Abstract
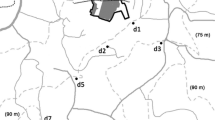
The application of treated animal wastewater produced in intensive fog farming operations (IHFOs) on surface soil, leads to groundwater contamination. In this study, the contamination of a Mediterranean aquifer caused by long-term application of treated wastewater, produced by an IHFO, on a plot with a geologic fault within the IHFO boundaries, was investigated. Groundwater samples were taken from monitoring wells close to the IHFO. A significant increase of chemical oxygen demand (COD), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), total viable count (TVC) and total coliform (TC) concentrations was found in wells, compared to control monitoring well, which were mainly affected by the subsurface flow of contaminated water, due to the presence of the geologic fault. During the winter, significant increases in concentrations of COD, BOD5, TVC and TC were noted and attributed to increased precipitation, which assisted in the accelerated transport of organic compounds and microbial load, through geologic fault, to groundwater.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (eds) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public health association, Washington, DC
Fridrich B, Krčmar D, Dalmacija B, Molnar J, Pešić V, Kragulj M, Varga N (2014) Impact of wastewater from pig farm lagoons on the quality of local groundwater. Agric Water Manage 135:40–53
Fulford MR, Walker JT, Martin MV, Marsh PD (2004) Total viable counts, ATP, and endotoxin levels as potential markers of microbial contamination of dental unit water systems. Br Dent J 196:157–159
Guan TY, Holley RA (2003) Pathogen survival in swine manure environments and transmission of human enteric illness: a review. J Environ Qual 32:383–392
Hellenic National Meteorological Service, www.hnms.gr. Accessed 13 July 2013
Krapac IG, Dey WS, Roy WR, Smyth CA, Storment E, Sargent SL, Steele JD (2002) Impacts of swine manure pits on groundwater quality. Environ Pollut 120:475–492
Levison JK, Novakowski KS (2012) Rapid transport from the surface to wells in fractured rock: a unique infiltration tracer experiment. J Contam Hydrol 131:29–38
Markantonatos G (1990) Treatment and disposal of wastewater, Papasotiriou edn. Athens, Greece (in Greek)
McBean EA, Rovers FA (1998) Statistical procedures for analysis of environmental monitoring data and risk assessment. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Michalopoulos C, Tzamtzis N, Liodakis S (2014a) Effects of an intensive hog farming operation on groundwater in east Mediterranean (I): a study on electrical conductivity, as well as nitrogen and sulfur nutrients. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93:683–687
Michalopoulos C, Tzamtzis N, Liodakis S (2014b) Effects of an intensive hog farming operation on groundwater in east Mediterranean (II): a study on K+, Na+, Cl−, PO4 3−–P, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+/Fe2+, Mn2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Ni2+. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93:688–693
Michalopoulou C (2004) Environmental law, ZITI edn. Salonika, Greece
Miller JN, Miller JC (2001) Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Essex
Naylor R, Steinfeld H, Falcon W, Galloway J, Smil V, Bradford E, Alder J, Mooney H (2005) Loosing the links between livestock and land. Science 310:1621–1622
Nicholson FA, Chambers BJ, Moore A, Nicholson RJ, Hickman G (2004) Assessing and managing the risks of pathogen transfer from livestock manures into the food chain. Water Environ J 18:127–189
Otabbong E, Arkhipchenko I, Orlova O, Barbolina I, Shubaeva M (2007) Impact of piggery slurry lagoon on the environment: a study of groundwater and river Igolinka at the Vostochnii pig farm, St. Petersburg, Russia. Acta Agric Scand B: Soil Plant Sci 57:74–81
Rowell DL (1994) Soil science: methods and applications. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Essex
Tymczyna L, Chmielowiec-Korzeniowska A, Saba L (2000) Effect of a pig farm on the physical and chemical properties of a river and groundwater. Pol J Environ Stud 9:97–102
US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (2001) Environmental assessment of proposed revisions to the national pollutant discharge elimination system regulation and the effluent guidelines for concentrated animal feeding operations. http://water.epa.gov/scitech/wastetech/guide/cafo/upload/2001_02_06_guide_cafo_EnvAssessPt1of2.pdf. Accessed 1 Feb 2015
Wang H, Magesan GN, Bolan NS (2004) An overview of the environmental effects of land application of farm effluents. N Z J Agric Res 47:389–403
Withers PJA, Lord EI (2002) Agricultural nutrient inputs to rivers and groundwaters in the UK: policy, environmental management and research needs. Sci Total Environ 282–283:9–24
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michalopoulos, C., Tzamtzis, N. & Liodakis, S. Groundwater Contamination Due to Activities of an Intensive Hog Farming Operation Located on a Geologic Fault in East Mediterranean: A Study on COD, BOD5 and Microbial Load. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96, 229–234 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1635-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1635-0