Abstract
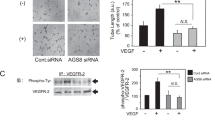
Choroidal neovascularization (CNV), an aberrant growth of blood vessels in the choroid layer of the eye, is a major cause of vision loss. In view of our recent finding that discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2), a collagen-binding receptor tyrosine kinase, is involved in control of vascular endothelial activity and tumor angiogenesis, the present study aims to investigate whether and how DDR2 affects the pathogenesis of CNV. We initially found that a spontaneous DDR2 mutant mouse colony (slie) exhibited enhanced amplitude of laser-induced CNV. The inhibitory role of DDR2 in CNV development was further confirmed by experiments through intravitreous injection of DDR2 small interference RNA (siRNA) or DDR2-expressing adenovirus. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and immunoblot analysis showed that DDR2 regulates the expression of several major pro-angiogenic factors in the laser-injured choroid as well as in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells. In addition, it was demonstrated that the CNV-induced increases in the phosphorylation levels of Akt and mTOR were affected by the upregulation or downregulation of DDR2. Thus, the data from this study for the first time revealed that DDR2 negatively regulates the development of experimental CNV in vivo, which may provide a novel target for preventing human pathological ocular neovascularization.
Key messages
-
DDR2 does not affect retinal development.
-
DDR2 inhibits laser-induced CNV.
-
DDR2 regulates angiogenic factor expression in CNV lesion as well as in RPE cells.
-
DDR2 is involved in modulation of CNV-induced activation of PI3K pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calabrese A, Bernard JB, Hoffart L, Faure G, Barouch F, Conrath J, Castet E (2011) Wet versus dry age-related macular degeneration in patients with central field loss: different effects on maximum reading speed. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:2417–2424
Campochiaro PA (2000) Retinal and choroidal neovascularization. J Cell Physiol 184:301–310
Torres RJ, Maia M, Muccioli C, Winter G, Souza GK, Pasqualotto LR, Luchini A, Precoma DB (2009) Modifiable risk factors for age-related macular degeneration. Arq Bras Oftalmol 72:406–412
Campa C, Costagliola C, Incorvaia C, Sheridan C, Semeraro F, De Nadai K, Sebastiani A, Parmeggiani F (2010) Inflammatory mediators and angiogenic factors in choroidal neovascularization: pathogenetic interactions and therapeutic implications. Mediat Inflamm 2010
Shi X, Semkova I, Muther PS, Dell S, Kociok N, Joussen AM (2006) Inhibition of TNF-alpha reduces laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. Exp Eye Res 83:1325–1334
Krzystolik MG, Afshari MA, Adamis AP, Gaudreault J, Gragoudas ES, Michaud NA, Li W, Connolly E, O'Neill CA, Miller JW (2002) Prevention of experimental choroidal neovascularization with intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody fragment. Arch Ophthalmol 120:338–346
Lazic R, Gabric N (2007) Intravitreally administered bevacizumab (Avastin) in minimally classic and occult choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Graefes arch Clin Exp Ophthalmology=Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klin Exp Ophthalmol 245:68–73
Barber NA, Ganti AK (2011) Pulmonary toxicities from targeted therapies: a review. Target Oncol 6:235–243
Buyukoglan H, Gulmez I, Tutar N, Oymak FS, Kanbay A, Demir R (2011) Gluteal abscess: an unusual complication of Bacille Calmette-Guerin. Anna Thorac Med 6:235–236
Obayashi Y, Yamadori I, Fujita J, Yoshinouchi T, Ueda N, Takahara J (1997) The role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 112:1338–1343
Vogel W, Gish GD, Alves F, Pawson T (1997) The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by collagen. Mol Cell 1:13–23
Vogel WF, Abdulhussein R, Ford CE (2006) Sensing extracellular matrix: an update on discoidin domain receptor function. Cell Signal 18:1108–1116
Badiola I, Olaso E, Crende O, Friedman SL, Vidal-Vanaclocha F (2012) Discoidin domain receptor 2 deficiency predisposes hepatic tissue to colon carcinoma metastasis. Gut 61:1465–1472
Olaso E, Arteta B, Benedicto A, Crende O, Friedman SL (2011) Loss of discoidin domain receptor 2 promotes hepatic fibrosis after chronic carbon tetrachloride through altered paracrine interactions between hepatic stellate cells and liver-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol 179:2894–2904
Olaso E, Lin HC, Wang LH, Friedman SL (2011) Impaired dermal wound healing in discoidin domain receptor 2-deficient mice associated with defective extracellular matrix remodeling. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 4:5
Xu L, Servais J, Polur I, Kim D, Lee PL, Chung K, Li Y (2010) Attenuation of osteoarthritis progression by reduction of discoidin domain receptor 2 in mice. Arthritis Rheum 62:2736–2744
Zhang S, Bu X, Zhao H, Yu J, Wang Y, Li D, Zhu C, Zhu T, Ren T, Liu X et al (2014) A host deficiency of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) inhibits both tumour angiogenesis and metastasis. J Pathol 232:436–448
Kano K, Marin de Evsikova C, Young J, Wnek C, Maddatu TP, Nishina PM, Naggert JK (2008) A novel dwarfism with gonadal dysfunction due to loss-of-function allele of the collagen receptor gene, Ddr2, in the mouse. Mol Endocrinol 22:1866–1880
Kim LG, Thompson SG, Marteau TM, Scott RA, Multicentre Aneurysm Screening Study G (2004) Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms: the effects of age and social deprivation on screening uptake, prevalence and attendance at follow-up in the MASS trial. J Med Screen 11:50–53
Zhang Y, Su J, Yu J, Bu X, Ren T, Liu X, Yao L (2011) An essential role of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) in osteoblast differentiation and chondrocyte maturation via modulation of Runx2 activation. J Bone Miner Res 26:604–617
Yang XM, Wang YS, Zhang J, Li Y, Xu JF, Zhu J, Zhao W, Chu DK, Wiedemann P (2009) Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK in mediating hypoxia-induced expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in laser-induced rat choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:1873–1879
Li X, Cai Y, Wang YS, Shi YY, Hou W, Xu CS, Wang HY, Ye Z, Yao LB, Zhang J (2012) Hyperglycaemia exacerbates choroidal neovascularisation in mice via the oxidative stress-induced activation of STAT3 signalling in RPE cells. PLoS One 7:e47600
Monteagudo B, Labandeira J, Cabanillas M, Acevedo A, Leon-Muinos E, Toribio J (2012) Prevalence of milia and palatal and gingival cysts in Spanish newborns. Pediatr Dermatol 29:301–305
Zhang Y, Tanner KE (2008) Effect of filler surface morphology on the impact behaviour of hydroxyapatite reinforced high density polyethylene composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:761–766
Campochiaro PA, Soloway P, Ryan SJ, Miller JW (1999) The pathogenesis of choroidal neovascularization in patients with age-related macular degeneration. Mol Vis 5:34
Nowak JZ (2006) Age-related macular degeneration (AMD): pathogenesis and therapy. Pharmacol Rep: PR 58:353–363
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, Yan M, Keyt BA, Dixit V, Ferrara N (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem 273:30336–30343
Gille H, Kowalski J, Yu L, Chen H, Pisabarro MT, Davis-Smyth T, Ferrara N (2000) A repressor sequence in the juxtamembrane domain of Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) constitutively inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation and endothelial cell migration. EMBO J 19:4064–4073
Maliba R, Lapointe S, Neagoe PE, Brkovic A, Sirois MG (2006) Angiopoietins-1 and −2 are both capable of mediating endothelial PAF synthesis: intracellular signalling pathways. Cell Signal 18:1947–1957
Wu X, Liu N (2010) The role of Ang/Tie signaling in lymphangiogenesis. Lymphology 43:59–72
Samalavichius NE (2004) [Preventive Turnbull ileostomy]. Khirurgiia (Mosk):50–52
Lee JE, Kang CS, Guan XY, Kim BT, Kim SH, Lee YM, Moon WS, Kim DK (2007) Discoidin domain receptor 2 is involved in the activation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells caused by type I collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:244–250
Baxa U, Taylor KL, Steven AC, Wickner RB (2004) Prions of saccharomyces and Podospora. Contrib Microbiol 11:50–71
Chen SC, Wang BW, Wang DL, Shyu KG (2008) Hypoxia induces discoidin domain receptor-2 expression via the p38 pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells to increase their migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:662–667
Lee NO, Park JW, Lee JA, Shim JH, Kong SY, Kim KT, Lee YS (2012) Dual action of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor on vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells: novel involvement of discoidin domain receptor 2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138:73–84
Acknowledgments
We greatly thank Dr. Wei Zhang (The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an, China) for providing us the DDR2-expressing adenovirus stock.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81070748, 81000392) and grants from the Chinese National Key Basic Research and Development Program (2011CB510200 and 2010CB529705).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Tong Zhu and Jie Zhu and Xin Bu equally contribute to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 542 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Zhu, J., Bu, X. et al. The anti-angiogenic role of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) in laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. J Mol Med 93, 187–198 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1213-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1213-7