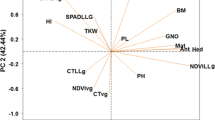
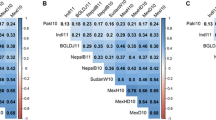
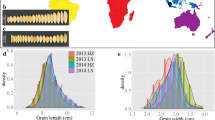
Abstract
Key message
SNP-based and InDel-based GWAS on multi-environment data identified genomic regions associated with barley grain size.
Abstract
Barley yield and quality are greatly influenced by grain size. Improving barley grain size in breeding programs requires knowledge of genetic loci and alleles in germplasm resources. In this study, a collection of 334 worldwide two-rowed barley accessions with extensive genetic diversity was evaluated for grain size including grain length (GL), grain width (GW), and thousand-grain weight (TGW) across six independent field trials. Significant differences were observed in genotype and environments for all measured traits. SNP- and InDel-based GWAS were applied to dissect the genetic architecture of grain size with an SLAF-seq strategy. Two approaches using the FarmCPU model revealed 38 significant marker-trait associations (MTAs) with PVE ranging from 0.01% to 20.68%. Among these MTAs, five were on genomic regions where no previously reported QTL for grain size. Superior alleles of TGW-associated SNP233060 and GL-associated InDel11006 exhibited significantly higher levels of phenotype. The significant MTAs could be used in marker-assisted selection breeding.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
References
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K (2009) Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res 19:1655–1664. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.094052.109
Ayoub M, Symons S, Edney M, Mather D (2002) QTLs affecting kernel size and shape in a two-rowed by six-rowed barley cross. Theor Appl Genet 105:237–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-0941-1
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth457
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Boden SA, Kavanová M, Finnegan EJ, Wigge PA (2013) Thermal stress effects on grain yield in brachypodium distachyon occur via H2A.Z-nucleosomes. Genome Biol 14:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-6-r65
Cai D, Xiao Y, Yang W et al (2014) Association mapping of six yield-related traits in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 127:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2203-9
Cheng X, Chai L, Chen Z et al (2015) Identification and characterization of a high kernel weight mutant induced by gamma radiation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genet 16:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-015-0285-x
Coventry SJ, Barr AR, Eglinton JK, McDonald GK (2003) The determinants and genome locations influencing grain weight and size in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Aust J Agric Res 54:1103. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR02194
Du B, Wang Q, Sun G et al (2019) Mapping dynamic QTL dissects the genetic architecture of grain size and grain filling rate at different grain-filling stages in barley. Sci Rep 9:18823. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53620-5
Fang Y, Zhang X, Zhang X et al (2020) A high-density genetic linkage map of SLAFs and QTL analysis of grain size and weight in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Front Plant Sci 11:620922. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.620922
Gong D, Wang Y, Zhang H et al (2022) Overexpression of ZmKL9 increases maize hybrid hundred kernel weight. Plant Biotechnol J 21(3):451. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13957
Gordon T, Wang R, Bowman B et al (2020) Agronomic and genetic assessment of terminal drought tolerance in two-row spring barley. Crop Sci 60:1415–1427. https://doi.org/10.1002/csc2.20040
Hong Y, Zhang M, Xu R (2023) Genetic localization and homologous genes mining for barley grain size. Int J Mol Sci 24:4932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054932
Hu J, Chen B, Zhao J et al (2022) Genomic selection and genetic architecture of agronomic traits during modern rapeseed breeding. Nat Genet 54:694–704. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01055-6
Jayakodi M, Padmarasu S, Haberer G et al (2020) The barley pan-genome reveals the hidden legacy of mutation breeding. Nature 588:284–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2947-8
Jiang D, Berger F (2017) Histone variants in plant transcriptional regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta - Gene Regul Mech 1860:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.07.002
Julie B (2013) SPSS survival manual: a step by step guide to data analysis using IBM SPSS. Aust N Z J Public Health 37:597–598. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-6405.12166
Kalladan R, Worch S, Rolletschek H et al (2013) Identification of quantitative trait loci contributing to yield and seed quality parameters under terminal drought in barley advanced backcross lines. Mol Breed 32:71–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9853-9
Kitagawa K, Kurinami S, Oki K et al (2010) A novel kinesin 13 protein regulating rice seed length. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1315–1329. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcq092
Komatsuda T, Pourkheirandish M, He C et al (2007) Six-rowed barley originated from a mutation in a homeodomain-leucine zipper I-class homeobox gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:1424–1429. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0608580104
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Liu L, Tong H, Xiao Y et al (2015) Activation of Big Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:11102–11107. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512748112
Lv Q, Li L, Meng Y et al (2022) Wheat E3 ubiquitin ligase TaGW2-6A degrades TaAGPS to affect seed size. Plant Sci 320:111274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111274
Mascher M, Wicker T, Jenkins J et al (2021) Long-read sequence assembly: a technical evaluation in barley. Plant Cell 33:1888–1906. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab077
Maurer A, Draba V, Pillen K (2016) Genomic dissection of plant development and its impact on thousand grain weight in barley through nested association mapping. J Exp Bot 67:2507–2518. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw070
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E et al (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.107524.110
Milner SG, Jost M, Taketa S et al (2019) Genebank genomics highlights the diversity of a global barley collection. Nat Genet 51:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0266-x
Nadolska-Orczyk A, Rajchel IK, Orczyk W, Gasparis S (2017) Major genes determining yield-related traits in wheat and barley. Theor Appl Genet 130:1081–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2880-x
Pan Y, Zhu J, Hong Y et al (2021) Identification of novel QTL contributing to barley yellow mosaic resistance in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare spp. spontaneum). BMC Plant Biol 21:560. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03321-x
Pan Y, Zhu J, Hong Y et al (2022) Screening of stable resistant accessions and identification of resistance loci to Barley yellow mosaic virus disease. PeerJ 10:e13128. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.13128
Pasam RK, Sharma R, Malosetti M et al (2012) Genome-wide association studies for agronomical traits in a worldwide spring barley collection. BMC Plant Biol 12:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-16
Pont C, Leroy T, Seidel M et al (2019) Tracing the ancestry of modern bread wheats. Nat Genet 51:905–911. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0393-z
Sharma R, Draicchio F, Bull H et al (2018) Genome-wide association of yield traits in a nested association mapping population of barley reveals new gene diversity for future breeding. J Exp Bot 69:3811–3822. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery178
Sun X, Liu D, Zhang X et al (2013) SLAF-seq: an efficient method of large-scale de novo SNP discovery and genotyping using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 8(3):e58700. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058700
Taketa S, Amano S, Tsujino Y et al (2008) Barley grain with adhering hulls is controlled by an ERF family transcription factor gene regulating a lipid biosynthesis pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4062–4067. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711034105
Tang Z, Gao X, Zhan X et al (2021) Natural variation in OsGASR7 regulates grain length in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 19:14–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13436
Walker CK, Ford R, Muñoz-Amatriaín M, Panozzo JF (2013) The detection of QTLs in barley associated with endosperm hardness, grain density, grain size and malting quality using rapid phenotyping tools. Theor Appl Genet 126:2533–2551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2153-2
Wang J, Sun G, Ren X et al (2016) QTL underlying some agronomic traits in barley detected by SNP markers. BMC Genet 17:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0409-y
Wang J, Wu X, Yue W et al (2021) Identification of QTL for barley grain size. PeerJ 9:e11287. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.11287
Wang Q, Sun G, Ren X et al (2019) Dissecting the genetic basis of grain size and weight in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) by QTL and comparative genetic analyses. Front Plant Sci 10:469. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00469
Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q et al (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44:950–954. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2327
Wang Z, Deng Z, Kong X et al (2022) InDels identification and association analysis with spike and awn length in Chinese wheat mini-core collection. Int J Mol Sci 23:5587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105587
Watt C, Zhou G, McFawn LA et al (2019) Fine mapping of qGL5H, a major grain length locus in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 132:883–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3243-y
Watt C, Zhou G, McFawn LA, Li C (2020) Fine mapping qGL2H, a major locus controlling grain length in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 133:2095–2103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03579-z
Xu X, Sharma R, Tondelli A et al (2018) Genome-wide association analysis of grain yield-associated traits in a pan-European Barley cultivar collection. Plant Genome 11:170073. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2017.08.0073
Yang J, Lee SH, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (2011) GCTA: a tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am J Hum Genet 88:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.11.011
Yang X, Zhang X, Yang Y et al (2021) The histone variant Sl_H2.AZ regulates carotenoid biosynthesis and gene expression during tomato fruit ripening. Hortic Res 8:85. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-021-00520-3
Yin L, Zhang H, Tang Z et al (2021) rMVP: a memory-efficient, visualization-enhanced, and parallel-accelerated tool for genome-wide association study. Genom Proteom Bioinform 19:619–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2020.10.007
Yuan H, Xu Z, Chen W et al (2022) OsBSK2, a putative brassinosteroid-signalling kinase, positively controls grain size in rice. J Exp Bot 73:5529–5542. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erac222
Zhang C, Dong SS, Xu JY et al (2019) PopLDdecay: a fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics 35:1786–1788. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty875
Zhou H, Liu S, Liu Y et al (2016) Mapping and validation of major quantitative trait loci for kernel length in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum). BMC Genet 17:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0438-6
Zhou H, Luo W, Gao S et al (2021) Identification of loci and candidate genes controlling kernel weight in barley based on a population for which whole genome assemblies are available for both parents. Crop J 9:854–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2020.07.010
Zhu J, Guo Y, Zhou H et al (2022) Genome wide association study and haplotype analysis reveals the role of HvHKT1;5 in potassium retention but not Na+ exclusion in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ Exp Bot 201:104973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.104973
Zohary D, Hopf M, Weiss E (2012) Domestication of plants in the old world. Oxford University Press
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD2301302); the National Modern Agriculture Industry Technology System, China (CARS-05); and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, China (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RX designed the research; YH and MZ analyzed all the data and wrote the manuscript. JZ, YZ, CL, BG, FW performed the experiments and recorded phenotypic data. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Gary Muehlbauer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Y., Zhang, M., Zhu, J. et al. Genome-wide association studies reveal novel loci for grain size in two-rowed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 137, 58 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-024-04562-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-024-04562-8