Abstract
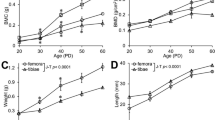
Previous studies have shown that aflatoxin B1 (AfB1) inhibits androgen biosynthesis as a result of its ability to form a high-affinity complex with the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. The results of the present study demonstrate the postnatal effects of in utero exposure to AfB1 in the rat. Pregnant Wistar rats were given 10, 20, or 50 μg AfB1/kg body weight daily from gestation day (GD) 12 to GD 19. At parturition, newborns were observed for clinical signs and survival. All animals were born alive and initially appeared to be active. Male pups from control and AfB1-exposed animals were weaned and maintained up to postnatal day (PD) 100. Litter size, birth weight, sex ratio, survival rate, and crown–rump length of the pups were significantly decreased in AfB1-exposed rats when compared to controls. Elapsed time (days) for testes to descend into the scrotal sac was significantly delayed in experimental pups when compared to control pups. Behavioral observations such as cliff avoidance, negative geotaxis, surface rightening activity, ascending wire mesh, open field behavior, and exploratory and locomotory activities were significantly impaired in experimental pups. Body weights and the indices of testis, cauda epididymis, prostate, seminal vesicles, and liver were significantly reduced on PD 100 in male rats exposed to AfB1 during embryonic development when compared with controls. Significant reduction in the testicular daily sperm production, epididymal sperm count, and number of viable, motile, and hypo-osmotic tail coiled sperm was observed in experimental rats. The levels of serum testosterone and activity levels of testicular hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases were significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner with a significant increase in the serum follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone in experimental rats. Deterioration in the testicular and cauda epididymal architecture was observed in experimental rats. The results of fertility studies revealed a significant decrease in the mating index in experimental rats with an increase in the pre- and post-implantation losses in rats mated with prenatal AfB1-exposed males, indicating poor male reproductive performance. These results indicate that in utero exposure to AfB1 severely compromised postnatal development of neonatal rats, and caused a delay in testes descent and reduction in steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis that were accomplished by suppressed reproduction at adulthood.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrazzaq YM, Osman N, Yousif ZM, Trad O (2004) Morbidity in neonates of mothers who have ingested aflatoxins. Ann Trop Pedtri 24:145–151
Agnes VF, Akbarsha MA (2003) Spermatotoxic effect of aflatoxin B (1) in albino mouse. Food Chem Toxicol 41:119–130
Avinash W, Lakkawar SK, Chattopaudhyay TJ (2004) Experimental aflatoxin B1 toxicosis in young rabbits—a clinical and pathoanatomical study. Slov Vet Res 41:73–81
Bashandy SAE, Galil MAE, Bashandy MAF (1994) Effect of dietary aflatoxin and vitamin C on gonadal activity in male rats. Bull Sci 5:697–707
Belsey MA, Moghissi KA, Eliasson R, Paulsen CA, Callegos AJ, Prasad MRN (1980) Laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and semen cervical mucus interaction. Press Concern, Singapore
Benetti F, Andrade de Araujo P, Sanvitto GL, Lucion AB (2007) Effects of neonatal novelty exposure on sexual behavior, fear, and stress-response in adult rats. Dev Psychol 49:258–264
Bennet JW, Klich M (2003) Mycotoxins. Clin Microbiol Rev 16:497–516
Bergmayer HU (1974) Methods of enzymatic analysis. pp 447–489. Weinheim/New York: Verlag Chemie/Academic Press
Blazak WF, Treinen KA, Juniewicz PE (1993) Application of testicular sperm head counts in the assessment of male reproductive toxicity. In: Chapin RE, Heindel JJ (eds) Methods in toxicology, male reproductive toxicology. Academic, San Diego, CA, pp 86–94
Blount WP (1961) Turkey X disease. Turkeys 52:55–61
Brancraft JD, Stevens A (1982) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 2nd edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York
Brevini TA, Zanetto SB, Cillo F (2005) Effects of endocrine disruptors on developmental and reproductive functions. current drug targets. Immune Endocr Metab Disord 5:1–10
Cheeke PK, Shull LR (1985) Natural toxicants in feeds and poisonous plants. Avi Publishing Company, ING, Westport, Connecticut
CPCSEA (2003) CPCSEA guidelines for laboratory animal facility. Indian J Pharmacol 35:257–274
Dewsbury DA, Oglesby JM, Shea SL, Connor JL (1979) Inbreeding and copulatory behavior in house mice: a further consideration. Behav Genet 9:151–163
Doerr JA, Ottinger MA (1980) Delayed reproductive development resulting from aflatoxicosis in juvenile Japanese quail. Poult Sci 59:1995–2001
Dohle GR, Smith M, Weber RFA (2003) Androgens and male fertility. World J Urol 2:341–345
Egbunike GN (1982) Steroidogenic and spermatogenic potentials of the male rat after acute treatment with aflatoxin B1. Andrologia 14:440–446
Faisal K, Periasamy VS, Sahabudeen S, Radha A, Anandhi R, Akbarsha MA (2008) Spermatotoxic effect of aflatoxin B1 in rat: extrusion of outer dense fibers and axonemal microtubule doublets of sperm flagellum. Reproduction 135:303–310
Faridha A, Faisal K, Akbarsha MA (2007) Aflatoxin treatment brings about generation of multinucleate giant spermatids (symplasts) through opening of cytoplasmic bridges: light and transmission electron microscopic study in Swiss mouse. Reprod Toxicol 24:403–408
Fisher JS (2004) Environmental anti-androgens and male reproductive health: focus on phthalates and testicular dysgenesis syndrome. Reproduction 127:305–315
Fisher JS, Macpherson S, Marchetti N, Sharpe RM (2003) Human ‘testicular dysgenesis syndrome’: a possible model using in-utero exposure of the rat to dibutyl phthalate. Human Reprod 18:1383–1394
Geissler F, Faustman EM (1988) Developmental toxicity of aflatoxin B1 in the rodent embryo in vitro: contribution of exogenous biotransformation systems to toxicity. Teratology 37:101–111
Gore AC (2008) Developmental programming and endocrine disruptor effects on reproductive neuroendocrine systems. Front Neuroendocrinology 29:358–374
Greenwood FC, Hunter WM, Clover JS (1963) The preparation of 131I labeled human growth hormone of high specific radio activity. J Biochem 89:114–123
Hasanzadeh S, Hosseini E, Rezazadeh L (2011) Effects of aflatoxin B1 on profiles of gonadotropic (FSH and LH), steroid (testosterone and 17b-estradiol) and prolactin hormones in adult male rat. Iran J Vet Res 12:332–336
Hassan AA, Rashid MA, Koratum KM (2010) Effect of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone and ochratoxin a on some hormones related to fertility in male rats. Life Sci J 7:3
Hutchings DE (1983) Behavioral teratology: a new frontier in neurobehavioral research. In Teratogenesis and reproductive toxicology. pp 207–235. (E. M. Johnson and D. M. Kochhar, Eds.), Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Ibeh IN, Saxena DK (1998) Effect of alpha-tocopherol supplementation on the impact of aflatoxin B1 on the testes of rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 50:221–224
Ibeh IN, Uraih N, Ogonar JL (1994) Dietary exposure to aflatoxin in human male infertility in Benin City, Nigeria. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud 39:208–214
Jeyendran RS, Van Der Ven HH, Zaneveld LJD (1992) The hypo-osmotic swelling test: an update. Arch Androl 29:105
Kasa RN, Nazira IF, Baharuddin S (2011) Occurrence of aspergillus spp. and aflatoxin B1 in Malaysian foods used for human consumption. J Food Sci 13:99–104
Kensler TW, Roebuck BD, Wogan GN, Groopman JD (2011) Aflatoxin: a 50-year odyssey of mechanistic and translational toxicology. Toxicol Sci 120:28–48
Kihara T, Matsuo T, Sakamoto M, Yasuda Y, Yamamoyo Y, Tanimura T (2000) Effects of prenatal aflatoxins B1 exposure on behaviors of rat offspring. Toxicol Sci 53:392–399
Klich MA, Mullaney EJ, Daly CB, Cary JW (2000) Molecular and physiological aspects of aflatoxin and sterigmatocystin biosynthesis by Aspergillus tamarii and A. ochraceoroseus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:605–609
Kochakian CD (1976) Anabolic-androgenic steroids. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Koppe JG, Olie K, Van Wijnen J (1992) Placental transport of dioxins from mother to fetus. Dev Pharm and Ther 18:9–13
Lin KC, Kawamura N, Okamura H, Mori T (1988) Inhibition of ovulation steroidogenesis and collagenolytic activity in rabbits by sulphide induced hyperprolactinemia. J Reprod Fertil 83:611–618
Lowry H, Rosebrough NI, Far AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Madrigal-Santillan E, Morales-Gonzalez J, Vargas-Mendoza N, Reyes-Ramirez P, Cruz- Jaime, S, Sumaya-Martinez T, Perez-Pasten R, Madrigal-Bujaidar E (2010) Antigenotoxic studies of different substances to reduce the DNA damage induced by aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A. Toxins 2: 738–757
Marvan E, Vernerova M, Samek H, Reisnervov H, Nemec J, Martakova R (1983) Aflatoxin B1 residues in the organs of young poultry. Biologicke Chem Vet 24:85–92
Maryamma KI, Sivadas CG (1975) Aflatoxicosis in goats. Ind Vet J 52:385–392
Mobarak YM (2007) Impacts of three naturally occurring mycotoxins (aflatoxins, ochratoxins, and zearalenone) on the embryonic development of vertebrates. Egy J Nat Toxins 4:108–131
O’Donnell L, McLachlan RI, Wreford NG, Robertson DM (1994) Testosterone promotes the conversion of round spermatids between stages VII and VIII of the rat spermatogenic cycle. Endocrinology 135:2608–2614
Ortatatli M, Ciftci MK, Tuzcu M, Kaya A (2002) The effects of aflatoxin on the reproductive system of roosters. Res Vet Sci 72:29–36
Peterson SW, Ito Y, Horn BW, Goto T (2001) Aspergillus bombycis, a new aflatoxigenic species and genetic variation in its sibling species. A nomius Mycologia 93:689–703
Pier AC, McLoughlin ME, Richard JL, Baetz AL, Dahlgren RR (1985) In utero transfer of aflatoxin and selected effects on neonatal pigs. In: Lacey J (ed) Trichothecenes and other mycotoxins. Wiley, New York, pp 495–506
Piskac A, Drabek J, Halouzka R, Groch L (1982) The effect of long term administration of aflatoxin on the health status of male rats and pigs with respect to morphological changes in testes. Vet Med 27:101–111
Prieto-Simon B, Noguer T, Campas M (2007) Emerging biotools for assessment of mycotoxins in the past decade. Trends Anal Chem 26:689–702
Rao AJ, Charaborti R, Kotagi SG, Ravindranath N (1990) Effect of constant infusion of gonadotropins releasing hormone GnRH against buserelin and antagonist CDB 2085 A using osmotic mini pumps on testicular function in adult male bonnet monkey Macaca radiata. Andrologia 22:567–573
Reddy BN, Raghavender CR (2007) Outbreaks of aflatoxicosis in India. Afr J Food Agric Nutr Dev 7:1–10
Sharlin JS, Howarth B, Thompson EN, Wyatt RD (1981) Decreased reproductive potential and reduced feed consumption in nature white leghorn males fed aflatoxin. Poult Sci 60:2701
Shuaib FMB, Jolly EP, Ehiri EJ, Jiang Y, Ellis WO, Stiles KJ, Yatich NJ, Funkhouser E, Person SD, Wilson C, Williams JH (2010) Association between anemia and aflatoxin B1 biomarker levels among pregnant women in Kumasi, Ghana. Am J Trop Med Hyg 83:1077–1083
Supriya C, Sreenivasula Reddy P (2014) Exposure to aflatoxin B1 disrupts fertility efficiency in adult male rats. J Toxicol Health 104:435–441
Supriya C, Girish BP, Sreenivasula Reddy P (2014) Aflatoxin B1-induced reproductive toxicity in male rats: possible mechanism of action. Int J Toxicol 33:155–161
Tajik H, Rohani SM, Moradi M (2007) Detection of aflatoxin M1 in raw and commercial pasteurized milk in Urmia, Iran. Pak J Biol Sci 10:4103–4107
Talbot P, Chacon RS (1981) A triple stain technique for evaluating normal acrosome reaction of human sperm. J Exp Zool 215:201–208
Turner PC, Collinson AC, Cheung YB, Gong Y, Hall AJ, Prentice AM, Wild CP (2007) Aflatoxin exposure in utero causes growth faltering in Gambian infants. Int J Epidemiol 36:1119–1125
Uriarte N, Ferreira A, Rosa XF, Sebben V, Lucion AB (2008) Overlapping litters in rats: effects on maternal behavior and offspring emotionality. Physiol Behav 93:1061–1070
Verma RJ, Nair A (2002) Effect of aflatoxins on testicular steroidogenesis and amelioration by vitamin E. Food Chem Toxicol 40:669–679
Wangikar PB, Dwivedi P, Sinha N (2004) Teratogenic effects of ochratoxin A in rabbits. World Rabbit Sci 12:159–171
Wangikar PB, Dwivedi AP, Sinha AN, Sharma AK, Telang AG (2005) Effects of aflatoxin B1 on embryo fetal development in rabbits. Food Chem Toxicol 43:607–615
Ward OB, Ward IL, Denning JH, French JA, Hendricks SE (2002) Post parturitional testosterone surge in male offspring of rats stressed and/or fed ethanol during late pregnancy. Horm Behav 41:229–235
Yousef M, Abdulrazzaq NO, Ahmed I (2002) Fetal exposure to aflatoxins in the United Arab Emirates. Ann Trop Paediatr 22:3–9
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. K.V.S. Sarma, Department of Statistics, S. V. University, for the analysis of data and Prof. P. Jacob Das, Head, for his encouragement and support. Support for the animal care was provided by Mr. S. Umasankar. All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee at S.V. University. The authors declare that the experiments conducted during these studies comply with the current laws of their country.
Conflict of interest
The authors also declare that there is no conflict of interest that would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Sven Thatje
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Supriya, C., Reddy, P.S. Prenatal exposure to aflatoxin B1: developmental, behavioral, and reproductive alterations in male rats. Sci Nat 102, 26 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-015-1274-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-015-1274-7