Abstract
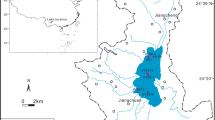
To reconstruct the history of environmental degradation in Sanliqi Lake (Daye City, central China), multiple proxies were analyzed in a sedimentary core which was dated using 137Cs and spheroidal carbonaceous particles (SCPs). The results show that Sanliqi Lake has experienced serious degradation during the past 60 years, resulting from a large influx of metals and nutrients. Expansion of agricultural and industrial activities between 1945 and 1993 enhanced nutrient and metal enrichment, indicated by increases in metals, SCPs, magnetic susceptibility, total phosphorus, total nitrogen and total organic carbon. Further enrichment of Zn, Cd, Ni and Cr after 1993 was linked to a recent intensification of mining activities. Decreases in Cu and Pb after 2006 probably resulted from recent environmental remediation. This study verified the coupling between lake sediment pollution and human activities in Daye City during the past 60 years. The reconstructed history of lake pollution can provide reference information for continued restoration of Sanliqi Lake and other similar heavily polluted lakes in the developing regions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battarbee RW, Jones VJ, Flower RJ, Cameron NG, Bennion H, Carvalho L, Juggins S (2001) Diatoms. Springer, Berlin
Boyle J, Rose N, Bennion H, Yang H, Appleby P (1999) Environmental impacts in the Jianghan Plain: evidence from lake sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut 112:21–40
Chen X, Mao X, Cao Y, Yang X (2013) Use of siliceous algae as biological monitors of heavy metal pollution in three lakes in a mining city, southeast China. Oceanol Hydrobiol Stud 42:233–242
Chen X, Li C, McGowan S, Yang X (2014) Diatom response to heavy metal pollution and nutrient enrichment in an urban lake: evidence from paleolimnology. Int J Limnol 2:121–130
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (1990) The environmental background value of soil in China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Compilation Commission of Daye (1990) County annals of Daye. Hubei Science Press, Wuhan
Dearing JA et al (2012) Extending the timescale and range of ecosystem services through paleoenvironmental analyses, exemplified in the lower Yangtze basin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E1111–E1120
Hu S, Wang Y, Appel E, Zhu Y, Hoffmann V, Shi C, Yu Y (2003) Magnetic responses to acidification in Lake Yangzonghai, SW China. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 28:711–717
Hubei Provincial Bureau of Statistics (1991–2010) Agricultural Statistical Yearbook of Hubei Province. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Järup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Li Z, Zhang Y (2010) Study on the water pollution control of Dayehu Lake. Science Press, Beijing
Liu J, Diamond J (2005) China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature 435:1179–1186
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger T (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Morin S et al (2008) Long-term survey of heavy-metal pollution, biofilm contamination and diatom community structure in the Riou Mort watershed, South-West France. Environ Pollut 151:532–542
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) An evaluation of technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments. J Hazard Mater 85:145–163
Norusis M (2010) SPSS 19.0 guide to data analysis. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Ochieng EZ, Lalah JO, Wandiga SO (2008) Water quality and trace metal distribution in a Pristine Lake in the Lake Basin in Kenya. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:362–368
Renberg I, Bindler R, Bradshaw E, Emteryd O, McGowan S (2001) Sediment evidence of early eutrophication and heavy metal pollution of Lake Mälaren, central Sweden. Ambio 30:496–502
Rose NL (2008) Quality control in the analysis of lake sediments for spheroidal carbonaceous particles. Limnol Oceanol Methods 6:172–179
Rose N et al (2004) Sedimentary evidence for changes in the pollution status of Taihu in the Jiangsu region of eastern China. J Paleolimnol 32:41–51
Statistical Office of Daye, Hubei (1970–2001) Statistical Yearbook of Daye
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang L, Wang L (2007) Survey of Cd, PB and As pollution in the water of Donggangqu Trench in Luoqiao, Daye City. Saf Environ Eng 14:16–19
Yang X, Anderson N, Dong X, Shen J (2008) Surface sediment diatom assemblages and epilimnetic total phosphorus in large, shallow lakes of the Yangtze floodplain: their relationships and implications for assessing long-term eutrophication. Freshw Biol 53:1273–1290
Yang G, Ma R, Zhang L, Jiang J, Yao S, Zhang M, Zeng H (2010) Lake status, major problems and protection strategy in China. J Lake Sci 22:799–810
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159:2575–2585
Zhang W, Yu L, Hutchinson S (2001) Diagenesis of magnetic minerals in the intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary, China, and its environmental significance. Sci Total Environ 266:169–175
Zhang J, Li Z, Chen J, Wang M, Tao R, Liu D (2014) Assessment of heavy metal contamination status in sediments and identification of pollution source in Daye Lake, Central China. Environ Earth Sci 72:1279–1288
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and Mark Stevenson for his helpful revisions to this manuscript. We thank Cao Yanmin, Zhu Yuxin, Xia Weilan and Liu Yilan for their help with laboratory analyses. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Found of China (41202248), the Open Research Programs from the State Key Laboratory of Biogeology and Environmental Geology (GBL21304) and the State Key Laboratory of Lake Science and Environment (2014SKL002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, L., Ning, D., Xu, L. et al. Sedimentary Evidence of Environmental Degradation in Sanliqi Lake, Daye City (A Typical Mining City, Central China). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95, 317–324 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1606-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1606-5