Abstract
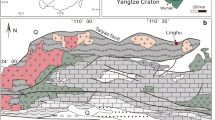
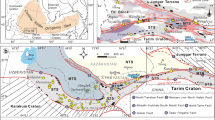
The large Hebaoshan gold deposit (41.5 t Au, average grade: 3.5 g/t) is located in a hitherto poorly documented gold province in the northeastern part of the South China Block. It is hosted by Precambrian metasedimentary rocks that experienced Triassic greenschist- to amphibolite-facies metamorphism. Three hydrothermal stages can be distinguished: quartz + sericite + pyrite + pyrrhotite (stage I), quartz + magnetite + sulfide (stage II), and quartz + carbonate + pyrite + hematite (stage III). Auriferous pyrite samples yielded a Rb-Sr isochron age of 234 ± 3 Ma (2σ, MSWD = 0.24), and ore-related hydrothermal sericite yielded a 40Ar-39Ar plateau age of 226.4 ± 2.0 Ma (2σ, MSWD = 1.01), which are distinctly younger than ca. 430 Ma granitic rocks in the mining district and older than 170–130 Ma granites in the region, ruling out any genetic link between granite emplacement and gold mineralization. The mineralizing fluid system can be described as carbonic-aqueous with low to moderate salinity (2.2–10.1 wt% NaCl equiv.) and medium temperature of 290 to 350 °C (stage I) and 230 to 280 °C (stage II). The δ18O quartz ranges from 13.3 to 15.4 ‰, and the δD values for fluid inclusions in quartz range from − 97 to − 60 ‰. The calcite has C-isotopes ranging from − 6.1 to − 3.8 ‰ and O-isotopes from 2.8 to 13.6 ‰. H-O-C isotope data are consistent with a metamorphic fluid derived from devolatilization of Neoproterozoic basement rocks during regional metamorphism in the Late Triassic Indosinian period. The δ34S values of sulfides for stages I, II, and III are 0.1 to 7.8 ‰, − 10.6 to 5.1 ‰, and − 18.9 to − 14.1 ‰, respectively, indicating an increase in oxygen fugacity during fluid ascent which resulted in more negative sulfur isotope values of sulfides and precipitation of gold. Pyrite separates have 206Pb/204Pb ratios of 17.340 to 17.687, 207Pb/204Pb ratios of 15.539 to 15.604, and 208Pb/204Pb ratios of 37.749 to 38.094. The S-Pb isotope data suggest derivation of S and Pb from the Precambrian metasedimentary country rocks. Auriferous pyrite yielded elevated 3He/4He ratios (0.78–1.46 Ra), which suggest a mantle component as can be expected from fluids derived from a subduction setting. It is concluded that Hebaoshan is an orogenic gold deposit that formed during Triassic flat-slab subduction of the paleo-Pacific plate beneath the South China Block and thus constitutes the first Triassic deposit of this type recognized in the coastal area of Southeast China.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MR, Rankin A, Spiro B (1992) Fluid mixing in the generation of mesothermal gold mineralization in the Transvaal Sequence, Transvaal, South Africa. Eur J Mineral 4:933–948
Bakker RJ (1999) Adaptation of the Bowers and Helgeson (1983) equation of state to the H2O-CO2-CH4-N2-NaCl system. Chem Geol 154:225–236
Ballentine CJ, Burgess R, Marty B (2002) Tracing fluid origin, transport and interaction in the crust. Rev Mineral Geochem 47:539–614
Bao SZ (2015) Study on the ore-control geological conditions and prospecting foreground of gold ores in Fujian Province. Geol Fujian 4:289–297 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Bottinga Y (1968) Calculation of fractionation factors for carbon and oxygen isotopic exchange in the system calcite-carbon dioxide-water. J Phys Chem 72:800–808
Bowers TS, Helgeson HC (1983) Calculation of the thermodynamic and geochemical consequences of nonideal mixing in the system H2O-CO2-NaCl on phase relations in geologic systems; metamorphic equilibria at high pressures and temperatures. Am Mineral 68:1059–1075
Brown PE, Hagemann SG (1995) MacFlincor and its application to fluids in Archaean lode-gold deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:3943–3952
Cai JX, Zhang KJ (2009) A new model for the Indochina and South China collision during the Late Permian to the Middle Triassic. Tectonophysics 467:35–43
Cai BJ, Chen BL, Chen HX (1994) The study of the gold mineralization laws in the middle part of Chongan-Shicheng tectonic belt. Seismological Press, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cameron EM, Hattori K (1987) Archean gold mineralization and oxidized hydrothermal fluids. Econ Geol 82(5):1177–1191
Cartigny P, Harris JW, Javoy M (1998) Eclogitic diamond formation at Jwaneng: No room for a recycled component. Science 280:1421–1424
Cathelineau M, Marignac C (1994) Use of fluid inclusions for a better understanding intracontinental geothermal activities. In: De Vivo B, Frezzotti ML (eds) Fluid inclusions in minerals: methods and applications. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksbug, pp 309–326
Cao L, Duan QF, Zhou Y (2015) Rb-Sr dating of sphalerites from the Aozigang zinc deposit in Hubei Province and its geological significance. Geol China 42:235–247 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Charvet J (2013) The Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the South China Block: an overview. J Asian Earth Sci 74:198–209
Charvet J, Shu LS, Faure M, Choulet F, Wang B, Lu HF, Breton NL (2010) Structural development of the Lower Paleozoic belt of South China: genesis of an inttacontinental orogen. J Asian Earth Sci 39:309–330
Chen GJ (2016) The metallogensis and prospecting prediction of the Hebaoshan gold ore field, Taining County, Fujian Province. Geol Fujian 35:46–54
Chen W, Zhang W, Zhang YQ, Jin GS, Wang QL (2006) Late Cenozoic eposidic uplifting in southeastern part of the Tibetan plateau-evidence from Ar-Ar thermochronology. Acta Petrol Sin 22:867–872 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen GJ, Zhang WB, Liu JT (2015) LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geological features of Changxing intrusion in the Hebaoshan gold deposit, Taining County, Fujian Province. Geol China 42(2):547–555 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Clayton RN, Mayeda TK (1963) The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 27:43–52
Clayton RN, O’Neil JL, Meyeda TK (1972) Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water. J Geophys Res 77:3057–3067
Clout JMF (1989) Structural and isotopic studies of the Golden Mile gold-telluride deposit, Kalgoorlie, WA. PhD Thesis, Monash University
Deines P, Gold DP (1973) The isotopic composition of carbonatite and kimberlite carbonates and their bearing on the isotopic composition of deep-seated carbon. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37:1709–1733
Deng J, Yang L-Q, Groves DI, Liang Z, Qiu K-F, Wang Q-F (2020) An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, Eastern China. Earth-Sci Rev 208:103274
Deng J, Wang QF (2016) Gold mineralization in China: metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Res 36:219–274
Drummond SE, Ohmoto H (1985) Chemical evolution and mineral deposition in boiling hydrothermal systems. Econ Geol 80(1):126–147
Dugdale AL, Hagemann SG (2001) The Bronzewing lode-gold deposit, Western Australia: P-T-X evidence for fluid immiscibility caused by cyclic decompression in gold-bearing quartz-veins. Chem Geol 173:59–90
Dunai TJ, Baur H (1995) Helium, neon, and argon systematics of the European subcontinental mantle: implications for its geochemical evolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:2767–2783
Faure M, Wei L, Yang C, Lepvrier C (2016) Triassic tectonic of the southern margin of the South China block. CR Geosci 348:5–14
Firth EA, Holwell DA, Oliver NHS, Mortensen JK, Rovardi MP, Boyce AJ (2015) Constraints on the development of orogenic style gold mineralisation at Mineral de Talca, Coastal Range, central Chile: evidence from a combined structural, mineralogical, S and Pb isotope and geochronological study. Miner Deposita 50:675–696
Friedman I (1953) Deuterium content of natural waters and other substances. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 4:89–103
Frimmel HE (2018) Episodic concentration of gold to ore grade through Earth’s history. Earth-Sci Rev 180:148–158
Goldfarb RJ, Groves DI (2015) Orogenic gold: common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time. Lithos 233:2–26
Goldfarb RJ, Newberry RJ, Pickthorn WJ, Gent CA (1991) Oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur isotope studies in the Juneau gold belt, south-eastern Alaska: constraints on the origin of hydrothermal fluids. Econ Geol 86:66–80
Goldfarb RJ, Groves DI, Gardoll S (2001) Orogenic gold and geologic time: a global synthesis. Ore Geol Rev 18:1–75
Goldfarb RJ, Baker T, Dube B, Groves DI, Hart CJR, Gosselin P (2005) Distribution, character, and genesis of gold deposits in metamorphic terranes. Ecnomic Geology 100th Anniversary 407−450
Goldfarb R, Qiu K, Deng J, Chen Y, Yang L (2019) Orogenic gold deposits of China. SEG special publications 22:263–324
Goldstein RH, Reynolds TJ (1994) Systematics of fluid inclusions in diagenetic minerals. Soc. Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Short course 32:1–53
Goodwin NJR, Burgess R, Craw D, Teagle DAH, Ballentine CJ (2017) Nobel gases fingerprint a metasedimentary fluid source in the Macraes orogenic gold deposit, New Zealand. Mineral Deposita 52:1–13
Graupner T, Niedermann S, Kemep U, Klemd R, Bechtel A (2006) Origin of ore fluids in the Muruntau gold system: constraints from noble gas, carbon isotope and halogen data. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:5356–5370
Groves DI (1993) The crustal continuum model for the late-Archean lode-gold deposits of the Yilgarn block, Western-Australia. Miner Deposita 28:366–374
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Gebre-Mariam M, Hagemann SG, Robert F (1998) Orogenic gold deposits: a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types. Ore Geol Rev 13:7–27
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Knox-Robinson CM, Ojala J, Gardoll S, Yun G, Holyland P (2000) Late-kinematic timing oforogenic gold deposits and significance for computer-based exploration techniques with emphasis on the Yilgarn block, Western Australia. Ore Geol Rev 17:1–38
Groves DI, Santosh M, Deng J, Wang QF, Yang LQ, Zhang L (2019) A holistic model for the origin of orogenic gold deposits and its implications for exploration. Miner Deposita in press
Hagemann SG, Lüders V (2003) P-T-X conditions of hydrothermal fluids and precipitation mechanism of stibnite-gold mineralization at the Wiluna lode-gold deposits, Western Australia: conventional and infrared microthermometric constraints. Miner Deposita 38:936–952
Hedenquist JW, Lowenstern JB (1994) The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits. Nature 370:495–510
Hodkiewicz PE, Groves DI, Davidson GJ, Weinberg RF, Hagemann SG (2009) Influence of structural setting on sulphur isotopes in Archean orogenic gold deposits, Eastern Goldfields Province, Yilgarn Western Australia. Miner Deposita 44:129–234
Hoefs J (2009) Stable isotope geochemistry, 6th edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg 285 p
Hollister LS (1990) Enrichment of CO2 in fluid inclusions in quartz by remove of H2O during crystal -plastic deformation. J Struct Geol 12:895–901
Hu RZ, Burnard PG, Turner G, Bi X (1998) Helium and argon isotope systematics in fluid inclusions of Machangqing copper deposit in west Yunnan Province, China. Chem Geol 146:55–63
Hu RZ, Chen WT, Xu DR, Zhou MF (2017) Reviews and new metallogenic models of mineral deposits in South China: an introduction. J Asian Earth Sci 137:1–8
Huang CP (2001) Reach on the metallogenic characteristics and forecast of gold deposits in Fujian province, China. Ph. D. dissertation, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jia Y, Kerrich R, Goldfarb R (2003) Metamorphic origin of ore-forming fluids for orogenic gold -bearing quartz vein systems in the North American Cordillera: constraints from a reconnaissance study of δ15N, δD, and δ18O. Econ Geol 98:109–123
Jia Y, Li X, Kerrich R (2001) Stable isotope (O, H, S, C, and N) systematics of quartz vein systems in the turbidite-hosted central and north deborah gold deposits of the bendigo gold field, Central Victoria, Australia: Constraints on the origin of ore-forming fluids. Econ Geol 96(4):705–721
Keeling CD, Bacastow RB, Carter AF, Piper SC, Whorf TP, Heimann M, Mook WG, Roeloffzen H (1989) A three-dimensional model of atomospheric CO2 transport based on observed winds: 1. Analysis of observational data. In: Peterson DH (ed) Aspects of climate variability in the Pacific and the Western Americas, Geophysical Monograph Series 55, pp 165–236
Kerrich R (1989) Geochemical evidence on the source of fluids and solutes for shear zone hosted mesothermal Au deposits. In: Bursnall JT (ed) Mineralization and shear zones. Geological Association of Canada short course 6, pp 129–197
Kerrich R, Fryer BJ, King RW, Willmore LM, van Hees E (1987) Crustal outgassing and LILE enrichment in major lithospheric structures, Archean Abitibi greenstone belt: evidence on the source reservoir from strontium and carbon isotope tracers. Contrib Mineral Petr 97:156–168
Klein EL, Ribeiro JW, Harris C, Moura CAV, Ciret A (2008) Geology and fluid characteristics of the Mina Velha and Mandiocal orebodies and implications for the genesis of the orogenic Chega Tudo gold deposit, Gurupi Belt, Brazil. Econ Geol 103:957–980
Klemd R, Oberthür T, Ouedrago A (1997) Gold-telluride mineralisation in the Birimian at Diabatou, Burkina Faso. J Afr Earth Sci 24:227–239
Koppers AAP (2002) ArArCALC: software for 40Ar/39Ar age calculations. Comput Geosci 28:605–619
Li J-W, Li Z-K, Zhou M-F, Chen L, Bi S-J, Deng X-D, Qiu H-N, Cohen B, Selby D, Zhao X-F (2012) The early cretaceous yangzhaiyu lode gold deposit, North China Craton: a link between craton reactivation and gold veining. Econ Geol 107(1):43–79
Li ZX, Li XH (2007) Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magamatic province in Mesozoic South China: a flat-salb subduction model. Geology 35:179–182
Li ZX, Li XH, Wartho JA, Clark C, Li WX, Zhang CL, Bao CM (2010) Magmatic and metamorphic events during the early Paleozoic Wuyi-Yunkai orogeny, southeastern South China: new age constraints and pressure-temperature conditions. Geol Soc Am Bull 122:772–793
Lin QT (1993) On the genesis of Hebaoshan gold ores in Fujiang Province. Geol Fujian 12(4):239–247
Lin QT, Su C (1993) Characteristics of Chongan-Shicheng structural belt in northern Fujian. Geol Fujian 1:41–47 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mamyrin BA, Tolstikhin IN (1984) Helium isotopes in nature. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–267
Mao JW, Li Y, Goldfarb R, He Y, Zaw K (2003) Fluid inclusions and noble gas studies of the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, China: a mantle connection for mineralization. Econ Geol 98:517–534
McCuaig TC, Hronsky JMA (2014) The mineral system concept: the key to exploration targeting. Society of Exploration Geologists Special Publications 18:153–175
McCuaig TC, Kerrich R (1998) P-T-t-deformation-fluid characteristics of lode gold deposits: evidence from alteration systematics. Ore Geol Rev 12:381–453
Nesbitt BE, Muehlenbachs K, Murowchick JB (1989) Genetic implications of stable isotope characteristics of mesothermal Au deposits and related Sb and Hg deposits in the Canadian Cordillera. Econ Geol 84:1489–1506
Ohmoto H (1972) Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ Geol 67:551–578
Ohmoto H, Goldhaber MB (1997) Sulfur and carbon isotopes. In: Barns HL (ed) Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Wiley, New York, pp 509–567
Ohmoto H, Rye R (1979) Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In: Barnes HL (ed) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, pp 509–567
O'Neil JR, Clayton RN, Mayeda TK (1969) Oxygen isotope fractionation in divalent metal carbonates. J Chem Phys 51:5547–5558
Ozima M, Podosek FA (2002) Noble gas geochemistry. 286 p. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Palin J, Xu Y (2000) Gilt by association? Origins of pyretic gold ores in the victory mesothermal gold deposit, Western Australia. Econ Geol 85:1627–1634
Partington GA, Williams PJ (2000) Proterozoic lode gold and (iron)-copper-gold deposits—a comparison of Australian and global examples. Rev Econ Geol 13:69–101
Phillips GN, Powell R (2010) Formation of gold deposits: a metamorphic devolatilization model. J Metamorph Geol 28:689–718
Pitcairn IK, Teagle DAH, Craw D, Olivo GR, Kerrich R, Brewer TS (2006) Sources of metals and fluids in orogenic gold deposits: insights from the Otago and Alpine Schists, New Zealand. Econ Geol 101:1525–1546
Polito PA, Boneb Y, Clarke JDA, Mernagh TP (2001) Compositional zoning of fluid inclusions in the Archaean Junction gold deposit, Western Australia: a process of fluid-wall-rock interaction? Aust J Earth Sci 43:833–855
Rezeau H, Moritz R, Beaudoin G (2017) Formation of Archean batholith-hosted gold veins at Lac Herbin deposit, Val-d’Or district, Canada: mineralogical and fluid inclusion constraints. Miner Deposita 52:421–442
Ridley JR, Diamond LW (2000) Fluid chemistry of orogenic lode gold deposits and implications for genetic models. Rev Econ Geol 13:141–162
Sánchez-España J, Velasco F, Boyce AJ, Fallick AE (2003) Source and evolution of ore-forming hydrothermal fluids in the northern Iberian pyrite belt massive sulphide deposits (SW Spain): Evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. Mineral Deposita 38:519–537
Shu LS, Wang B, Cawood PA, Santosh M, Xu ZQ (2015) Early Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic intraplate tectonic and magmatic events in the Cathaysia Block. South China. Tectonics 34:1600–1621. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015TC003835
Song M, Shu L, Santosh M, Li J (2015) Late Early Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic intracontinental orogeny in the South China Craton: geochronological and geochemical evidence. Lithos 232:360–374
Steiger RH, Jager E (1977) Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on use of decay constants in geochronology and cosmochronology. Earth Planet Sc Lett 36:359–362
Stuart FM, Burnard PG, Taylor RP, Turner G (1995) Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralisation, South Korea. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:4663–4673
Sun XM, Yu SG, Ye CH (1993) Main geological features of gold deposits in the Taiyangshan ductile shear zone, northern Fujian. Geol Prospec 10:22–26 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun XM, Zhang Y, Xiong D, Sun W, Shi GY, Zhai W, Wang SW (2009) Crustal and mantle contributions to gold-forming process at the Daping deposit, Aliaoshan gold belt, Yunnan, China. Ore Geol Rev 36:235–249
Taylor HP (1974) The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition: Econ. Geol. 69:843–883
Taylor BE (1986) Mamgatic volatiles: isotopic variation of C, H, and S. Rev Mineral 16:185–225
Todt W, Cliff RA, Hanser A, Hofmann AW (1996) Evaluation of a 202Pb-205Pb double spike for high-precision lead isotope analysis. Geophys Monograph Ser 95:429–437
Valley JW (1986) Stable isotope geochemistry of metamorphic rocks. Rev Mineral Geochem 16:445–489
Wan YS, Liu DY, Xu MH, Zhuang JM, Song B, Shi YR, Du LL (2007) SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks in Northwestern Fujian, Cathaysia block, China: tectonic implications and the need to redefine lithostratigraphic units. Gondwana Res 12:223–234
Wan B, Hegner E, Zhang LC, Rocholl A, Chen ZG, Wu HY, Chen FK (2009) Rb-Sr geochronology of chalcopyrite form the Chehugou porphyry Mo-Cu deposit (Northeast China) and geochemical constraints on the origin of hosting granites. Econ Geol 104:351–363
Wang SS (1983) Age determinations of 40Ar-40K, 40Ar-39Ar and radiogenic 40Ar released characteristics on K-Ar geostandards of China. Sci Geol Sin 4:315–323 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YJ, Zhang AM, Fan WM, Zhang YJ, Zhang YZ (2011) Kwangsian crustal anatexis within the eastern South China Block: geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic fingerprints from the gneissoid granites of Wugong and Wuyi-Yunkai Domains. Lithos 127:239–260
Wang YJ, Wu CM, Zhang AM, Fan WM, Zhang YH, Zhang YZ, Peng TP, Yin CQ (2012) Kwangsian and Indosinian reworking of the eastern South China Block: constraints on zircon U-Pb geochronology and metamorphism of amphibolites and granulites. Lithos 150:227–242
Wang YJ, Fan WM, Zhang GW, Zhang YH (2013) Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block: Key observations and conroversies. Gondwana Res 23:1273–1305
Wang ZL, Yang LQ, Guo LN, Marsh E, Wang JP, Liu Y, Zhang C, Li RH, Zhang L, Zheng XL, Zhao RX (2015) Fluid immiscibility and gold deposition in the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: a fluid inclusion study. Ore Geol Rev 65:707–717
Wang GC, Jiang YH, Liu Z, Ni CY, Qing L, Zhang Q, Zhu SQ (2016) Multiple origins for the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous high-K calcalkaline I-type granites in northwestern Fujian province, SE China and tectonic implications. Lithos 246-247:197–211
Xiao WJ, He HQ (2005) Early Mesozoic thrust tectonics of the northwest Zhejiang region (Southeast China). Geo Soc Am Bull 117:945–961
Xie CM (2014) Characteristics of ore-controlling structure and ore-searching direction of the Hebaoshan gold deposit in Taining County, Fujian Province. Geol Fujian 2:87–93 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu BT, Li CJ, Chen HS (1994) Mineralization chronology and isotopic geochemistry of the Haoshi silver deposit in Zhejiang Province. Miner Depos 13:271–281 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu XB, Zhang YQ, Shu LS, Jia D (2011) LA-ICP-MS U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the sheared metamorphic rocks in the Wuyishan: constraints on the timing of Early Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic tectono-thermal events in SE China. Tectonophysics 501:71–86
Xu YF, Ni P, Wang GG, Pan JY, Guan SJ, Chen H, Ding JY, Li L (2016) Geology, fluid inclusion and stable isotope study of the Huangshan orogenic gold deposit: implications for future exploration along the Jiangshan-Shaoxing fault zone, South China. J Geochem Explor 171:37–54
Yang XQ, Li ZL, Yu SQ (2016) Phase equilibrium modelling, fluid inclusions and origin of charnockites in the Datian region of the northeastern Cathaysia block, South China. J Asian Earth Sci 126:14–28
Yang JB, Zhao ZD, Hou QY, Niu YL, Mo XX, Sheng D, Wang LL (2018) Petrogenesis of Cretaceous (133-84 Ma) intermediate dykes and host granites in southeastern China: implications for lithospheric extension, continental crustal growth, and geodynamics of Palaeo-Pacific subduction. Lithos 296−299:195–211
Yu XQ, Wu GG, Zhao XX, Zhang D, Di YJ, Qiu JT, Dai YP, Li CL (2012) New geochronological data from the Paleozoic and Mesozoic nappe structures, igneous rocks, and molybdenite in the North Wuyi area, Southeast China. Gondwana Res 22:519–533
Yuan HX, Chen H, Hu RH (2017) Geological characteristics and research progress of Hebaoshan gold deposit in Fujian Province. Acta Mineral Sin Supplement:797–798 (in Chinese)
Zeng W, Zhang L, Zhou HW, Zhong ZQ, Xiang H, Liu R, Jin S, Lu XQ, Li CZ (2008) Caledonian reworking of Paleoproterozoic basement in the Cathaysia Block: constraints from zircon U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements. Chinese Sci Bull 53:895–904
Zhang YG, Frantz JD (1987) Determination of the homogenization temperatures and densities of supercritical fluids in the system NaCl-KCl-CaCl2-H2O using synthetic fluid inclusions. Chem Geol 64:335–350
Zhang Q, Jiang YH, Wang GC, Liu Z, Ni CY, Qing L (2015) Origin or Silurian gabbros and I-type granites in central Fujian, SE China: implications for the evolution of the early Paleozoic orogen of South China. Lithos 216−217:285–297
Zhang L, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Sun SC, Liu Y, Wang JY, Li RH, Wu SG, Gao L, Guo JL, Chen XG, Chen JH (2019) An overview of timing and structural geometry of gold, gold-antimony and antimony mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogen, southern China. Ore Geol Rev 115:103173
Zhao JH, Zhou MF, Yan DP, Zheng JP, Li JW (2011) Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China: no connection with the Grenvillian orogeny. Geology 39:299–302
Zhao C, Ni P, Wang GG, Ding JY, Chen H, Zhao KD, Cai YT, Xu YF (2013) Geology, fluid inclusion, and isotope constraints on roe genesis of the Neoproterozoic Jinshan orogenic gold deposit. South China: Geofluids 13:506–527
Zheng Y, Zhou YZ, Wang YJ, Shen WJ, Yang ZJ, Li XY, Xiao F (2016) A fluid inclusion study of the Hetai goldfield in the Qinzhou Bay-Hangzhou Bay metallogenic belt, South China. Ore Geol Rev 73:346–353
Zhu ZY, Cook NJ, Yang T, Ciobanu CL, Zhao KD, Jiang SY (2016) Mapping of S isotopes and trace elements in sulfides by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS: potential analytical problems, improvements and implications. Minerals 6:110
Zhu KY, Li ZX, Xia QK, Xu XS, Wilde SA, Chen HL (2017) Revisiting Mesozoic felsic intrusions in eastern South China: spatial and temporal variations and tectonic significance. Lithos 294−295:147–163
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Zhuang Lin and Jianwen Du from the Fujian Institute of Geological Survey and Research for invaluable assistance during the fieldwork. Drs. Kui-Dong Zhao, De-Fang Wan, Zeng-Jie Zhang, Mou-Chun He, Wei Chen, Hai-Xiang Zhao, Yao-Ming Xu, Rui-Chun Duan, Jia-Xin She, and Xu Dai are also thanked for their kind help with lab work. This paper has been greatly improved by a thorough review from two anonymous reviewers, associate editor Prof. Ruizhong Hu, and editor Prof. Bernd Lehmann.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41973044), the National 111 Project (B20045), the MOST Special Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences (No. MSFGPMR03-2), and the Fundamental Research Funds for National Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (grant no 2201610076). Mr. Ying Ma gratefully acknowledges financial support from the China Scholarship Council (grant no. 201906410039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Editorial handling: R. Hu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1329 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Jiang, SY., Frimmel, H.E. et al. Genesis of the Hebaoshan gold deposit in Fujian Province of Southeast China: constraints from a combined fluid inclusion, H-O-C-S-Pb-He-Ar isotope and geochronological study. Miner Deposita 57, 13–34 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01046-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01046-3