Abstract
Key message
Sequence analysis revealed that an SNP (A1855G) in CsBADH of cucumber accession PK2011T202 causes amino acid change in a highly conserved motif, Y163C. Gene mapping showed association between the SNP and the fragrance.
Abstract
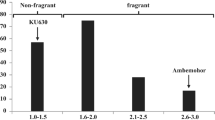
Pandan-like fragrance is a value-added trait in several food crops such as rice, vegetable soybean and sorghum. The fragrance is caused by the volatile chemical 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP). Mutation(s) in betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (BADH2; also known as aminoaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) gene causes defective BADH2 and results in biosynthesis of 2AP. Recently, cucumber cultivars possessing pandan-like fragrance were discovered in Thailand. In this study, we report an association between CsBADH and the fragrance in cucumber accession “PK2011T202”. Gene expression analysis of CsBADH in leaves of PK2011T202 and “301176” (non-fragrant) at various growth stages revealed that CsBADH was expressed in both accessions. Sequence comparison of CsBADH showed that PK2011T202 possesses a single base substitution (A1855G) in exon 5 which causes an amino acid change in a highly conserved motif of BADH, Y163C. Single nucleotide-amplified polymorphism markers were developed to detect the SNP polymorphism between the wild-type and fragrance alleles. Since CsBADH is located on chromosome 1, quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping was conducted for this chromosome using an F2 and a backcross populations developed from the cross between PK2011T202 and 301176. QTL analysis in both populations showed that the major QTL for fragrance, qFgr, was co-localized with the CsBADH. We concluded that the defect function of CsBADH is responsible for fragrance in cucumber PK2011T202.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarawathi Y, Singh R, Singh AK, Singh VP, Mohapatra T, Sharma TR, Singh NK (2008) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for basmati quality traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 21:49–65
Arikit S, Yoshihashi T, Wanchana S, Uyen TT, Huong NTT, Wongpornchai S, Vanavichit A (2010) Deficiency in the amino aldehyde dehydrogenase encoded by GmAMADH2, the homologue of rice Os2AP, enhances 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline biosynthesis in soybeans (Glycine max L.). Plant Biotechnol J 9:75–87
Arumanagathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:229–241
AVRDC (2003) AVRDC progress report 2002. AVRDC-The World Vegetable Center, Shanhua
Ayyangar GNR (1938) Studies in sorghum. J Madras Univ 11:131–143
Berner DK, Hoff BJ (1986) Inheritance of scent in American long grain rice. Crop Sci 26:876–878
Bradbury LMT, Fitzgerald TL, Henry RJ, Jin QS, Waters DLE (2005) The gene for fragrance in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 3:363–370
Bradbury LMT, Gillies SA, Brushett DJ, Waters DLE, Henry RJ (2008) Inactivation of an aminoaldehyde dehydrogenase is responsible for the fragrance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 68:443–449
Buttery RG, Ling LC, Juliano BO, Turnbaugh JG (1983) Cooked rice aroma and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline. J Agric Food Chem 31:823–826
Chen S, Yang Y, Shi W, Ji Q, He F, Zhang Z, Cheng Z, Liu X, Xu M (2008) Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. Plant Cell 20:1850–1861
de Wilde WJJO, Duyfjes BEE (2010) Cucumis sativus L. forma hardwickii (Royle) W.J. de Wilde & Duyfjes and feral forma sativus. Thai For Bull (BOT) 38:98–107
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie JM, Gascuel O (2008) Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36:465–469
Díaz-Sánchez ÁG, González-Segura L, Mújica-Jiménez C, Rudiño-Piñera E, Montiel C, Martínez-Castilla LP, Muñoz-Clares RA (2012) Amino acid residues critical for the specificity for betaine aldehyde of the plant ALDH10 isoenzyme involved in the synthesis of glycine betaine. Plant Physiol 158:1570–1582
Drenkard E, Richter BG, Rozen S, Stutius LM, Angell NA, Mindrinos M, Cho RJ, Oefner PJ, Davis RW, Ausubel FM (2000) A simple procedure for the analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms facilitates map-based cloning in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:1483–1492
Fitzgerald TL, Waters DLE, Henry RJ (2008) The effect of salt on betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase transcript levels and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline concentration in fragrant and non-fragrant rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Sci 174:539–546
Food and Agriculture Organization (2013) FAOSTAT. http://faostat.fao.org. Accessed 5 March 2014
Fushimi T, Masuda R (2001) 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline concentration of the vegetable soybean. In: Lumpkin T, Shanmugasundaram S (eds) Proceeding of the 2nd international vegetable soybean conference. Washington State University, Pullman, p 39
Huang TC, Teng CH, Chang JL, Chuang HS, Ho CT, Wu ML (2008) Biosynthetic mechanism of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and its relationship with Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid and methylglyoxal in aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.) callus. J Agric Food Chem 56:7399–7404
Huang S, Li R, Zhang Z, Li L, Gu X, Fan Lucas WJ, Wang X, Xie B, Ni P, Ren Y, Zhu H, Li J, Lin K, Jin W, Fei Z, Li G, Staub J, Kilian A, van der Vossen EAG, Wu Y, Guo J, He J, Jia Z, Ren Y, Tian G, Lu Y, Ruan J, Qian W, Wang M, Huang Q, Li B, Xuan Z, Cao J, Asan WZ, Zhang J, Cai Q, Bai Y, Zhao B, Han Y, Li Y, Li X, Wang S, Shi Q, Liu S, Cho WK, Kim J, Xu Y, Heller-Uszynska K, Miao H, Cheng Z, Zhang S, Wu J, Yang Y, Kang H, Li M, Liang H, Ren X, Shi Z, Wen M, Jian M, Yang H, Zhang G, Yang Z, Chen R, Liu S, Li J, Ma L, Liu H, Zhou Y, Zhao J, Fang X, Li G, Fang L, Li Y, Liu D, Zheng H, Zhang QN, Li Z, Yang G, Yang S, Bolund L, Kristiansen K, Zheng H, Li S, Zhang X, Yang H, Wang J, Sun R, Zhang B, Jiang S, Wang J, Du Y, Li S (2009) The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat Genet 41:1275–1281
Juwattanasomran R, Somta P, Chankaew S, Shimizu T, Wongpornchai S, Kaga A, Srinives P (2011) A SNP in GmBADH2 gene associates with fragrance in vegetable soybean variety ‘‘Kaori’’ and SNAP marker development for the fragrance. Theor Appl Genet 122:533–541
Juwattanasomran R, Somta P, Kaga A, Chankaew S, Shimizu T, Sorajjapinun W, Srinives P (2012) Identification of a new fragrance allele in soybean and development of its functional marker. Mol Breed 29:13–21
Kirch HH, Schlingensiepen S, Kotchoni S, Sunkar R, Bartels D (2005) Detailed expression analysis of selected genes of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene superfamily in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 57:315–332
Kopečný D, Tylichová M, Snegaroff J, Popelková H, Šebela M (2011) Carboxylate and aromatic active-site residues are determinants of high-affinity binding of ω-aminoaldehydes to plant aminoaldehyde dehydrogenases. FEBS J278:3130–3139
Kopečný D, Končitíková R, Tylichová M, Vigouroux A, Moskalíková H, Soural M, Šebela M, Moréra S (2013) Plant ALDH10 family: identifying critical residues for substrate specificity and trapping a thiohemiacetal intermediate. J Biol Chem 288:9491–9507
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kovach MJ, Calingacion MN, Fitzgerald SR McCough (2009) The origin and evolution of fragrance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14444–14449
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg LA (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408
Lodhi MA, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1994) A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars and Vitis species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 12:6–13
Lorieux M, Petrov M, Huang N, Guiderdoni E, Ghesquiere A (1996) Aroma in rice: genetic analysis of a quantitative trait. Theor Appl Genet 93:1145–1151
Murty DS, Nicodemus KD, House LR (1982) Inheritance of basmati and dimpled seed in sorghum. Crop Sci 22:1080–1082
Niu X, Tang W, Huang W, Ren G, Wang Q, Luo D, Xiao Y, Yang S, Wang F, Lu BL, Gao F, Lu T, Liu Y (2008) RNAi-directed downregulation of OsBADH2 results in aroma (2-acetyl-1-pyrroline) production in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 8:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-8-100
Pramnoi P, Somta P, Chankaew S, Juwattanasomran R, Srinives P (2013) A single recessive gene controls fragrance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Genet 92:147–149
R Development Core Team (2010) A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Ren Y, Zhang Z, Liu J, Staub JE, Han Y, Cheng Z, Li X, Lu J, Miao H, Kang H, Xie B, Gu X, Wang X, Du Y, Jin W, Huang S (2009) An integrated genetic and cytogenetic map of the cucumber genome. PLoS ONE 4:e5795
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 365–386
Shao GN, TangA Tang SQ, Luo J, Jiao GA, Wu JL, Hu PS (2011) A new deletion mutation of fragrant gene and the development of three molecular markers for fragrance in rice. Plant Breed 130:172–176
Shi WW, Yang Y, Chen SH, Xu ML (2008) Discovery of a new fragrance allele and the development of functional markers for the breeding of fragrant rice varieties. Mol Breed 22:185–192
Somta P, Musch W, Kongsamai B, Chanprame S, Nakasathien S, Toojinda T, Sorajjapinun W, Seehaluk W, Tragoonrung S, Srinives P (2008) New microsatellite markers isolated from mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek). Mol Ecol Resour 8:1155–1157
Sood BG, Siddiq EA (1978) A rapid technique for scent determination in rice. Indian J Genet 38:268–275
Wanchana S (2005) Identification of genes controlling grain aroma and amylose content for positional cloning and marker-assisted selection program in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Kasetsart University, Thailand
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics. North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Wu ML, Chou KL, Wu CR, Chen JK, Huang TC (2009) Characterization and the possible formation mechanism of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline in aromatic vegetable soybean. J Food Sci 74:192–197
Yundaeng C, Somta P, Tangphatsornruang S, Wongpornchai S, Srinives P (2013) Gene discovery and functional marker development for fragrance in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). Theor Appl Genet 126:2897–2906
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Scholarship and the TRF Research Career Development Grant (RSA5580057) both of which co-funded by the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) and Kasetsart University to P. Somta and C. Yundaeng.
Ethical standards and conflict of interest
All the experiments performed in this study comply with the current laws of Thailand. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. J. Bervillé.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yundaeng, C., Somta, P., Tangphatsornruang, S. et al. A single base substitution in BADH/AMADH is responsible for fragrance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.), and development of SNAP markers for the fragrance. Theor Appl Genet 128, 1881–1892 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2554-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2554-5