Abstract
Elevated LRP16 expression is associated with poor clinical outcomes in multiple malignancies. We detected LRP16 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and found that it was downregulated in tumor samples and HCC cell lines. In a cohort of 80 HCC patients, high level of LRP16 expression in HCC tumors was associated with well differentiation, less lymph node metastasis, and good overall survival (OS). Overexpression of LRP16 in the HepG2 and MHCC-97L cell lines increased cell apoptosis, attenuated cell proliferation, migration, and invasion ability in vitro, and drastically diminished tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. Silencing LRP16 in HCC-LM3 and SMMC-7721 cell lines showed opposite results. Microarray evaluation of tumor cells overexpressing LRP16 revealed the effects on decreased activity in the Wnt signaling pathway. These results were confirmed by qRT-PCR and Western blots. Furthermore, inhibition of Wnt signaling decreased proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cell lines. Mechanism conducted showed that LRP16 overexpression could prevent β-catenin from entering the nucleus. Our study demonstrated that LRP16 suppresses tumor growth in HCC by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Key messages
-
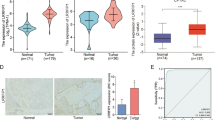
LRP16 was low expression in HCC tissue and cell lines.
-
Low expression of LRP16 in HCC was associated with poor prognosis.
-
LRP16 inhibits activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in HCC.
-
LRP16 prevents β-catenin from entering the nucleus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han WD, Yu L, Lou FD, Wang QS, Zhao Y, Shi ZJ, Jin HJ (2001) The application of RACE technique to clone the full-length cDNA of a novel leukemia associated gene LRP16. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 9(1):18–21
Li YZ, Zhao P, Han WD (2009) Clinicopathological significance of LRP16 protein in 336 gastric carcinoma patients. World J Gastroenterol 15(38):4833–4837
Liao DX, Han WD, Zhao YL, Pu YD, Mu YM, Luo CH, Li XH (2006) Expression and clinical significance of LRP16 gene in human breast cancer. Chin J Cancer 25(7):866–870
Shao Y, Li X, Lu Y, Liu L, Zhao P (2015) Aberrant LRP16 protein expression in primary neuroendocrine lung tumors. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(6):6560–6565
Xi HQ, Zhao P, Han WD (2010) Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of LRP16 expression in colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 16(13):1644–1648
Han WD, Mu YM, Lu XC, Xu ZM, Li XJ, Yu L, Song HJ, Li M, Lu JM, Zhao YL et al (2003) Up-regulation of LRP16 mRNA by 17beta-estradiol through activation of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha), but not ERbeta, and promotion of human breast cancer MCF-7 cell proliferation: a preliminary report. Endocr Relat Cancer 10(2):217–224
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):87–108
El-Serag HB (2012) Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 142(6):1264–1273 e1261
Wang J, He XD, Yao N, Liang WJ, Zhang YC (2013) A meta-analysis of adjuvant therapy after potentially curative treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Can J Gastroenterol 27(6):351–363
Privette Vinnedge LM, Benight NM, Wagh PK, Pease NA, Nashu MA, Serrano-Lopez J, Adams AK, Cancelas JA, Waltz SE, Wells SI (2015) The DEK oncogene promotes cellular proliferation through paracrine Wnt signaling in Ron receptor-positive breast cancers. Oncogene 34(18):2325–2336
Tong X, Li L, Li X, Heng L, Zhong L, Su X, Rong R, Hu S, Liu W, Jia B et al (2014) SOX10, a novel HMG-box-containing tumor suppressor, inhibits growth and metastasis of digestive cancers by suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 5(21):10571–10583
Fatima S, Lee NP, Tsang FH, Kolligs FT, Ng IO, Poon RT, Fan ST, Luk JM (2012) Dickkopf 4 (DKK4) acts on Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by influencing beta-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 31(38):4233–4244
Stow JL (2004) ICAT is a multipotent inhibitor of beta-catenin. Focus on “role for ICAT in beta-catenin-dependent nuclear signaling and cadherin functions”. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286(4):C745–C746
Tsutsui M, Iizuka N, Moribe T, Miura T, Kimura N, Tamatsukuri S, Ishitsuka H, Fujita Y, Hamamoto Y, Tsunedomi R et al (2010) Methylated cyclin D2 gene circulating in the blood as a prognosis predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta 411(7–8):516–520
Kim SU, Park JH, Kim HS, Lee JM, Lee HG, Kim H, Choi SH, Baek S, Kim BK, Park JY et al (2015) Serum Dickkopf-1 as a biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Yonsei Med J 56(5):1296–1306
Park J, Schlederer M, Schreiber M, Ice R, Merkel O, Bilban M, Hofbauer S, Kim S, Addison J, Zou J et al (2015) AF1q is a novel TCF7 co-factor which activates CD44 and promotes breast cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 6(24):20697–20710
Chen WY, Liu SY, Chang YS, Yin JJ, Yeh HL, Mouhieddine TH, Hadadeh O, Abou-Kheir W, Liu YN (2015) MicroRNA-34a regulates WNT/TCF7 signaling and inhibits bone metastasis in Ras-activated prostate cancer. Oncotarget 6(1):441–457
Hay E, Faucheu C, Suc-Royer I, Touitou R, Stiot V, Vayssiere B, Baron R, Roman-Roman S, Rawadi G (2005) Interaction between LRP5 and Frat1 mediates the activation of the Wnt canonical pathway. J Biol Chem 280(14):13616–13623
Pennanen PT, Sarvilinna NS, Toimela T, Ylikomi TJ (2011) Inhibition of FOSL1 overexpression in antiestrogen-resistant MCF-7 cells decreases cell growth and increases vacuolization and cell death. Steroids 76(10–11):1063–1068
van Amerongen R, Nawijn MC, Lambooij JP, Proost N, Jonkers J, Berns A (2010) Frat oncoproteins act at the crossroad of canonical and noncanonical Wnt-signaling pathways. Oncogene 29(1):93–104
Wang R, Sun Q, Wang P, Liu M, Xiong S, Luo J, Huang H, Du Q, Geller DA, Cheng B (2016) Notch and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway play important roles in activating liver cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 7(5):5754–5768
Teufel A, Marquardt JU, Galle PR (2013) Next generation sequencing of HCC from European and Asian HCC cohorts. Back to p53 and Wnt/beta-catenin. J Hepatol 58(3):622–624
Monga SP (2015) Beta-catenin signaling and roles in liver homeostasis, injury, and tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 148(7):1294–1310
Meng Y, Wu Z, Yin X, Zhao Y, Chen M, Si Y, Yang J, Fu X, Han W (2009) Keratin 18 attenuates estrogen receptor alpha-mediated signaling by sequestering LRP16 in cytoplasm. BMC Cell Biol 10:96
Zhao YL, Han WD, Li Q, Mu YM, Lu XC, Yu L, Song HJ, Li X, Lu JM, Pan CY (2005) Mechanism of transcriptional regulation of LRP16 gene expression by 17-beta estradiol in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Mol Endocrinol 34(1):77–89
Han WD, Si YL, Zhao YL, Li Q, Wu ZQ, Hao HJ, Song HJ (2008) GC-rich promoter elements maximally confers estrogen-induced transactivation of LRP16 gene through ERalpha/Sp1 interaction in MCF-7 cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 109(1–2):47–56
Han WD, Zhao YL, Meng YG, Zang L, Wu ZQ, Li Q, Si YL, Huang K, Ba JM, Morinaga H et al (2007) Estrogenically regulated LRP16 interacts with estrogen receptor alpha and enhances the receptor's transcriptional activity. Endocr Relat Cancer 14(3):741–753
Wu Z, Li Y, Li X, Ti D, Zhao Y, Si Y, Mei Q, Zhao P, Fu X, Han W (2011) LRP16 integrates into NF-kappaB transcriptional complex and is required for its functional activation. PLoS One 6(3):e18157
Wu Z, Wang C, Bai M, Li X, Mei Q, Li X, Wang Y, Fu X, Luo G, Han W (2015) An LRP16-containing preassembly complex contributes to NF-kappaB activation induced by DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res 43(6):3167–3179
Li X, Wu Z, An X, Mei Q, Bai M, Hanski L, Li X, Ahola T, Han W (2017) Blockade of the LRP16-PKR-NF-kappaB signaling axis sensitizes colorectal carcinoma cells to DNA-damaging cytotoxic therapy. eLife 6. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27301
Moravec M (2012) Colorectal cancer and canonical Wnt signalling pathway. Cas Lek Cesk 151(7):335–342
Mir R, Pradhan SJ, Patil P, Mulherkar R, Galande S (2016) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulated SATB1 promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis and progression. Oncogene 35(13):1679–1691
Zhang Y, Li T, Guo P, Kang J, Wei Q, Jia X, Zhao W, Huai W, Qiu Y, Sun L et al (2014) MiR-424-5p reversed epithelial-mesenchymal transition of anchorage-independent HCC cells by directly targeting ICAT and suppressed HCC progression. Sci Rep 4:6248
Freeman J, Smith D, Latinkic B, Ewan K, Samuel L, Zollo M, Marino N, Tyas L, Jones N, Dale TC (2015) A functional connectome: regulation of Wnt/TCF-dependent transcription by pairs of pathway activators. Mol Cancer 14:206
Pez F, Lopez A, Kim M, Wands JR, Caron de Fromentel C, Merle P (2013) Wnt signaling and hepatocarcinogenesis: molecular targets for the development of innovative anticancer drugs. J Hepatol 59(5):1107–1117
Mohammed MK, Shao C, Wang J, Wei Q, Wang X, Collier Z, Tang S, Liu H, Zhang F, Huang J et al (2016) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal, tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis 3(1):11–40
Kim M, Suh YA, Oh JH, Lee BR, Kim J, Jang SJ (2016) KIF3A binds to beta-arrestin for suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signalling independently of primary cilia in lung cancer. Sci Rep 6:32770
Wang Y, Bu F, Royer C, Serres S, Larkin JR, Soto MS, Sibson NR, Salter V, Fritzsche F, Turnquist C et al (2014) ASPP2 controls epithelial plasticity and inhibits metastasis through beta-catenin-dependent regulation of ZEB1. Nat Cell Biol 16(11):1092–1104
Acknowledgements
We thank Zizheng Wang at the Hepatological Surgery Department of PLA for his analysis assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science & Technology (“973” projects) (No. 2012CB917104) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81341069; 81172853).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, L., Jing, W., Wang, L. et al. LRP16 prevents hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Mol Med 96, 547–558 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1639-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1639-4