J, Adams SL (2013) Comparative cryopreservation study of trochophore larvae from two species of bivalves: Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and Blue mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Cryobiology 67:274–279
Tian S, Pan L, Sun X (2013) An investigation of endocrine disrupting effects and toxic mechanisms modulated by benzo[a]pyrene in female scallop Chlamys farreri. Aquat Toxicol 144–145:162–171
USEPA (1997) Simultaneous analysis of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water by microextraction. EPRI Report TR-Research Project
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Wang Q, Yang H, Liu B, Wang X (2012) Toxic effects of benzo[a]pyrene (bap) and aroclor1254 on embryogenesis, larval growth, survival and metamorphosis of the bivalve Meretrix meretrix. Ecotoxicology 21:1617–1624
Wessel N, Rousseau S, Caisey X, Quiniou F, Akcha F (2007) Investigating the relationship between embryotoxic and genotoxic effects of benzo[a]pyrene, 17alpha-ethinylestradiol and endosulfan on Crassostrea gigas embryos. Aquat Toxicol 85:133–142
Wurl O, Lam PKS, Obbard JP (2006) Occurrence and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the dissolved and suspended phases of the sea-surface microlayer and seawater in Hong Kong, China. Chemosphere 65:1660–1666
Zhao Y, Luo K, Fan Z, Huang C, Hu J (2013) Modulation of benzo[a]pyrene-induced toxic effects in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) by 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Environ Sci Technol 47:13068–13076
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KZZD-EW-14), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41576122), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA11020702), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS (2016196).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, J., Yang, D., Sun, X. et al. Individual and Combined Toxicities of Benzo[a]pyrene and 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether on Early Life Stages of the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 582–588 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2164-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2164-9