Abstract
Key message
Identification and genomic characterization of major resistance locus against cotton bacterial blight (CBB) using GWAS and linkage mapping to enable genomics-based development of durable CBB resistance and gene discovery in cotton.
Abstract
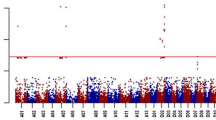
Cotton bacterial leaf blight (CBB), caused by Xanthomonas citri subsp. malvacearum (Xcm), has periodically been a damaging disease in the USA. Identification and deployment of genetic resistance in cotton cultivars is the most economical and efficient means of reducing crop losses due to CBB. In the current study, genome-wide association study (GWAS) of CBB resistance using an elite diversity panel of 380 accessions, genotyped with the cotton single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) 63 K array, and phenotyped with race-18 of CBB, localized the CBB resistance to a 2.01-Mb region in the long arm of chromosome D02. Molecular genetic mapping using an F6 recombinant inbred line (RIL) population showed the CBB resistance in cultivar Arkot 8102 was controlled by a single locus (BB-13). The BB-13 locus was mapped within the 0.95-cM interval near the telomeric region in the long arm of chromosome D02. Flanking SNP markers, i04890Gh and i04907Gh of the BB-13 locus, identified from the combined linkage analysis and GWAS, targeted it to a 371-Kb genomic region. Candidate gene analysis identified thirty putative gene sequences in the targeted genomic region. Nine of these putative genes and two NBS-LRR genes adjacent to the targeted region were putatively involved in plant disease resistance and are possible candidate genes for BB-13 locus. Genetic mapping and genomic targeting of the BB13 locus in the current study will help in cloning the CBB-resistant gene and establishing the molecular genetic architecture of the BB-13 locus towards developing durable resistance to CBB in cotton.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The plant material and datasets employed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdelraheem A, Elassbli H, Zhu Y, Kuraparthy V, Hinze L, Stelly D, Wedegaertner T, Zhang J (2019) A genome-wide association study uncovers consistent quantitative trait loci for resistance to verticillium wilt and fusarium wilt race 4 in the US upland cotton. Theor Appl Genet 133:563–577
Alexander AS (2009) Isolation frequency of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. malvacearum from acid delinted and easiflo treated cotton seed. Dissertation, Texas Tech University
Andrade AC, Viana JM, Pereira HD, Pinto VB, Silva FEF (2019) Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype block patterns in popcorn populations. PLoS ONE 14(9):e0219417. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219417
Atkinson GF (1892) Diseases of cotton. In: Results of experiments on cotton in alabama. Alabama experiment station, Auburn, pp 1–32
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of ld and haplotype maps. Bioinform 21:263–265
Bhandari HR, Bhanu AN, Srivastava K, Singh MN, Shreya HA (2017) Assessment of genetic diversity in crop plants—an overview. Adv Plants Agric Res 7:279–286
Bird LS (1982) The MAR (multi-adversity resistance) system for genetic improvement of cotton. Plant Dis 66:172–176
Bird LS, Blank LM (1951) Breeding strains of cotton resistant to bacterial blight. Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, Texas, USA
Bourland FM, Bridge RR (1988) Registration of miscot t8–27 cotton germplasm. Crop Sci 28:1035–1035
Bourland FM, McGowan JRE, Johnson JT (1997) Registration of arkot 8102, arkot 8506, and arkot 8514 germplasm lines of cotton. Crop Sci 37:1397. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1997.0011183X003700040086x
Bourland FM (2018) Breeding for bacterial blight resistance in cotton. In: Proceedings of the beltwide cotton conference. San Antonio, TX, pp 19–22.
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) Tassel: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinform 23:2633–2635
Broman KW, Wu H, Sen S, Churchill GA (2003) R/qtl: qtl mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinform 19:889–890
Browning BL, Zhou Y, Browning SR (2018) A one-penny imputed genome from next-generation reference panels. Am J Hum Genet 103(3):338–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.07.015
Browning BL, Tian X, Zhou Y, Browning SR (2021) Fast two-stage phasing of large-scale sequence data. Am J Hum Genet 108(10):1880–1890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.08.005
Buckler ES, Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh Bi I, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB, Kresovich S (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Chang CW, Fridman E, Mascher M, Himmelbach A, Schmid K (2022) Physical geography, isolation by distance and environmental variables shape genomic variation of wild barley (Hordeum vulgare L. ssp. spontaneum) in the southern levant. Heredity 128:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-021-00494-x
Cheema J, Dicks J (2009) Computational approaches and software tools for genetic linkage map estimation in plants. Brief Bioinform 10:595–608
Chen ZJ, Sreedasyam A, Ando A, Song Q, De Santiago LM, Hulse-Kemp AM, Ding M, Ye W, Kirkbride RC, Jenkins J, Plott C (2020) Genomic diversifications of five Gossypium allopolyploid species and their impact on cotton improvement. Nat Genet 52(5):525–533
Cheong WH, Tan YC, Yap SJ, Ng KP (2015) ClicO FS: an interactive web-based service of circos. Bioinform 31:3685–3687
Daniels MJ, Barber CE, Turner PC, Cleary WG, Sawczyc MK (1984) Isolation of mutants of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris showing altered pathogenicity. Microb 130:2447–2455
De Young BJ, Innes RW (2006) Plant nbs-lrr proteins in pathogen sensing and host defense. Nat Immunol 7(12):1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1410
De Vleesschauwer D, Seifi HS, Filipe O, Haeck A, Huu SN, Demeestere K, Höfte M (2016) The della protein srl1 integrates and amplifies salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-dependent innate immunity in rice. Plant Physiol (Bethesda) 170:1831–1847
Delannoy E, Lyon BR, Marmey P, Jalloul A, Daniel JF, Montillet JL, Mm E, Nicole M (2005) Resistance of cotton towards Xanthomonas campestris pv. malvacearum. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:63–82. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.040204.140251
Doyle EL, Stoddard BL, Voytas DF, Bogdanove AJ (2013) Tal effectors: highly adaptable phytobacterial virulence factors and readily engineered DNA-targeting proteins. Trends Cell Mol Biol 23(8):390–398
Earl DA, VonHoldt BM (2011) Structure harvester: a website and program for visualizing structure output and implementing the evanno method. Conservation Genet Resour 4:359–361
Elassbli H, Abdelraheem A, Zhu Y, Teng Z, Wheeler TA, Kuraparthy V, Hinze L, Stelly DM, Wedegaertner T, Zhang J (2021) Evaluation and genome-wide association study of resistance to bacterial blight race 18 in US upland cotton germplasm. Mol Genet Genom 296:719–729
Endo TR, Gill BS (1996) The deletion stocks of common wheat. J Hered 87(4):295–307
Feng F, Zhou JM (2012) Plant–bacterial pathogen interactions mediated by type III effectors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15(4):469–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2012.03.004
Feuillet C, Travella S, Stein N, Albar L, Nublat A, Keller B (2003) Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(25):15253–15258.
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.09.090171.001423
Gilroy EM, Hein I, Van Der Hoorn R, Boevink PC, Venter E, McLellan H, Kaffarnik F, Hrubikova K, Shaw J, Holeva M, López EC (2007) Involvement of cathepsin b in the plant disease resistance hypersensitive response. Plant J 52(1):1–3
Girardot B, Héquet E, Yehouessi MT, Guibordeau P (1986) Demonstration of a variety of Gossypium hirsutum L. resistant to strains of Xanthomonas campestris pv. malvacearum (Smith) dye virulent on major gene associations (B2–B3 or B9L–B10L). Cotton Tropical Fibres 41:67–69
Green JM, Brinkerhoff LA (1956) Inheritance of three genes for bacterial blight resistance in upland Cotton 1. Agronomy J 48:481–485
Hinze LL, Hulse-Kemp AM, Wilson IW, Zhu Q, Llewellyn DJ, Taylor JM, Spriggs A, Fang DD, Ulloa M, Burke JJ, Giband M, Lacape J, Van Deynze A, Udall JA, Scheffler JA, Hague S, Wendel JF, Pepper AE, Frelichowski J, Lawley CT, Jones DC, Percy RG, Stelly DM (2017) Diversity analysis of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) germplasm using the CottonSNP63k array. BMC Plant Biol 17(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-0981-y
Hochberg Y (1988) A sharper bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika 75:800–802
Hou X, Lee LYC, Xia K, Yan Y, Yu H (2010) Dellas modulate jasmonate signaling via competitive binding to JAZs. Dev Cell 19:884–894
Hulse-Kemp AM, Lemm J, Plieske J, Ashrafi H, Buyyarapu R, Fang DD, Frelichowski J, Giband M, Hague S, Hinze LL, Kochan KJ, Riggs PK, Scheffler JA, Udall JA, Ulloa M, Wang SS, Zhu Q, Bag SK, Bhardwaj A, Burke JJ, Byers RL, Claverie M, Gore MA, Harker DB, Islam MS, Jenkins JN, Jones DC, Lacape J, Llewellyn DJ, Percy RG, Pepper AE, Poland JA, Mohan Rai K, Sawant SV, Singh SK, Spriggs A, Taylor JM, Wang F, Yourstone SM, Zheng X, Lawley CT, Ganal MW, Van Deynze A, Wilson IW, Stelly DM (2015) Development of a 63k snp array for cotton and high-density mapping of intraspecific and interspecific populations of Gossypium spp. G3 (Bethesda) 5:1187–1209
Hunter RE, Brinkerhoff LA, Bird LS (1968) Development of a set of upland cotton lines for differentiating races of Xanthomonas malvacearum. Phytopathology 58(6):830–832
Innes NL (1969) Inheritance of resistance to bacterial blight of cotton: IV. Tanzania selections. J Agric Sci 72:41–57
Innes NL, Brown SJ, Walker JT (1974) Genetical and environmental variation for resistance to bacterial blight of upland cotton. Hered 32(1):53–72
Kamvar ZN, Brooks JC, Grünwald NJ (2015) Novel r tools for analysis of genome-wide population genetic data with emphasis on clonality. Front Genet 6:208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00208
Kaneda T, Taga Y, Takai R, Iwano M, Matsui H, Takayama S, Isogai A, Che F (2009) The transcription factor osnac4 is a key positive regulator of plant hypersensitive cell death. EMBO J 28:926–936
Knight RL (1944) The genetics of blackarm resistance. J Genet 46(1):1–27
Knight RL (1963) The genetics of blackarm resistance XII. Transference of resistance from Gossypium herbaceum to G. barbadense. J Genet 3:328–346
Knight RL, Clouston TW (1939) The genetics of black-arm resistance. Factors B2 and B3. J Genet 38:133–159
Kumar NV, Katageri IS, Gowda SA, Adiger S, Yadava SK, Lachagari VB (2019) 63K SNP chip based linkage mapping and qtl analysis for fiber quality and yield component traits in Gossypium barbadense L. cotton. Euphytica 215:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2326-9
Letunic I, Bork P (2021) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 49:293–296. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab301
Li J, Zhao C, Batoux M, Nekrasov V, Roux M, Chinchilla D, Zipfel C, Jones JDG (2009) Specific er quality control components required for biogenesis of the plant innate immune receptor efr. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:15973–15978
Li C, Dong Y, Zhao T, Li L, Li C, Yu E, Mei L, Daud MK, He Q, Chen J, Zhu S (2016) Genome-wide snp linkage mapping and qtl analysis for fiber quality and yield traits in the upland cotton recombinant inbred lines population. Front Plant Sci 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01356
Liu X, Yang L, Wang J, Wang Y, Guo Z, Li Q, Yang J, Wu Y, Chen L, Teng Z, Liu D, Liu D, Guo K, Zhang Z (2021) Analyzing quantitative trait loci for fiber quality and yield-related traits from a recombinant inbred line population with Gossypium hirsutum race palmeri as one parent. Front Plant Sci 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.817748
Matsukawa M, Shibata Y, Ohtsu M, Mizutani A, Mori H, Wang P, Ojika M, Kawakita K, Takemoto D (2013) Nicotiana benthamiana calreticulin 3a is required for the ethylene-mediated production of phytoalexins and disease resistance against oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:880–892
Meyer LA (2021) Cotton and wool outlook: December 2021. U.S. Department of agriculture, economic research service. https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/outlooks/102828/cws-21k.pdf?v=5542. Accessed 1 March 2022
Nagaraj S, Senthil-Kumar M, Ramu VS, Wang K, Mysore KS (2015) Plant ribosomal proteins, rpl12 and rpl19, play a role in nonhost disease resistance against bacterial pathogens. Front Plant Sci 6:1192–1202. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01192
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106(949):283–292
Panahabadi R, Ahmadikhah A, McKee LS, Ingvarsson PK, Farrokhi N (2021) Genome-wide association mapping of mixed linkage (1, 3; 1, 4)-β-glucan and starch contents in rice whole grain. Front Plant Sci:1781. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.665745
Paradis E, Schliep K (2019) Ape 5.0: an environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in r. Bioinform 35(3):526–528. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty633
Park SR, Kim HS, Lee KS, Hwang D, Bae S, Ahn I, Lee SH, Kim ST (2017) Overexpression of rice nac transcription factor osnac58 on increased resistance to bacterial leaf blight. J Plant Biotechnol 44:149–155
Phillips AZ, Berry JC, Wilson MC, Vijayaraghavan A, Burke J, Bunn JI, Allen TW, Wheeler T, Bart RS (2017) Genomics-enabled analysis of the emergent disease cotton bacterial blight. PLoS Genet 9:1–23
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genet (austin) 155:945–959
Ramesh UM, Methre R, Kumar N, Katageri IS, Gowda SA, Adiger S, Yadava SK, Lachagari VB (2019) Genome mapping and molecular markers identification for yield, yield component and fibre quality traits in tetraploid cotton. Plant Breed 138:880–896
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484
Roberts P (2016) Bacterial Blight Update (Bob Kemerait, UGA Plant Pathologist). Georgia cotton news. http://physicsweb.org/articles/news/11/6/16/1. Accessed 06 March 2022
Rungis D, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Lyon BR (2002) Investigation of the chromosomal location of the bacterial blight resistance gene present in an Australian cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivar. Aust J Agric Res 53:551–560
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Semizer CD, Altan F, Akdemir H, Tosun M, Gurel A, Tanyolac B (2015) Qtl analysis of fiber color and fiber quality in naturally green colored cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Turkish J Field Crops 20:49–58
Shabab M, Shindo T, Gu C, Kaschani F, Pansuriya T, Chintha R, Harzen A, Colby T, Kamoun S, van der Hoorn RA (2008) Fungal effector protein avr2 targets diversifying defense-related cys proteases of tomato. Plant Cell 20(4):1169–1183
Shan W, Jiang Y, Han J, Wang K (2016) Comprehensive cytological characterization of the Gossypium hirsutum genome based on the development of a set of chromosome cytological markers. Crop J 4:256–265
Shim H, Chasman DI, Smith JD, Mora S, Ridker PM, Nickerson DA, Krauss RM, Stephens M (2015) A multivariate genome-wide association analysis of 10 ldl subfractions, and their response to statin treatment, in 1868 Caucasians. PLoS ONE 10:1–20
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen LL, Kim HS, Pi LY, Holsten T, Gardner J, Wang B, Zhai WX, Zhu LH, Fauquet C (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, xa21. Science 270(5243):1804–1806
Song J, Win J, Tian M, Schornack S, Kaschani F, Ilyas M, van der Hoorn RA, Kamoun S (2009) Apoplastic effectors secreted by two unrelated eukaryotic plant pathogens target the tomato defense protease Rcr3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(5):1654–1659
Song C, Li W, Pei X, Liu Y, Ren Z, He K, Zhang F, Sun K, Zhou X, Ma X, Yang D (2019) Dissection of the genetic variation and candidate genes of lint percentage by a genome-wide association study in upland cotton. Theor Appl Genet 132:1991–2002
Song X, Zhu G, Hou S, Ren Y, Amjid MW, Li W, Guo W (2021) Genome-wide association analysis reveals loci and candidate genes involved in fiber quality traits under multiple field environments in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Front Plant Sci 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.695503
Tan Z, Zhang Z, Sun X, Li Q, Sun Y, Yang P, Wang W, Liu X, Chen C, Liu D, Teng Z, Guo K, Zhang J, Liu D, Zhang Z (2018) Genetic map construction and fiber quality qtl mapping using the cottonSNP80k array in upland cotton. Front Plant Sci 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00225
Team RC (2021) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. r foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria
Turner SD (2018) qqman: an r package for visualizing gwas results using q-q and manhattan plots. J Open Source Softw 25:1–2
Tyagi P, Gore MA, Bowman DT, Campbell BT, Udall JA, Kuraparthy V (2014) Genetic diversity and population structure in the US upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 127:283–295
Ulloa M, Hulse-Kemp AM, De Santiago LM, Stelly DM, Burke JJ (2017) Insights into upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) genetic recombination based on 3 high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism and a consensus map developed independently with common parents. Genom Insights 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178631017735104
Üstün S, Börnke F (2014) Interactions of Xanthomonas type-III effector proteins with the plant ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like pathways. Front Plant Sci 5:1–6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00736
Van Ooijen JW (2018) JoinMap 5, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations of diploid species. Kyazma. https://www.kyazma.nl/index.php/JoinMap/. Accessed 1 March 2022
Van HO, Stam P, Richard GF, Herman VJ, Eck V (2005) Record: a novel method for ordering loci on a genetic linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 112:30–40
VanRaden PM (2008) Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci 91:4414–4423
Voora V, Larrea C, Bermudez S (2020) Global market report: cotton. iisd.org. https://www.iisd.org/system/files/publications/ssi-global-market-report-cotton.pdf. Accessed 01 March 2022
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and qtls. J Heredity 93:77–78
Wallace TP, El-Zik KM (1989) Inheritance of resistance in three cotton cultivars to the hv1 isolate of bacterial blight. Crop Sci 29:1114–1119
Wang Z, Zhang D, Wang X, Tan X, Guo H, Paterson AH (2013) A whole-genome DNA marker map for cotton based on the d-genome sequence of Gossypium raimondii L. G3 (Bethesda) 3(10):1759–1767. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.113.006890
Wang F, Zhang J, Chen Y, Zhang C, Gong J, Song Z, Zhou J, Wang J, Zhao C, Jiao M, Liu A, Du Z, Yuan Y, Fan S, Zhang J (2019) Identification of candidate genes for key fibre‐related qtls and derivation of favourable alleles in Gossypium hirsutum recombinant inbred lines with G. barbadense introgressions. Plant Biotechnol J 18(3):707–720
Wendel JF, Grover CE (2015) Taxonomy and evolution of the cotton genus, Gossypium. Cotton 57(1):25–44
Wheeler TA, Harris T, Bart RS, Isakeit T, Woodward J, Allen TW, Kemerait RC (2021) Response of Xanthomonas citri pv. malvacearum isolates to cotton differing in susceptibility to the bacterium and their predicted type III effectors. Plant Health Progress 23:40–44. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-06-21-0090-RS
Wild MJ, Davière S, Cheminant T, Regnault N, Baumberger D, Heintz R, Baltz P, Genschik Achard P (2012) Thearabidopsis DELLA RGA-LIKE3 is a direct target of MYC2 and modulates jasmonate signaling responses. Plant Cell 24:3307–3319
Wright RJ, Thaxton PM, El-Zik KM, Paterson AH (1998) D-subgenome bias of Xcm resistance genes in tetraploid Gossypium (cotton) suggests that polyploid formation has created novel avenues for evolution. Genet 149:1987–1996
Xian LS, Xue ZS, Tian ZZ (2006) Segregation distortion and its effect on genetic mapping in plants. Chin J Agric Biotechnol 3:163–169
Xiao J, Fang DD, Bhatti M, Hendrix B, Cantrell R (2009) A snp haplotype associated with a gene resistant to Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. malvacearum in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breed 25:593–602
Yang Z, Ge X, Qin W, Sun G, Wang Z, Li Z, Liu J, Wu J, Wang Y (2019) Extensive intraspecific gene order and gene structural variations in upland cotton cultivars. Nat Commun 10:1–13
Yang Z (2013) Fine mapping a bacterial blight resistance gene in the cotton cultivar s295 (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Dissertation, Texas Tech University
Yin L, Zhang H, Tang Z, Xu J, Yin D, Zhang Z, Yuan X, Zhu M, Zhao S, Li X (2021) rMVP: a memory-efficient, visualization-enhanced, and parallel-accelerated tool for genome-wide association study. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2020.10.007
Yu J, Jung S, Cheng C, Lee T, Zheng P, Buble K, Crabb J, Humann J, Hough H, Jones D, Campbell JT, Udall J, Main D (2021) CottonGen: the community database for cotton genomics. Genet Breed Res Plants (Basel) 10:1–16
Yuan Y, Wang X, Wang L, Xing H, Wang Q, Saeed M, Tao J, Feng W, Zhang G, Song X, Sun X (2018) Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes related to seed oil composition and protein content in Gossypium hirsutum L. Front Plant Sci 9:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01359
Zhang K, Kuraparthy V, Fang H, Zhu L, Sood S, Jones DC (2019) High-density linkage map construction and qtl analyses for fiber quality, yield and morphological traits using cottonSNP63K array in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). BMC Genom 20:1–26
Zhang J, Bourland F, Wheeler T, Wallace T (2020) Bacterial blight resistance in cotton: genetic basis and molecular mapping. Euphytica 216:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02630-w
Zhou J, Loh YT, Bressan RA, Martin GB (1995) The tomato gene Pti1 encodes a serine/threonine kinase that is phosphorylated by Pto and is involved in the hypersensitive response. Cell 83(6):925–935
Zhou F, Kurth J, Wei F, Elliott C, Valè G, Yahiaoui N, Keller B, Somerville S, Wise R, Schulze-Lefert P (2001) Cell-autonomous expression of barley Mla1 confers race-specific resistance to the powdery mildew fungus via a rar1-independent signaling pathway. Plant Cell 13(2):337–350
Zhu T, Liang C, Meng Z, Sun G, Meng Z, Guo S, Zhang R (2017) CottonFGD: an integrated functional genomics database for cotton. BMC Plant Biol 17:101–111
Zhu L, Andres RJ, Zhang K, Kuraparthy V (2021) High-density linkage map construction and qtl analysis of fiber quality and lint percentage in tetraploid cotton. Crop Sci 61:3340–3360
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the funding support provided by Cotton Incorporated (CI) and North Carolina Cotton Producers’ Association for the current research and an assistantship to Navin Shrestha. We also thank Kelli Kochan of Texas A&M University for her help with genotyping the lines using the Cotton 63K SNP array. Thanks to Marisa Yoder and Alex Weil at the Danforth Plant Science Center for their help with bacterial infiltrations and cotton planting. We appreciate Josh Udall, James Frelichowski and Janna Love of the Crop Germplasm Research, USDA-ARS, College Station, TX for providing the Upland cotton accessions used in this study.
Funding
Funding support for this research provided by Cotton Incorporated (projects: projects: 19-969 and 19-952) and North Carolina Cotton Producers’ Association (project 19-796NC) to Vasu Kuraparthy, National Science Foundation 2014192836 and 1928344 to Anne Phillips and Rebecca Bart, respectively. Taylor Harris is supported by a NIGMS-funded Initiative for Maximizing Student Development grant to Washington University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAG performed data analysis on the GWAS and bi-parental mapping population. AZP screened the NAM parents for resistance to CBB. TH performed additional screening of NAM parents and the bi-parental mapping population and contributed to writing of the manuscript. NS, KZ and HF developed the RIL population. FB developed and contributed Arkot lines of cotton used in the research. VK and SS genotyped the RILs and DIV panel. RB oversaw the phytopathology experiments, provided general feedback on the mapping and interpretation of data and contributed to writing of the manuscript. VK conceived of the project and oversaw all aspects of the work. SAG and VK co-wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Tianzhen Zhang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gowda, S.A., Shrestha, N., Harris, T.M. et al. Identification and genomic characterization of major effect bacterial blight resistance locus (BB-13) in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 135, 4421–4436 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04229-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04229-2