Abstract
Key message
SiDWF1 encodes a gibberellin receptor GID1B-like protein controlling the internode length and plant height in sesame.
Abstract
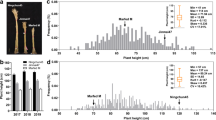
Sesame is a high-height crop. Here we systematically analyzed the morphological and genetic characters of the sesame dwarf mutant dw607 (dwf1 type). The plant height and the internode length of dw607 significantly declined, while the thousand seed weight (TSW) significantly increased (P < 0.01). The cell size of stem parenchyma and pith tissue reduced, and vascular bundle cells and parenchyma tissue arranged much tighter in the dwarf mutant. Based on the cross-population association mapping of a RIL population of the cross ‘dw607 (dwf1) × 15N41 (wt type),’ the target interval linked to the short internode length was located on C9.scaffold2 of SiChr.4 in sesame. We further screened the 58 variants using the genomic variant data of 824 germplasm and BSA DNA pools and determined the target gene Sidwf1. The SNP mutation of C1057 to T1057 resulted in the amino acid change of P150 (proline) to S150 (serine) in SiDWF1. SiDWF1 gene allele is 1,638 bp and encodes a gibberellin receptor GID1B-like protein. Transcription profile assay reflected that Sidwf1 is highly expressed in leaf, stem, bud, and capsule tissues. The dynamic variation in endogenous GA3 content in dw607 and the wild type was also monitored in this study. The results revealed the molecular genetic mechanism of the internode length and plant height trait in sesame for the first time. The findings supply the theoretical and material basis for developing the marker-assisted selection (MAS) breeding in sesame.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The cDNA sequence of SiDWF1 gene was available in NCBI with Accession No. KY649623. The BSA data of the dwf1 and the wild type were available in NCBI under bioproject PRJNA555174 with SRA Accession No. SRR9733676-SRR9733681.
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- BR:
-
Brassinosteroid
- BSA:
-
Bulked segregant analysis
- DAS:
-
Days after sowing
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- EMS:
-
Ethyl methanesulfonate
- Ep:
-
Epidermis
- FAA:
-
Formalin–glacial acetic acid–alcohol
- GAs:
-
Gibberellins
- GID1:
-
Gibberellin-insensitive dwarf 1
- GLM:
-
General linear model
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association studies
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- InDel:
-
Insertion–deletion
- LG:
-
Linkage group
- JA:
-
Jasmonate
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- NGS:
-
Next-generation sequencing technology
- NR:
-
Non-redundant
- PC:
-
Parenchyma cell
- PE:
-
Paired end
- Pi:
-
Pith
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- TSW:
-
Thousand seed weight
- VC:
-
Vascular bundle cells
References
Aleman L, Kitamura J, Abdel-mageed H, Lee J, Sun Y, Nakajima M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M, Allen RD (2008) Functional analysis of cotton orthologs of GA signal transduction factors GID1 and SLR1. Plant Mol Biol 68:1–16
Ashikari M, Wu J, Yano M, Sasaki T, Yoshimura A (1999) Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant gene Dwarf 1 encodes the alpha-subunit of GTP-binding protein. P Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10284–10289
Avila LM, Cerrudo D, Swanton C, Lukens L (2016) Brevis plant1, a putative inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, is required for internode elongation in maize. J Exp Bot 67(5):1577–1588
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120
Chandler PM, Harding CA, Ashton AR, Mulcair MD, Dixon NE, Mander LN (2008) Characterization of gibberellin receptor mutants of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Mol Plant 1:285–294
Chen J, Zhao H, Zheng X, Liang K, Guo Y, Sun X (2017) Recent amplification of Osr4 LTR-retrotransposon caused rice D1 gene mutation and dwarf phenotype. Plant Divers 39(2):73–79
Feng Y, Yin Y, Fei S (2015) Down-regulation of BdBRI1, a putative brassinosteroid receptor gene produces a dwarf phenotype with enhanced drought tolerance in Brachypodium distachyon. Plant Sci 234:163–173
Gazara RK, Moharana KC, Bellieny-Rabelo D, Venancio TM (2018) Expansion and diversification of the gibberellin receptor GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 (GID1) in land plants. Plant Mol Biol 97(4–5):435–449
Griffiths J, Murase K, Rieu I, Zentella R, Zhang Z, Powers SJ, Gong F, Phillips AL, Hedden P, Sun T, Thomas SG (2006) Genetic characterization and functional analysis of the GID1 gibberellin receptors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:3399–3414
Hirano K, Nakajima M, Asano K, Nishiyama T, Sakakibara H, Kojima M, Katoh E, Xiang H, Tanahashi T, Hasebe M, Banks JA, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M (2007) The GID1-mediated gibberellin perception mechanism is conserved in the Lycophyte Selaginella moellendorffii but not in the Bryophyte Physcomitrella patens. Plant Cell 19:3058–3079
Hirano K, Yoshida H, Aya K, Kawamura M, Hayashi M, Hobo T, Sato-lzawa K, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M (2017) SMALL ORGAN SIZE 1 and SMALL ORGAN SIZE 2/DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING form a complex to integrate auxin and brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Mol plant 10(4):590–604
Jimoh WA, Aroyehun HT (2011) Evaluation of cooked and mechanically defatted sesame (Sesamum indicum) seed meal as a replacer for soybean meal in the diet of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Turkish J Fish Aquat Sci 11(2):185–190
Kurotani K, Hattori T, Takeda S (2015) Overexpression of a CYP94 family gene CYP94C2b increases internode length and plant height in rice. Plant Signal Behav 10(7):e1046667
Langham DR (2008) Growth and development of sesame. American Sesame Grower Association, San Antonio, p 44
Langham DR, Wiemers T, Janick J, Whipkey A (2002) Progress in mechanizing sesame in the US through breeding. In: Janick J (ed) Trends in new crops and new uses, ASHS Press, Alexandria, pp:157–173.
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinfomatics 25(14):1754–1760
Li A, Yang W, Li S, Liu D, Guo X, Sun J, Zhang A (2013) Molecular characterization of three GIBBERELLIN-INSENSITIVE DWARF1 homologous genes in hexaploid wheat. Plant Physiol 170:432–443
Li J, Ali SA, Xiao G, Chen F, Yuan L, Gu R (2018a) Phenotypic characterization and genetic map of the dwarf mutant m34 in maize. J Integr Agr 17:60345–60347
Li Z, Guo Y, Ou L, Hong H, Wang J, Liu Z, Guo B, Zhang L, Qiu L (2018b) Identification of the dwarf gene GmDW1 in soybean (Glycine max L.) by combining mapping-by-sequencing and linkage analysis. Theor Appl Genet 131:1001–1016
Liang H, Wang C, Li Z, Luo XZ, Zou G (2008) Improvement of the silver-stained technique of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Hereditas 30(10):1379–1382
Makinde FM, Akinoso R (2013) Nutrient composition and effect of processing treatments on antinutritional factors of Nigerian sesame (Sesamum indicum Linn) cultivars. Int Food Res J 20(5):2293–2300
Monna L, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y (2002) Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: rice “green revolution gene” encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis. DNA Res 9(1):11–17
Peng J, Richards DE, Hartley NM, Murphy GP, Devos KM, Flintham JE, Beales J, Fish LJ, Worland AJ, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape JW, Gale MD, Harberd NP (1999) ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 400(6741):256–261
Poplin R, Ruano-Rubio V, DePristo MA, Fennell TJ, Carneiro MO, Van der Auwera GA, Kling DE, Gauthier LD, Levy-Moonshine A, Roazen D, Shakir K, Thibault J, Chandran S, Whelan C, Lek M, Gabriel S, Daly MJ, Neale B, MacArthur DG, Banks E (2017) Scaling accurate genetic variant discovery to tens of thousands of samples. BioRxiv (https://doi.org/10.1101/201178).
Prakash K, Naik SN (2014) Bioactive constituents as a potential agent in sesame for functional and nutritional application. J Bioresour Eng Technol 1:48–66
Rebetzke GJ, Ellis MH, Bonnett DG, Condon AG, Falk D, Richiards RA (2011) The Rht13 dwarfing gene reduces peduncle length and plant height to increase grain number and yield of wheat. Field Crops Res 124(3):323–331
Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush GS, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2002) Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 416(6882):701–702
Satish RG (2013) Genetic analysis of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) for traits related to moisture stress tolerance with reference to root traits. Doctoral dissertation, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bengaluru
Sene B, Sarr F, Sow MS, Diouf D, Niang M, Traore D (2017) Physico-chemical composition of the sesame variety (Sesamum indicum L.) 32–15 and characterization of its derived products (seeds, oil and oilcake) in Senegal. Food Sci Qual Manag 65:5–10
Sharmila V, Ganeshi SK, Gunasekaran M (2007) Generation mean analysis for quantitative traits in sesame (sesamum indicum l.) crosses. Genet Mol Biol 30(1):80–84
Suzuki H, Park S, Okubo K, Kitamura J, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Iuchi S, Katoh E, Kobayashi M, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M, Asami T, Nakajima M (2009) Differential expression and affinities of Arabidopsis gibberellin receptors can explain variation in phenotypes of multiple knock-out mutants. Plant J 60:48–55
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Thomas SG (2017) Novel Rht-1 dwarfing genes: tools for wheat breeding and dissecting the function of DELLA proteins. J Exp Bot 68(3):354–358
Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Nakajima M, Itoh H, Katoh E, Kobayashi M, Chow TY, Hsing YI, Kitano H, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M (2005) GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin. Nature 437:693–698
Wang L, Xia Q, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Zhu X, Li D, Ni X, Gao Y, Xiang H, Wei X, Yu J, Quan Z, Zhang X (2016) Updated sesame genome assembly and fine mapping of plant height and seed coat color QTLs using a new high-density genetic map. BMC Genomics 17(1):31
Wang H, Zhang H, Ma Q, Wei L, Ju M, Li C, Duan Y, Miao H (2017a) Optimization of EMS mutagenesis condition and screening of mutants in sesame. J Henan Agri Sci 46(1):36–41
Wang N, Xing Y, Lou Q, Feng P, Liu S, Zhu M, Yin W, Fang S, Lin Y, Zhang T, Sang X, He G (2017b) Dwarf and short grain 1, encoding a putative U-box protein regulates cell division and elongation in rice. J Plant Physiol 209:84–94
Wei L, Miao H, Zhao R, Han X, Zhang T, Zhang H (2013) Identification and testing of reference genes for Sesame gene expression analysis by quantitative real-time PCR. Planta 237(3):873–889
Wei L, Miao H, Li C, Duan Y, Niu J, Zhang T, Zhao Q, Zhang H (2014) Development of SNP and InDel markers via de novo transcriptome assembly in Sesamum indicum L. Mol Breed 34(4):2205–2217
Wei X, Liu K, Zhang Y, Feng Q, Wang L, Zhao Y, Li D, Zhao Q, Zhu X, Zhu X, Li W, Fan D, Gao Y, Lu Y, Zhang X, Tang X, Zhou C, Zhu C, Liu L, Zhong R, Tian Q, Wen Z, Weng Q, Han B, Huang X, Zhang X (2015) Genetic discovery for oil production and quality in sesame. Nat Commun 6:8609
Yan J, Liao X, He R, Zhong M, Feng P, Li X, Tang D, Liu X, Zhao X (2017) Ectopic expression of GA 2-oxidase 6 from rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) causes dwarfism, late flowering and enhanced chlorophyll accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Bioch 111:10–19
Zeng X, Zhu L, Chen Y, Qi L, Pu Y, Wen J, Yi B, Shen J, Ma C, Tu J, Fu T (2011) Identification, fine mapping and characterisation of a dwarf mutant (bnaC.dwf) in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 122:421–428
Zhang H, Wang X, Wang H, Wei S (2012) Sesame production technology. Henan People Press, Zhengzhou, p p203
Zhang H, Miao H, Wang L, Qu L, Liu H, Wang Q, Yue M (2013) Genome sequencing of the important oilseed crop Sesamum indicum L. Genome Biol 14(1):401
Zhang H, Miao H, Li C, Wei L, Duan Y, Ma Q, Kong J, Xu F, Chang S (2016) Ultra-dense SNP genetic map construction and identification of SiDt gene controlling the determinate growth habit in Sesamum indicum L. Sci Rep 6:31556
Zhang H, Miao H, Wei L, Li C, Duan Y, Xu F, Qu W, Zhao R, Ju M, Chang S (2018) Identification of a SiCL1 gene controlling leaf curling and capsule indehiscence in sesame via cross-population association mapping and genomic variants screening. BMC Plant Biol 18(1):296
Zhang H, Miao H, Ju M (2019) Potential for adaption to climate change through genomic breeding in sesame. In: Kole C (ed) Genomic designing of climate-smart oilseed crops. Springer press, USA, pp 371–440
Zhao R, Miao H, Song W, Chen C, Zhang H (2018) Identification of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) chromosomes using the BAC-FISH system. Plant Biol 20(1):85–92
Zhong J, Peng Z, Peng Q, Cai Q, Peng W, Chen M, Yao J (2018) Regulation of plant height in rice by the Polycomb group genes OsEMF2b, OsFIE2 and OsCLF. Plant Sci 267:157–167
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Laboratory of Specific Oilseed Crops Genomics of Henan Province. This work was financially supported by the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-14), the Plan for Scientific Innovation Talent of Henan Province (184200510002), the Key Project of Science and Technology in Henan Province (151100111200), the Henan Province Specific Professor Position Program (SPPP2016), the Distinguished Professor Program of Institutions of Higher Learning in Henan Province (DPPIHL2017), the Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province (ISTTCPHP2016), the Henan Natural Science Foundation (162300410159), and the International Cooperation and Exchanges Project of Henan Province (182102410040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZH conceived the technical route and guided the manuscript for publishing. MH guided the experiments, performed the data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. LC and DY conducted the main data analysis and experiments. WL and JM performed the genetic experiments and participated in result validation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Matthew N Nelson.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2019_3441_MOESM1_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary Table 1 Growth profile comparison of dw607 and Yuzhi11. * Data are collected at Yuanyang experimental station in 2013; Supplementary Table 2 Variant information of the candidate interval controlling the short internode length trait in sesame; Supplementary Table 3 Variants information of 824 sesame germplasm accessions in target region; Supplementary Table 4 Information of candidate variants screened using genome resequencing data of 824 sesame germplasm accessions; Supplementary Table 5 Genome re-sequencing information of the BSA pools for internode length trait. a: The genome coverage is calculated based on the sesame genome size of 354 Mb estimated by K-mer (Zhang et al. 2013); Supplementary Table 6 Information of the five candidate variants for short internode length trait in sesame; Supplementary Table 7 Primer pair information of the SNP marker design of Sidwf1 gene alleles; Supplementary Table 8 Primer pair information of the cDNA and DNA sequences of SiDWF1 Supplementary file1 (XLSX 21888 kb)
122_2019_3441_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of plant height of dw607 and Yuzhi 11 during cycle life. Data are collected at Yuanyang experimental station in 2013; Supplementary Figure 2 Amplification validation of the SiSNPdwf1 marker using the test population and germplasm accessions. M: DNA marker; Lane 1–10: F2-3 individuals with short internode length trait (dwf1 type); Lane 11–20: F2-3 individuals with normal internode length trait (wt); Lane 21–40: 20 sesame accessions with normal internode length trait (wt); Supplementary Figure 3 Dynamic content variation of GA3, IAA, ABA, BR and ZR in shoot tip, root tip, and leaf of dw607 and Yuzhi11. a-c: Dynamic variation of GA3 content in shoot tip, root tip, and leaf of dw607 and Yuzhi11, respectively; d-f: Dynamic variation of IAA content in shoot tip, root tip, and leaf of dw607 and Yuzhi11, respectively; g-i: indicate the dynamic variation of ABA content in shoot tip, root tip, and leaf of dw607 and Yuzhi11, respectively; j-l: Dynamic variation of BR content in shoot tip, root tip, and leaf of dw607 and Yuzhi11, respectively Supplementary file2 (PDF 532 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, H., Li, C., Duan, Y. et al. Identification of a Sidwf1 gene controlling short internode length trait in the sesame dwarf mutant dw607. Theor Appl Genet 133, 73–86 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03441-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03441-x