Abstract
Introduction
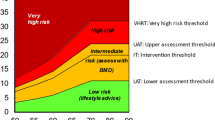
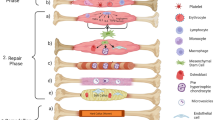
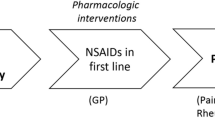
Long bone fractures (LBF) often cause severe pain, impacting patients’ quality of life. This prospective, randomized, double-blind study aimed to compare the analgesic efficacy of dexketoprofen (Dex) and ibuprofen (Ibu) in LBF patients in the emergency department.
Methods
Conducted between August 10, 2023, and January 17, 2024, the study included 100 eligible patients randomized into Dex and Ibu groups. Visual analog scale (VAS) scores were measured at baseline and at 30, 60, and 120 min. DeltaVAS (ΔVAS) values and ΔVAS percentages (ΔVAS%) were calculated. Primary endpoints were ΔVAS scores (ΔVAS 30-60-120) and ΔVAS% for comparative analysis.
Results
Statistical analysis showed no significant difference in ΔVAS30 (p = 0.359). However, ΔVAS60 exhibited a significant difference (p = 0.027), as did ΔVAS120 (p = < 0.001). ΔVAS%30 showed no significance (p = 0.224), but ΔVAS%60 and ΔVAS%120 were clinically and statistically significant (p = 0.017 and p = < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion
Ibuprofen 800 mg demonstrated superior analgesic efficacy at 60 and 120 min compared to Dex in long bone fractures. These findings suggest ibuprofen’s potential as an effective pain management option in emergency departments.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Woolf CJ. Central sensitization: implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain. 2011;152(3 Suppl):S2–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2010.09.030.
Hall JK, Boswell MV. Ethics, law, and pain management as a patient right. Pain Physician. 2009;12(3):499–506.
Yılmaz M, Kudu E, Sanri E, Karacabey S, Akoglu H, Denizbasi A. Comparison of the analgesic effects of low-dose ketamine versus fentanyl in patients with long bone fractures in the emergency department: a prospective observational study. Cureus. 2023;15(10):e46344. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.46344.
Cetin M, Kaya B, Kilic TY, Hanoğlu ND, Gökhan Ş, Eroğlu SE, &, et al. Pain management practices in the emergency departments in Turkey. Turk J Emerg Med. 2021;21(4):189–97. https://doi.org/10.4103/2452-2473.329633.
Lewis LM, Lasater LC, Brooks CB. Are emergency physicians too stingy with analgesics? South Med J. 1994;87(1):7–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007611-199401000-00002.
Awolola AM, Campbell L, Ross A. Pain management in patients with long-bone fractures in a district hospital in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2015;7(1):818. https://doi.org/10.4102/phcfm.v7i1.818.
Minick P, Clark PC, Dalton JA, Horne E, Greene D, Brown M. Long-bone fracture pain management in the emergency department. J Emerg Nurs. 2012;38(3):211–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jen.2010.11.001.
Elsevier H, Cannada LK. Management of pain associated with fractures. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(3):130–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-020-00578-3.
Amaechi O, Huffman MM, Featherstone K. Pharmacologic therapy for acute pain. Am Fam Physician. 2021;104(1):63–72.
Blondell RD, Azadfard M, Wisniewski AM. Pharmacologic therapy for acute pain. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87(11):766–72.
Inal S, Kabay S, Cayci MK, Kuru HI, Altikat S, Akkas G, &, et al. Comparison of the effects of dexketoprofen trometamol, meloxicam and diclofenac sodium on fibular fracture healing, kidney and liver: an experimental rat model. Injury. 2014;45(3):494–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2013.10.002.
Ergin M, Girisgin AS, Dundar ZD, Calik GS, Ertas I, Egici MT. Is it possible to objectify the visual pain scale? Pak J Med Sci. 2015;31(6):1527–32. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.316.8269.
Friday JH, Kanegaye JT, McCaslin I, Zheng A, Harley JR. Ibuprofen provides analgesia equivalent to acetaminophen-codeine in the treatment of acute pain in children with extremity injuries: a randomized clinical trial. Acad Emerg Med Off J Soc Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16(8):711–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2009.00471.x.
Maleki Verki M, Mozafari J, Tirandaz F, Motamed H, Khazaeli A. Efficacy of nebulized fentanyl and low dose ketamine for pain control of patients with long bone fractures: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Afr J Emerg Medi : Revue africaine de la medecine d’urgence. 2019;9(3):119–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afjem.2019.02.003.
Pines JM, Hollander JE. Emergency department crowding is associated with poor care for patients with severe pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2008;51(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2007.07.008.
Jahanian F, Hosseininejad SM, AminiAhidashti H, Bozorgi F, GoliKhatir I, Montazar SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of morphine and low dose ketamine for pain control of patients with long bone fractures: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2018;6(1):31–6. https://doi.org/10.29252/beat-060105.
Majidinejad S, Esmailian M, Emadi M. Comparison of intravenous ketamine with morphine in pain relief of long bones fractures: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Emergency. 2014;2(2):77–80 (Tehran, Iran).
Moore RA, Derry S, Wiffen PJ, Straube S, Aldington DJ. Overview review: comparative efficacy of oral ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen) across acute and chronic pain conditions. Eur J Pain. 2015;19(9):1213–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.649. (London, England).
Dogan C, Yilmaz A, Ozen M, Seyit M, Oskay A, Kemanci A, et al. Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of intravenous paracetamol, dexketoprofen and ibuprofen in acute low back pain. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;56:223–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.017.
Dönmez S, Erdem AB, Şener A, Kocak AO. Randomized double-blind comparison of intravenous ibuprofen and dexketoprofen in the acute treatment of tension-type headache. Dünya Sağlık ve Tabiat Bilimleri Dergisi. 2022;5(2):116–22.
Şafak S, Çorbacioğlu ŞK, Korucu O, Emektar E, Çevik Y. Comparison of ibuprofen and dexketoprofen in the management of migraine-related headache in the emergency department. Notfall+ Rettungsmedizin. 2022;25(Suppl 2):31–37.
Özdemir M, Çığşar G, Bağcıoğlu M, Çiftçi H, Günal E. Comparison of the analgesic effects of intravenous dexketoprofen, ibuprofen and fentanyl in patients suffering from renal colic pain in the emergency department. Eurasian J Emerg Med. 2023;22(1):18–23
Drendel AL, Gorelick MH, Weisman SJ, Lyon R, Brousseau DC, Kim MK. A randomized clinical trial of ibuprofen versus acetaminophen with codeine for acute pediatric arm fracture pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2009;54(4):553–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2009.06.005.
Lyngstad G, Skjelbred P, Swanson DM, Skoglund LA. Analgesic effect of oral ibuprofen 400, 600, and 800 mg; paracetamol 500 and 1000 mg; and paracetamol 1000 mg plus 60 mg codeine in acute postoperative pain: a single-dose, randomized, placebo-controlled, and double-blind study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;77(12):1843–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-021-03231-9.
Yilmaz A, Sabirli R, Ozen M, Turkcuer I, Erdur B, Arikan C, et al. Intravenous paracetamol versus dexketoprofen in acute musculoskeletal trauma in the emergency department: a randomised clinical trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(5):902–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2018.08.023.
Dogruyol S, Gur STA, Akbas I, Kocak MB, Kocak AO, Ceylan M, et al. Intravenous ibuprofen versus sodium valproate in acute migraine attacks in the emergency department: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;55:126–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.02.046.
Karacabey S, Sanri E, Yalcinli S, Akoglu H. Which is more effective for the treatment of acute migraine attack: dexketoprofen, ibuprofen or metoclopramide? Pak J Med Sci. 2018;34(2):418–23. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.342.13815.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.D., A.S., N.I.I.: writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, visualization, validation, supervision, software, resources, project administration, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, data curation, conceptualization. B.K., K.Y.: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, validation, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. I.A: writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, resources, project administration, investigation, formal analysis, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dönmez, S., Sener, A., Ishak Isık, N. et al. Comparison of analgesic efficacy of ibuprofen and dexketoprofen in pain management of long bone fractures: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-024-02515-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-024-02515-w