Abstract
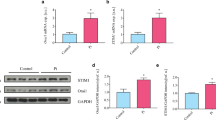
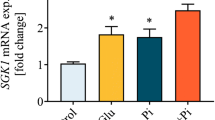
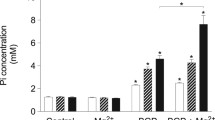
Vascular calcification may result from stimulation of osteogenic signalling with upregulation of the transcription factors CBFA1, MSX2 and SOX9, as well as alkaline phosphatase (ALPL), which degrades and thus inactivates the calcification inhibitor pyrophosphate. Osteogenic signalling further involves upregulation of the Ca2+-channel ORAI1. The channel is activated by STIM1 and then accomplishes store-operated Ca2+ entry. ORAI1 and STIM1 are upregulated by the serum & glucocorticoid inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) which is critically important for osteogenic signalling. Stimulators of vascular calcification include vasopressin. The present study explored whether exposure of human aortic smooth muscle cells (HAoSMCs) to vasopressin upregulates ORAI1 and/or STIM1 expression, store-operated Ca2+ entry and osteogenic signalling. To this end, HAoSMCs were exposed to vasopressin (100 nM, 24 h) without or with additional exposure to ORAI1 blocker MRS1845 (10 μM) or SGK1 inhibitor GSK-650394 (1 μM). Transcript levels were measured using q-RT-PCR, cytosolic Ca2+-concentration ([Ca2+]i) by Fura-2-fluorescence, and store-operated Ca2+ entry from increase of [Ca2+]i following re-addition of extracellular Ca2+ after store depletion with thapsigargin (1 μM). As a result, vasopressin enhanced the transcript levels of ORAI1 and STIM1, store-operated Ca2+ entry, as well as the transcript levels of CBFA1, MSX2, SOX9 and ALPL. The effect of vasopressin on store-operated Ca2+ entry as well as on transcript levels of CBFA1, MSX2, SOX9 and ALPL was virtually abrogated by MRS1845 and GSK-650394. In conclusion, vasopressin stimulates expression of ORAI1/STIM1, thus augmenting store-operated Ca2+ entry and osteogenic signalling. In HAoSMCs, vasopressin (VP) upregulates Ca2+ channel ORAI1 and its activator STIM1. VP upregulates store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) and osteogenic signalling (OS). VP-induced SOCE, OS and Ca2+-deposition are disrupted by ORAI1 inhibitor MRS1845. VP-induced SOCE, OS and Ca2+-deposition are disrupted by SGK1 blocker GSK-650394.
Key messages
• In HAoSMCs, vasopressin (VP) upregulates Ca2+ channel ORAI1 and its activator STIM1.
• VP upregulates store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) and osteogenic signalling (OS).
• VP-induced SOCE, OS and Ca2+-deposition are disrupted by ORAI1 inhibitor MRS1845.
• VP-induced SOCE, OS and Ca2+-deposition are disrupted by SGK1 blocker GSK-650394.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Haarhaus M, Brandenburg V, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Stenvinkel P, Magnusson P (2017) Alkaline phosphatase: a novel treatment target for cardiovascular disease in CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(7):429–442
Fadini GP, Pauletto P, Avogaro A, Rattazzi M (2007) The good and the bad in the link between insulin resistance and vascular calcification. Atherosclerosis 193(2):241–244
Towler DA, Shao JS, Cheng SL, Pingsterhaus JM, Loewy AP (2006) Osteogenic regulation of vascular calcification. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1068:327–333
Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, London GM (2001) Arterial calcifications, arterial stiffness, and cardiovascular risk in end-stage renal disease. Hypertension 38(4):938–942
London GM, Guerin AP, Marchais SJ, Metivier F, Pannier B, Adda H (2003) Arterial media calcification in end-stage renal disease: impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18(9):1731–1740
Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ (1998) Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 32(5 Suppl 3):S112–S119
Mizobuchi M, Towler D, Slatopolsky E (2009) Vascular calcification: the killer of patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(7):1453–1464
Kapustin AN, Chatrou ML, Drozdov I, Zheng Y, Davidson SM, Soong D, Furmanik M, Sanchis P, De Rosales RT, Alvarez-Hernandez D, Shroff R, Yin X, Muller K, Skepper JN, Mayr M, Reutelingsperger CP, Chester A, Bertazzo S, Schurgers LJ, Shanahan CM (2015) Vascular smooth muscle cell calcification is mediated by regulated exosome secretion. Circ Res 116(8):1312–1323
Lang F, Ritz E, Alesutan I, Voelkl J (2014) Impact of aldosterone on osteoinductive signaling and vascular calcification. Nephron Physiol 128(1–2):40–45
Lang F, Ritz E, Voelkl J, Alesutan I (2013) Vascular calcification--is aldosterone a culprit? Nephrol Dial Transplant 28(5):1080–1084
Steitz SA, Speer MY, Curinga G, Yang HY, Haynes P, Aebersold R, Schinke T, Karsenty G, Giachelli CM (2001) Smooth muscle cell phenotypic transition associated with calcification: upregulation of Cbfa1 and downregulation of smooth muscle lineage markers. Circ Res 89(12):1147–1154
Voelkl J, Luong TT, Tuffaha R, Musculus K, Auer T, Lian X, Daniel C, Zickler D, Boehme B, Sacherer M, Metzler B, Kuhl D, Gollasch M, Amann K, Muller DN, Pieske B, Lang F, Alesutan I (2018) SGK1 induces vascular smooth muscle cell calcification through NF-kappaB signaling. J Clin Invest 128(7):3024–3040
Lang F, Shumilina E (2013) Regulation of ion channels by the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase SGK1. FASEB J 27(1):3–12
Lang F, Guelinckx I, Lemetais G, Melander O (2017) Two liters a day keep the doctor away? Considerations on the pathophysiology of suboptimal fluid intake in the common population. Kidney Blood Press Res 42(3):483–494
Sahu I, Pelzl L, Sukkar B, Fakhri H, Al-Maghout T, Cao H, Hauser S, Gutti R, Gawaz M, Lang F (2017) NFAT5-sensitive ORAI1 expression and store-operated Ca(2+) entry in megakaryocytes. FASEB J 31(8):3439–3448
Ma K, Liu P, Al-Maghout T, Sukkar B, Cao H, Voelkl J, Alesutan I, Pieske B, Lang F (2019) Phosphate-induced ORAI1 expression and store-operated Ca(2+) entry in aortic smooth muscle cells. J Mol Med 97(10):1465–1475
Nishiwaki-Yasuda K, Suzuki A, Kakita A, Sekiguchi S, Asano S, Nishii K, Nagao S, Oiso Y, Itoh M (2007) Vasopressin stimulates Na-dependent phosphate transport and calcification in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Endocr J 54(1):103–112
Ding Y, Winters A, Ding M, Graham S, Akopova I, Muallem S, Wang Y, Hong JH, Gryczynski Z, Yang SH, Birnbaumer L, Ma R (2011) Reactive oxygen species-mediated TRPC6 protein activation in vascular myocytes, a mechanism for vasoconstrictor-regulated vascular tone. J Biol Chem 286(36):31799–31809
Tsai YM, Jones F, Mullen P, Porter KE, Steele D, Peers C, Gamper N (2020) Vascular Kv7 channels control intracellular Ca(2+) dynamics in smooth muscle. Cell Calcium 92:102283
Brueggemann LI, Mackie AR, Mani BK, Cribbs LL, Byron KL (2009) Differential effects of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on vascular smooth muscle ion channels may account for differences in cardiovascular risk profiles. Mol Pharmacol 76(5):1053–1061
Mackie AR, Byron KL (2008) Cardiovascular KCNQ (Kv7) potassium channels: physiological regulators and new targets for therapeutic intervention. Mol Pharmacol 74(5):1171–1179
Jones BF, Boyles RR, Hwang SY, Bird GS, Putney JW (2008) Calcium influx mechanisms underlying calcium oscillations in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 48(4):1273–1281
Piron M, Villereal ML (2013) Chronic exposure to stress hormones alters the subtype of store-operated channels expressed in H19-7 hippocampal neuronal cells. J Cell Physiol 228(6):1332–1343
Aoyagi T, Koshimizu TA, Tanoue A (2009) Vasopressin regulation of blood pressure and volume: findings from V1a receptor-deficient mice. Kidney Int 76(10):1035–1039
Jeffries O, McGahon MK, Bankhead P, Lozano MM, Scholfield CN, Curtis TM, McGeown JG (2010) cAMP/PKA-dependent increases in Ca Sparks, oscillations and SR Ca stores in retinal arteriolar myocytes after exposure to vasopressin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(3):1591–1598
Byron KL (1996) Vasopressin stimulates Ca2+ spiking activity in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells via activation of phospholipase A2. Circ Res 78(5):813–820
Ratni H, Rogers-Evans M, Bissantz C, Grundschober C, Moreau JL, Schuler F, Fischer H, Alvarez Sanchez R, Schnider P (2015) Discovery of highly selective brain-penetrant vasopressin 1a antagonists for the potential treatment of autism via a chemogenomic and scaffold hopping approach. J Med Chem 58(5):2275–2289
Borst O, Schmidt EM, Münzer P, Schönberger T, Towhid ST, Elvers M, Leibrock C, Schmid E, Eylenstein A, Kuhl D, May AE, Gawaz M, Lang F (2012) The serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) influences platelet calcium signaling and function by regulation of Orai1 expression in megakaryocytes. Blood 119(1):251–261
Schmid E, Bhandaru M, Nurbaeva MK, Yang W, Szteyn K, Russo A, Leibrock C, Tyan L, Pearce D, Shumilina E, Lang F (2012) SGK3 regulates Ca(2+) entry and migration of dendritic cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 30(6):1423–1435
Tran TD, Yao S, Hsu WH, Gimble JM, Bunnell BA, Cheng H (2015) Arginine vasopressin inhibits adipogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 406:1–9
Hummerich W, Konrads A, Roesch R, Sofroniew M (1983) Radioimmunoassay of arginine-vasopressin in human plasma: development and clinical application. Klin Wochenschr 61(4):203–208
Di Giglio MG, Muttenthaler M, Harpsøe K, Liutkeviciute Z, Keov P, Eder T, Rattei T, Arrowsmith S, Wray S, Marek A, Elbert T, Alewood PF, Gloriam DE, Gruber CW (2017) Development of a human vasopressin V(1a)-receptor antagonist from an evolutionary-related insect neuropeptide. Sci Rep 7:41002
Serradeil-Le Gal C, Herbert JM, Delisee C, Schaeffer P, Raufaste D, Garcia C, Dol F, Marty E, Maffrand JP, Le Fur G (1995) Effect of SR-49059, a vasopressin V1a antagonist, on human vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Phys 268(1 Pt 2):H404–H410
Lang F, Eylenstein A, Shumilina E (2012) Regulation of Orai1/STIM1 by the kinases SGK1 and AMPK. Cell Calcium 52(5):347–354
Schmidt S, Liu G, Liu G, Yang W, Honisch S, Pantelakos S, Stournaras C, Honig A, Lang F (2014) Enhanced ORAI1 and STIM1 expression as well as store operated Ca2+ entry in therapy resistant ovary carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 5(13):4799–4810
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the meticulous preparation of the manuscript by Lejla Subasic.
Funding
Xuexue Zhu, Kuo Zhou and Jibin Liu are supported by the Chinese Scholarship Council. The sponsor(s) had no role in study design, the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report, and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ, KM, KZ and JL performed the experiments and analysed the data; FL and BN designed the research, FL drafted and wrote the manuscript. All authors corrected and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Ma, K., Zhou, K. et al. Vasopressin-stimulated ORAI1 expression and store-operated Ca2+ entry in aortic smooth muscle cells. J Mol Med 99, 373–382 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-02016-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-02016-4