Abstract
Purpose
This retrospective study aimed to assess the safety and technical efficacy of preoperative direct puncture embolization using a nonadhesive ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) copolymer-based liquid embolic agent (LEA) combined with balloon occlusion at the origin of the external carotid artery for head and neck paragangliomas (HNP).
Methods
We conducted a review of all consecutive cases of HNPs treated with direct puncture embolization using EVOH-based LEAs between 2017 and 2022 in 2 tertiary high-volume hospitals.
Results
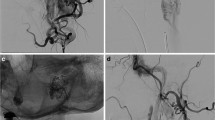
A total of 25 cases of HNPs in 24 patients underwent direct puncture embolization (12 males, 12 females, mean age 50.9 ± 15.6 years). The average lesion volume was 299.95 mm3. The mean procedure time was 139.11 min, and the mean volume of EVOHs used per case was 19.38 mL. Successful complete devascularization was achieved in all cases, with a homogeneous and deep penetration of the embolic agent into the tumor vessel bed regardless of the LEA type.
Conclusion
Preoperative embolization of HNPs using a direct puncture technique and EVOHs is a safe, efficient, and feasible treatment option with a low risk of complications. This procedure facilitates surgery by transforming tumors into avascular masses that are well-delineated against the surrounding normal tissue.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Data are available upon reasonable request.
References
Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, Brugge K. Temporal and cervical tumors. In: Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, Brugge, editors. Surgical neuroangiography: Clinical and endovascular treatment of craniofacial lesions. Aspects in adults. 2nd ed. New York: Springer; 2004. pp. 127–62.
Van Den Berg G, Rodesch G, Lasjaunias P. Management of paragangliomas: clinical and angiographic Aspects. Interv Neuroradiol. 2002;8:127:134.
Borges LF, Heros RC, DeBrun G. The carotid body tumors managed with preoperative embolization: Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1983;59:867–70.
Erickson D, Kudva YC, Ebersold MJ, et al. Benign paragangliomas: Clinical presentation and treatment outcomes in 236 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:5210–6.
Casasco A, Herbreteau D, Houdart E, et al. Devascularization of craniofacial tumors by percutaneous tumor puncture. Am J Neuroradiol. 1994;15:1233–9.
Chaloupka JC, Mangla S, Huddle DC, et al. Evolving experience with direct puncture therapeutic embolization for adjunctive and palliative management of head and neck hypervascular neoplasms. Laryngoscope. 1999;109:1864–72.
Texakalidis P, Charisis N, Giannopoulos S, et al. Role of preoperative embolization in carotid body tumor surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;129:503–13.
Casasco A, Houdart E, Biondi A, et al. Major complications of percutaneous embolization of skull-base tumors. Ajnr Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20(1):179–81.
Telischak N, Gross BA, Zeng Y, et al. The glomic artery supply of carotid body tumors and implications for embolization. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(7):1176–9.
Wanke I, Jackel MC, Goericke S, et al. Percutaneous embolization of carotid paragangliomas using solely Onyx. Ajnr Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(8):1594–7.
Akmangit I, Daglioglu E, Kaya T, et al. Preliminary experience with squid: a new liquid embolizing agent for AVM, AV fistulas and tumors. Turk Neurosurg. 2014;24(4):565–70.
Murayama Y, Viñuela F, Ulhoa A, et al. Nonadhesive liquid embolic agent for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: preliminary histopathological studies in swine rete mirabile. Neurosurgery. 1998;43(5):1164–75.
Puri AS, Thiex R, Zarzour H, Rahbar R, Orbach DB. Trigeminocardiac reflex in a child during pre-Onyx DMSO injection for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma embolization. A case report. Interv Neuroradiol. 2011;17(1:13–6.
Mounayer C, Hammami N, Piotin M, et al. Nidal embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations using Onyx in 94 patients. Ajnr Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(3):518–23.
Vollherbst DF, Chapot R, Bendszus M, Möhlenbruch MA. Glue, Onyx, Squid or PHIL? Liquid Embolic Agents for the Embolization of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas. Clin Neuroradiol. 2022;32(1):25–38.
Abud DG, Mounayer C, Benndorf G, Piotin M, Spelle L, Moret J. Intratumoral injection of cyanoacrylate glue in head and neck paragangliomas. Ajnr Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(9):1457–62.
Vollherbst DF, Otto R, Hantz M, et al. Investigation of a New Version of the Liquid Embolic Agent PHIL with Extra-Low-Viscosity in an Endovascular Embolization Model. Ajnr Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39(9):1696–702.
Gonzalez-Urquijo M, Hinojosa-Gonzalez D, Viteri-Pérez VH, et al. An analysis from the CAPACITY database of outcomes of preoperative embolization before carotid body tumor surgery compared with resection alone. J Vasc Surg. 2023;77(5):1447–52.
Pedicelli A, Lozupone E, Valente I, et al. Pre-operative direct puncture embolization of head and neck hypervascular tumors using SQUID 12. Interv Neuroradiol. 2020;26(3):346–53.
Han T, Pu J, Tang H, et al. Retrospective, multicenter study of surgical treatment for carotid body tumors with or without preoperative embolization. Front Oncol. 2023;2;13:1123430.
De Marini P, Greget M, Boatta E, et al. Safety and technical efficacy of pre-operative embolization of head and neck paragangliomas: A 10-year mono-centric experience and systematic review. Clin Imaging. 2021;80:292–9.
Paolucci A, Ierardi AM, Hohenstatt S, et al. Pre-surgical embolization of carotid body paragangliomas: advantages of direct percutaneous approach and transitory balloon-occlusion at the origin of the external carotid artery. Radiol Med. 2022;127(4):433–9.
Shah HM, Gemmete JJ, Chaudhary N, Pandey AS, Ansari SA. Preliminary experience with the percutaneous embolization of paragangliomas at the carotid bifurcation using only ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) Onyx. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012;4(2):125–9.
Elhammady MS, Peterson EC, Johnson JN, et al. Preoperative Onyx embolization of vascular head and neck tumors by direct puncture. World Neurosurg. 2012;77:725–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A.M. Alexandre, L. Scarcia, F. Clarençon, A. Camilli, A. Bartolo, F. Incandela, D.A. Mele, M. Rigante, M. Natola, I. Valente, F. D’Argento, J. Galli, Y. Tshomba and A. Pedicelli declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study is part of a nonprofit research protocol approved by the ethics committee of the coordinating center (Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A.Gemelli IRCCS, protocol ID 3957). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in our series.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandre, A.M., Scarcia, L., Clarençon, F. et al. Preoperative Direct Puncture Embolization Using a Nonadhesive Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol (EVOH) Liquid Embolic Agent for Head and Neck Paragangliomas. Clin Neuroradiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-023-01364-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-023-01364-1