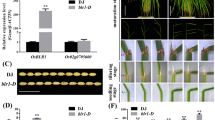
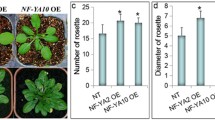
Abstract
Key message
RIP2 serves as a negative regulator of leaf inclination through the coordination of BR signaling in rice.
Abstract
Leaf angle is considered as an important morphological trait in rice. Appropriate leaf angle increases the efficiency of sunlight capture and maintains a high level of photosynthesis, ultimately improving crop yield. Our present study demonstrates that RIP2 encodes a RING finger E3 ligase protein that directly binds to ROLLED AND ERECT LEAF 1 (REL1), a key regulator of leaf morphogenesis. Further studies reveal that RIP2 is extensively involved in leaf inclination through the coordination of BR signaling. Repression of RIP2 led to altered phenotypes, including enlarged leaf inclination and fewer tillers. Conversely, rice overexpressing RIP2 exhibited erect leaves. The double mutant rel1 rip2 displayed phenotypes similar to those of rel1, characterized by rolled leaves. Transcriptome profiling of WT, rel1, rip2, and rel1 rip2 mutants revealed that BR and IAA signaling pathways were impaired in rip2. Moreover, rel1, rip2, and rel1 rip2 were insensitive to BR treatment. In summary, these findings demonstrate that RIP2 serves as a negative regulator of leaf inclination, and therefore, provides an approach for the optimization of an ideal plant type.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai MY, Zhang LY, Gampala SS, Zhu SW, Song WY, Chong K, Wang ZY (2007) Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc Nat Acad Sci 104(34):13839–13844
Best NB, Hartwig T, Budka J, Fujioka S, Johal G, Schulz B, Dilkes BP (2016) nana plant2 encodes a maize ortholog of the Arabidopsis brassinosteroid biosynthesis gene DWARF1, identifying developmental interactions between brassinosteroids and gibberellins. Plant Physiol 171(4):2633–2647
Chen QL, Xie QJ, Gao J, Wang WY, Sun B, Liu BH, Zhu HT, Peng HF, Zhao HB, Liu CH, Wang J, Zhang JL, Zhang GQ, Zhang ZM (2015) Characterization of Rolled and Erect Leaf 1 in regulating leave morphology in rice. J Exp Bot 66(19):6047–6058
Feng ZM, Wu CY, Wang CM, Roh J, Zhang L, Chen J, Zhang SZ, Zhang H, Yang CY, Hu JL, You XM, Liu X, Yang XM, Guo XP, Zhang X, Wu FQ, Terzaghi W, Kim SK, Jiang L, Wan JM (2016) SLG controls grain size and leaf angle by modulating brassinosteroid homeostasis in rice. J Exp Bot 67(14):4241–4253
Hirano K, Yoshida H, Aya K, Kawamura M, Hayashi M, Hobo T, Sato-Izawa K, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M (2017) SMALL ORGAN SIZE 1 and SMALL ORGAN SIZE 2/DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING form a complex to integrate auxin and brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Mol Plant 10(4):590–604
Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2003) A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell 15(12):2900–2910
Hussain MA, Fahad S, Sharif R, Jan MF, Mujtaba M, Ali Q, Ahmad A, Ahmad H, Amin N, Ajayo BS, Sun CB, Gu LY, Ahmad I, Jiang ZM, Hou JC (2020) Multifunctional role of brassinosteroid and its analogues in plants. Plant Growth Regul 92(2):141–156
Jaillais Y, Vert G (2016) Brassinosteroid signaling and BRI1 dynamics went underground. Curr Opin Plant Biol 33:92–100
Jang S, An G, Li HY (2017) Rice leaf angle and grain size are affected by the OsBUL1 transcriptional activator complex. Plant Physiol 173(1):688–702
Ku LX, Zhao WM, Zhang J, Wu LC, Wang CL, Wang PA, Zhang WQ, Chen YH (2010) Quantitative trait loci mapping of leaf angle and leaf orientation value in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 121(5):951–959
Li L, Shi ZY, Li L, Shen GZ, Wang XQ, An LS, Zhang JL (2010) Overexpression of ACL1 (abaxially curled leaf 1) increased bulliform cells and induced abaxial curling of leaf blades in rice. Molecular Plant 3(5):807–817
Li X, Wu PF, Lu Y, Guo SY, Zhong ZJ, Shen RX, Xie QJ (2020) Synergistic interaction of phytohormones in determining leaf angle in crops. Int J Mol Sci 21(14):5052
Lim SD, Cho HY, Park YC, Ham DJ, Lee JK, Jang CS (2013) The rice RING finger E3 ligase, OsHCI1, drives nuclear export of multiple substrate proteins and its heterogeneous overexpression enhances acquired thermotolerance. J Exp Bot 64(10):2899–2914
Liu KY, Cao J, Yu KH, Liu XY, Gao YJ, Chen Q, Zhang WJ, Peng HR, Du JK, Xin MM, Hu ZR, Guo WL, Rossi V, Ni ZF, Sun QX, Yao YY (2019) Wheat TaSPL8 modulates leaf angle through auxin and brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Physiol 181(1):179–194
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):1–21
Luo XY, Zheng JS, Huang RY, Huang YM, Wang HC, Jiang LR, Fang XJ (2016) Phytohormones signaling and crosstalk regulating leaf angle in rice. Plant Cell Rep 35(12):2423–2433
Nam KH, Li JM (2002) BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110(2):203–212
Nolan TM, Vukašinović N, Liu DR, Russinova E, Yin YH (2020) Brassinosteroids: multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell 32(2):295–318
Oard JH, Linscombe SD, Braverman MP, Jodari F, Blouin DC, Leech M, Kohli A, Vain P, Cooley JC, Christou P (1996) Development, field evaluation, and agronomic performance of transgenic herbicide resistant rice. Mol Breeding 2(4):359–368
Ohnishi T, Godza B, Watanabe B, Fujioka S, Hategan L, Ide K, Shibata K, Yokota T, Szekeres M, Mizutani M (2012) CYP90A1/CPD, a brassinosteroid biosynthetic cytochrome P450 of Arabidopsis, catalyzes C-3 oxidation. J Biol Chem 287(37):31551–31560
Peng YC, Chen LL, Li SJ, Zhang YY, Xu R, Liu ZP, Liu WX, Kong JJ, Huang XH, Wang YC, Cheng BJ, Zheng LY, Li YH (2018) BRI1 and BAK1 interact with G proteins and regulate sugar-responsive growth and development in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 9(1):1–13
Qiao SL, Sun SY, Wang LL, Wu ZH, Li CX, Li XM, Wang Tao, Leng LN, Tian WS, Lu TG, Wang XL (2017) The RLA1/SMOS1 transcription factor functions with OsBZR1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and rice architecture. Plant Cell 29(2):292–309
Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2006) Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nature Biotechnol 24(1):105–109
Sinclair TR, Horie T (1989) Leaf nitrogen, photosynthesis, and crop radiation use efficiency: a review. Crop Sci 29(1):90–98
Sinclair TR, Sheehy JE (1999) Erect leaves and photosynthesis in rice. Science 283(5407):1456–1456
Sun SY, Chen DH, Li XM, Qiao SL, Shi CN, Li CX, Shen HY, Wang XL (2015) Brassinosteroid signaling regulates leaf erectness in Oryza sativa via the control of a specific U-type cyclin and cell proliferation. Dev Cell 34(2):220–228
Takeno K, Pharis RP (1982) Brassinosteroid-induced bending of the leaf lamina of dwarf rice seedlings: an auxin-mediated phenomenon. Plant Cell Physiol 23(7):1275–1281
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7(3):562–578
Wada K, Marumo S, Ikekawa N, Morisaki M, Mori K (1981) Brassinolide and homobrassinolide promotion of lamina inclination of rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 22(2):323–325
Wang XF, Goshe MB, Soderblom EJ, Phinney BS, Kuchar JA, Li J, Asami T, Yoshida S, Huber SC, Clouse SD (2005) Identification and functional analysis of in vivo phosphorylation sites of the Arabidopsis BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE1 receptor kinase. Plant Cell 17(6):1685–1703
Wang L, Xu YY, Zhang C, Ma QB, Joo SH, Kim SK, Xu ZH, Chong K (2008) OsLIC, a novel CCCH-type zinc finger protein with transcription activation, mediates rice architecture via brassinosteroids signaling. PLoS ONE 3(10):e3521
Wang K, Li MQ, Chang YP, Zhang B, Zhao QZ, Zhao WL (2020) The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor OsBLR1 regulates leaf angle in rice via brassinosteroid signalling. Plant Mol Biol 102(6):589–602
Wu XR, Tang D, Li M, Wang KJ, Cheng ZK (2013) Loose Plant Architecture1, an INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein involved in shoot gravitropism, regulates plant architecture in rice. Plant Physiol 161(1):317–329
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, Tanksley SD (1996) Identification of QTLs affecting traits of agronomic importance in a recombinant inbred population derived from a subspecific rice cross. Theor Appl Genet 92(2):230–244
Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2000) Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 12(9):1591–1605
Zhang Y, Su JB, Duan S, Ao Y, Dai JR, Liu J, Wang P, Li YG, Liu B, Feng DR, Wang JF, Wang HB (2011) A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods 7(1):1–14
Zhang RJ, Xia XJ, Lindsey K, da Rocha PSF (2012a) Functional complementation of dwf4 mutants of Arabidopsis by overexpression of CYP724A1. J Plant Physiol 169(4):421–428
Zhang C, Xu YY, Guo SY, Zhu JY, Huan Q, Liu HH, Wang Lei, Luo GZ, Wang XJ, Chong K (2012b) Dynamics of brassinosteroid response modulated by negative regulator LIC in rice. PLoS Genet 8(4):e1002686
Zhang C, Bai MY, Chong K (2014) Brassinosteroid-mediated regulation of agronomic traits in rice. Plant Cell Rep 33(5):683–696
Zhang XQ, Sun J, Cao XF, Song XW (2015) Epigenetic Mutation of RAV6 Affects Leaf Angle and Seed Size in Rice. Plant Physiol 169(3):2118–2128
Zhang G, Song XG, Guo HY, Wu Y, Chen XY, Fang RX (2016) A small G protein as a novel component of the rice brassinosteroid signal transduction. Mol Plant 9(9):1260–1271
Zhao SQ, Hu J, Guo LB, Qian Q, Xue HW (2010) Rice leaf inclination2, a VIN3-like protein, regulates leaf angle through modulating cell division of the collar. Cell Res 20(8):935–947
Zhao SQ, Xiang JJ, Xue HW (2013) Studies on the rice LEAF INCLINATION1 (LC1), an IAA–amido synthetase, reveal the effects of auxin in leaf inclination control. Mol Plant 6(1):174–187
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2018B020202012), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (31671645).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ and ZZ designed the project; QZ, GL, JJ, and JL performed the experiments; QZ, GL, JZ, HP, WW, and ZZ analyzed and interpreted the data; QZ, WW and ZZ wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Matthias Wissuwa.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Liu, G., Jin, J. et al. RIP2 interacts with REL1 to control leaf architecture by modulating brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Theor Appl Genet 135, 979–991 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-04011-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-04011-w