Abstract
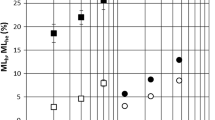
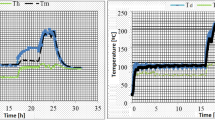
A major function of resin in trees is to provide defense against external attacks by releasing the resin flow in the attacked or damaged area. Nonetheless, leakage of resin on the surface can have negative aesthetic and economic impacts on wood materials. The aim of this study was to investigate how heat treatment affects the physico-chemical properties of the resin of Pinus sylvestris L. to hinder exudation on wood surfaces during service. To reduce the fluidity of the resin, it is necessary to remove the volatile fraction of resin, and several studies have been carried out in this direction, providing useful information about this process. The results from thermal analyses (DSC, TGA) confirmed that heat treatment at mild temperatures, 80 °C, 90 °C and 100 °C had a positive effect on increasing the glass transition temperature Tg and that the Tg and the residual volatile content were strongly correlated. FTIR spectroscopy, before and after heat treatment, did not reveal major changes in chemical structure, while UHPLC-DAD-MS analysis revealed significant differences in the ratios of compounds, which are the result of possible chemical reactions, such as dehydrogenation, oxidation and isomerization.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Amiralian N, Annamalai PK, Fitzgerald C et al (2014) Optimisation of resin extraction from an Australian arid grass 'Triodia pungens' and its preliminary evaluation as an anti-termite timber coating. Ind Crops Prod 59:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.04.045
Auders AG, Spicer DP (2012) Encyclopedia of conifers. Volume II, Kingsblue Publishing Limited, Nicosia, Cyprus, p 1095
Azemard C, Menager M, Vieillescazes C (2016) Analysis of diterpenic compounds by GC-MS/MS: contribution to the identification of main conifer resins. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:6599–6612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9772-9
Cabaret T, Harfouche N, Leroyer L et al (2019a) A study of the physico-chemical properties of dried maritime pine resin to better understand the exudation process. Holzforschung 73:1093–1102. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2018-0264
Cabaret T, Gardere Y, Frances M et al (2019b) Measuring interactions between rosin and turpentine during the drying process for a better understanding of exudation in maritime pine wood used as outdoor siding. Ind Crops Prod 130:325–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.12.080
Cabaret T, Mariet F, Li K et al (2019c) High temperature drying effect against resin exudation for maritime pine wood used as outdoor siding. Eur J Wood Prod 77:673–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-019-01425-8
Cao H, Huang S, Yi S et al (2023) The effects of superheated steam heat-treatment on turpentine content and softening point of resin. Ind Crops Prod 192:116139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.116139
Eberhardt TL, Sheridan PM, Mahfouz JM (2009) Monoterpene persistence in the sapwood and heartwood of longleaf pine stumps: Assessment of differences in composition and stability under field conditions. Can J Res 39:1357–1365. https://doi.org/10.1139/X09-063
Ferrenberg S, Kane JM, Mitton JB (2014) Resin duct characteristics associated with tree resistance to bark beetles across lodgepole and limber pines. Oecologia 174:1283–1292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-013-2841-2
Gaillard Y, Mija A, Burr A et al (2011) Green material composites from renewable resources: polymorphic transitions and phase diagram of beeswax/rosin resin. Thermochim Acta 521:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2011.04.010
http:// zalasmajas.lv/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/skaitlifakti_ENG_2022_mazs.pdf
Kaitera J, Piispanen J, Bergmann U (2021) Terpene and resin acid contents in scots pine stem lesions colonized by the rust fungus Cronartium pini. Pathol 51:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/efp.12700
Kersten PJ, Kopper BJ, Raffa KF, Illman BL (2006) Rapid analysis of abietanes in conifers. J Chem Ecol 32:2679–2685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9191-z
Knebel L, Robison DJ, Wentworth TR, Klepzig KD (2008) Resin flow responses to fertilization, wounding and fungal inoculation in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) in North Carolina. Tree Physiol 28:847–853. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/28.6.847
Krokene P, Nagy NE (2012) Anatomical aspects of resin-based defences in pine. In Fett-Neto AG, Rodrigues-Corrêa KCS (ed) Pine resin: biology, chemistry and applications, pp 67–86
Lai M, Zhang L, Lei L et al (2020) Inheritance of resin yield and main resin components in Pinus elliottii Engelm. At three locations in southern China. Ind Crops Prod 144:112065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.112065
Liu Q, Zhou Z, Fan H, Liu Y (2013) Genetic variation and correlation among resin yield, growth, and morphologic traits of Pinus massoniana. Silvae Genet 62:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1515/sg-2013-0005
Mengistu T, Sterck FJ, Fetene M, Bongers F (2013) Frankincense tapping reduces the carbohydrate storage of Boswellia trees. Tree Physiol 33:601–608. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpt035
Mondal S, Memmott P, Wallis L, Martin D (2012) Physico-thermal properties of spinifex resin bio-polymer. Mater Chem Phys 133:692–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.01.058
Neis FA, de Costa F, de Almeida MR et al (2019) Resin exudation profile, chemical composition, and secretory canal characterization in contrasting yield phenotypes of Pinus elliottii Engelm. Ind Crops Prod 132:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.02.013
Nerg A, Kainulainen P, Vuorinen M et al (1994) Seasonal and geographical variation of terpenes, resin acids and total phenolics in nursery grown seedlings of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L). New Phytol 128:703–713. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1994.tb04034.x
Odegaard N, Pool M, Bisulca C et al (2014) Pine Pitch: new treatment protocols for a brittle and crumbly conservation problem. Objects Spec Gr Postprints 21:21–41
Pastorova I, Van Der Berg KJ, Boon JJ, Verhoeven JW (1997) Analysis of oxidised diterpenoid acids using thermally assisted methylation with TMAH. J Anal Appl Pyrol 43:41–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(97)00058-2
Rissanen K, Hölttä T, Barreira LFM et al (2019) Temporal and spatial variation in scots Pine Resin pressure and composition. Front Glob Chang 2:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/ffgc.2019.00023
Rodríguez-García A, López R, Martín JA et al (2014) Resin yield in Pinus pinaster is related to tree dendrometry, stand density and tapping-induced systemic changes in xylem anatomy. Ecol Manage 313:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.10.038
Rubini M, Clopeau A, Sandak J et al (2022) Characterization and classification of Pinus oleoresin samples according to Pinus species, tapping method, and geographical origin based on chemical composition and chemometrics. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 42:102340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102340
Sansonetti E, Cirule D, Kuka E, Meile K (2023) Analysis of Pine Resin Properties as a way to Understand and prevent exudation from Wood Material. Adv Sci Technol 134 AST:21–28. https://doi.org/10.4028/p-L0uODz
Smith RH (2000) Xylem Monoterpenes of Pines: Distribution, Variation, Genetics, Function. 2000. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report PSW-GTR- pp 1–5
Trapp S, Croteau R (2001) Defensive resin biosynthesis in conifers. Annu Rev Plant Biol 52:689–724. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.689
Verkasalo E, Roitto M, Möttönen V et al (2022) Extractives of Tree Biomass of scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) for Biorefining in four climatic regions in Finland—Lipophilic compounds, stilbenes, and Lignans. Forests 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050779
Willför S, Hemming J, Reunanen M, Holmbom B (2003) Phenolic and lipophilic extractives in scots pine knots and stemwood. Holzforschung 57:359–372. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF.2003.054
Wiyono B, Tachibana S, Tinambunan D (2006) Chemical compositions of Pine Resin, Rosin and Turpentine Oil from West Java. Indones J Res 3:7–17. https://doi.org/10.20886/ijfr.2006.3.1.7-17
Wu H, Hu ZH (1997) Comparative anatomy of resin ducts of the Pinaceae. Trees - Struct Funct 11:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004680050069
Zulak KG, Bohlmann J (2010) Terpenoid biosynthesis and specialized vascular cells of conifer defense. J Integr Plant Biol 52:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00910.x
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Latvian State Institute of Wood Chemistry Bioeconomy Grant “Limitation of pine resin exudation” project No. 06–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.C. and E.K. wrote introduction. E.S. wrote abstract, materials and methods section, results and discussion, conclusions and prepared figures and tables, K.M. and L.V. contributed to the experimental section (methods). All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sansonetti, E., Cirule, D., Kuka, E. et al. Effect of heat treatment at mild temperatures on the composition and physico-chemical properties of Scots pine resin. Eur. J. Wood Prod. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-024-02087-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-024-02087-x