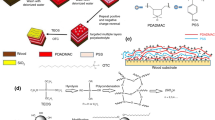
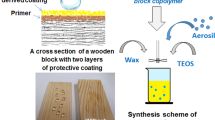
Abstract
As a potential building material, fast-growing wood (such as poplar) is prone to easy combustion and having poor mechanical properties, which limit its application range. In order to improve the reinforcing effect of SiO2 on poplar wood, we propose a method of immersing silica sol into wood smoothly. In this method, the sol and a non-ionic surfactant are first treated via organic–inorganic hybridization. This surfactant has a strong penetration effect, and the sol is introduced into the wood through hybridization. By impregnating the wood, the flexural strength and flexural modulus of elasticity increased by 79.7% and 89.5%, and the compressive strength along the grain increased by 105.1%. The treated wood also showed flame retardation, reducing the heat release rate (HRR), carbon dioxide yield (CO2Y), total heat release (THR), specific extinction area (SEA) and total smoke release (TSR), with delaying ignition and burn-through time. This method incorporates silica sol in wood via physical filling and chemical bonding, thereby improving the mechanical and flame retardation properties of wood as an outdoor building material.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data is available upon reasonable request.
References
Baishya P, Maji TK (2016) Functionalization of MWCNT and their application in properties development of green wood nanocomposite. Carbohydr Polym 149:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.117
Chai MY, Xie L, Yu X, Zhang XG, Yang Y, Rahmand MM, Blanco PH, Liu R, Bridgwater AV, Cai J (2021) Poplar wood torrefaction: kinetics, thermochemistry and implications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 143:110962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110962
Chen ZR, Zhang SD, Ding MY, Wang MZ, Xu X (2021) Construction of a phytic acid-silica system in wood for highly efficient flame retardancy and smoke suppression. Materials 14(15):4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154164
Colom X, Carrillo F, Nogués F, Garriga P (2003) Structural analysis of photodegraded wood by means of FTIR spectroscopy. Polym Degrad Stab 80(3):543–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(03)00051-X
Dong XY, Zhuo X, Wei J, Zhang G, Li YF (2017) Wood-based nanocomposite derived by in situ formation of organic-inorganic hybrid polymer within wood via a sol-gel method. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(10):9070–9078. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b01174
Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP, Gandini A, Fardim P, Holmbom B (2006) Surface characterization by XPS, contact angle measurements and ToF-SIMS of cellulose fibers partially esterified with fatty acids. J Colloid Interface Sci 301(1):205–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.04.074
Ghorbani M, Poorzahed N, Amininasab SM (2020) Morphological, physical, and mechanical properties of silanized wood-polymer composite. J Compos Mater 54(11):1403–1412. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998319881493
Girardi F, Cappelletto E, Sandak J, Bochicchio G, Tessadri B, Palanti S, Feci E, Di Maggio R (2014) Hybrid organic-inorganic materials as coatings for protecting wood. Prog Org Coat 77(2):449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2013.11.010
Guan XM, Guo MH, Sun LP (2010) Study on the relationship between surface color of veneer and dyeing technique for Pinus sylvest var. mongolica. Wood Process Mach 2:16–19
Hao XH, Li ML, Huang YS, Sun YH, Zhang KX, Guo CG (2022) High-strength, dimensionally stable, and flame-retardant fast-growing poplar prepared by ammonium polyphosphate–waterborne epoxy impregnation. ACS Appl Polym Mater 4(2):1305–1313. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.1c01712
Jasiūnas L, Peck G, Bridžiuvienė D, Mikniusa L (2020) Mechanical, thermal properties and stability of high renewable content liquefied residual biomass derived bio-polyurethane wood adhesives. Int J Adhes Adhes. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2020.102618
Jiang J, Zhou YJ, Mei CT, Cao JZ (2021) Polyethylene glycol and silica sol penetration improves hydrophobicity and dimensional stability of wood after a short-time treatment. Eur J Wood Prod 79:1395–1404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-021-01710-5
Kirilovs E, Kukle S, Gravitis J, Gusovius H (2017) Moisture absorption properties of hardwood veneers modified by a sol-gel process. Holzforschung 71(7–8):645–648. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2016-0151
Kuai BB, Wang ZH, Gao JS, Tong JW, Zhan TY, Zhang YL et al (2022) Development of densified wood with high strength and excellent dimensional stability by impregnating delignified poplar by sodium silicate. Constr Build Mater 344:128282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128282
Li P, Zhang Y, Zuo YF, Wu YQ, Yuan GM, Lu JX (2021) Comparison of silicate impregnation methods to reinforce Chinese fir wood. Holzforschung 75(2):126–137. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2020-0016
Liodakis S, Antonopoulos I, Tsapara V (2009) Forest fire retardancy evaluation of carbonate minerals using DTG and LOI. J Therm Anal Calorim 96:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9378-3
Lu Y, Feng M, Zhan H (2014) Preparation of SiO2–wood composites by an ultrasonic-assisted sol–gel technique. Cellulose 21:4393–4403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0437-6
Mirzaei G, Mohebby B, Ebrahimi G (2017) Glulam beam made from hydrothermally treated poplar wood with reduced moisture induced stresses. Constr Build Mater 135(15):386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.178
Miyafuji H, Saka S (2001) Na2O-SiO2 wood-inorganic composites prepared by the sol-gel process and their fire-resistant properties. J Wood Sci 47:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00767902
Olek W, Bonarski JT (2014) Effects of thermal modification on wood ultrastructure analyzed with crystallographic texture. Holzforschung 68(6):721–726. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2013-0165
Ping LJ, Chai YB, Sun BL, Liu JL (2020) Assessment of the physico-mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of rubber wood modified with silica sol in combination with GU/GMU resins. BioResources 15(4):8051–8064. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.4.8051-8064
Plötze M, Niemz P (2011) Porosity and pore size distribution of different wood types as determined by mercury intrusion porosimetry. Eur J Wood Prod 69:649–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0504-0
Pries M, Mai C (2013) Fire resistance of wood treated with a cationic silica sol. Eur J Wood Prod 71(2):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-013-0674-7
Seco AM, Goncalves MC, Rui MA (2000) Densification of hybrid silica–titania sol–gel films studied by ellipsometry and FTIR. Mater Sci Eng 76(3):193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5107(00)00442-6
Thakur AK, Kumar P, Parmar N, Shandil RK, Aggarwal G, Gaur A, Srivastava DK (2021) Achievements and prospects of genetic engineering in poplar: a review. New for 52:889–920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-021-09836-3
Vîlcu R, Irinei F, Ionescu-Bujor J, Olteanu M, Demetrescu I (1985) Kinetic parameters obtained from TG and DTG curves of acrylamide-maleic anhydride copolymers. J Therm Anal 30:495–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02156514
Wang GJ, Yang JY, Shi Q (2011) Preparation of transparent ultrahydrophobic silica film by sol-gel process. J Coat Technol Res 8:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-010-9270-5
Wang XJ, Tu DY, Chen CF, Zhou QF, Huang HX, Zheng ZH, Zhu Z (2021) A thermal modification technique combining bulk densification and heat treatment for poplar wood with low moisture content. Constr Build Mater 291:123395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123395
Xu DM, Ji Q, Tan LW, Tian GX, Quan FY, Xia YZ (2014) Influence of alkaline metal ions on flame retardancy and thermal degradation of cellulose fibers. Fibers Polym 15:220–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0220-1
Xu EG, Zhang YJ, Lin LY (2020) Improvement of mechanical, hydrophobicity and thermal properties of Chinese fir wood by impregnation of nano silica sol. Polymers 12(8):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081632
Yan W, Chen Z, Yu Q, Zhu W, Wang H, Du BQ (2016) Effects of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether AEO on PbO2 structure and electrodeposition behavior. J Electrochem Soc 163(8):D414. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0731608jes
Yan JY, Nie W, Xiu ZH, Yuan MY, Zhou WW, Bao Q, Peng H, Niu W, Yu F (2021) Development and characterization of a dust suppression spray agent based on an adhesive NaAlg-gln-poly/polysaccharide polymer. Sci Total Environ 785:147192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147192
Acknowledgements
We thank the financial supports from financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32260361) and National Natural Science Foundation of China Major Program (Grant No. 31890771), Guizhou Science and Technology Supporting Plan [Grant No. 2021:334] and [Grant No. 2021:186]. Guizhou forestry research project [Grant No. 2019:5] and [Grant No. 2022:14].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SY and ZL wrote the main manuscript text, ZL and ZW prepared figures 1–8. All authors reviewed the manuscript. ZL and SY contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Liu, Z., Wang, Z. et al. Organic–inorganic hybrid of silica sol to promote flame retardant and mechanical properties of wood. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 81, 1313–1325 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-023-01944-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-023-01944-5