Abstract
Purpose
Wall enhancement of intracranial aneurysms in vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been linked to aneurysm progression. The clinical significance of aneurysm enhancement after embolization has not yet been investigated. The goal of this study was to identify factors associated with aneurysm wall enhancement and reperfusion after embolization.
Methods
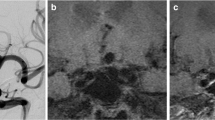
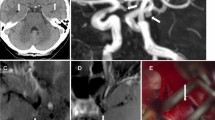
Patients who underwent treatment of intracranial aneurysms with coils or the Woven Endobridge (WEB) and follow-up MR vessel wall imaging were included. Enhancement of the treated aneurysms was separately recorded for the following locations: a) wall at the neck, b) wall at the dome, and c) in the aneurysmal cavity. Reperfusion was determined on follow-up digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and MR time of flight (TOF) angiography.
Results
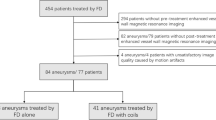
In this study 48 patients with 53 aneurysms were included. Wall enhancement at the neck and the dome of the aneurysm was significantly associated with time between embolization and follow-up MRI under 6 months. Enhancement inside the aneurysmal cavity was significantly associated with a follow-up time longer than 6 months, and with stable aneurysms without reperfusion.
Conclusion
Wall enhancement is a regular feature in intracranial aneurysms after embolization and decreases over time. Enhancement inside the aneurysmal cavity is associated with a stable state and could possibly serve as an imaging marker of completed aneurysm healing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edjlali M, Guédon A, Ben Hassen W, Boulouis G, Benzakoun J, Rodriguez-Régent C et al. Circumferential thick enhancement at vessel wall MRI has high specificity for Intracranial aneurysm instability. Radiology. 2018;289:181–7.
Fu Q, Guan S, Liu C, Wang K, Cheng J. Clinical significance of circumferential aneurysmal wall enhancement in symptomatic patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a high-resolution MRI study. Clin Neuroradiol. 2018;28:509–14.
Hartman JB, Watase H, Sun J, Hippe DS, Kim L, Levitt M, et al. Intracranial aneurysms at higher clinical risk for rupture demonstrate increased wall enhancement and thinning on multicontrast 3D vessel wall MRI. Br J Radiol. 2019;92:20180950.
Lv N, Karmonik C, Chen S, Wang X, Fang Y, Huang Q, et al. Relationship between aneurysm wall enhancement in vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging and rupture risk of unruptured Intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2019;84:E385–91.
Omodaka S, Endo H, Niizuma K, Fujimura M, Inoue T, Sato K, et al. Quantitative assessment of circumferential enhancement along the wall of cerebral aneurysms using MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37:1262–6.
Raymond J, Darsaut TE. An approach to recurrent aneurysms following endovascular coiling. J Neurointerv Surg. 2011;3:314–8.
Caroff J, Mihalea C, Klisch J, Strasilla C, Berlis A, Patankar T, et al. Single-Layer WEBs: Intrasaccular Flow Disrupters for Aneurysm Treatment—Feasibility Results from a European Study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36:1942–6.
Bavinzski G, Talazoglu V, Killer M, Richling B, Gruber A, Gross CE, et al. Gross and microscopic histopathological findings in aneurysms of the human brain treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Neurosurg. 1999;91:284–93.
Ishihara S, Mawad ME, Ogata K, Suzuki C, Tsuzuki N, Katoh H, et al. Histopathologic findings in human cerebral aneurysms embolized with platinum coils: report of two cases and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23:970–4.
Stiver SI, Porter PJ, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC. Acute human histopathology of an intracranial aneurysm treated using Guglielmi detachable coils: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1998;43:1203–7.
Groden C, Hagel C, Delling G, Zeumer H. Histological findings in ruptured aneurysms treated with GDcs: six examples at varying times after treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:579–84.
Horowitz MB, Purdy PD, Burns D, Bellotto D. Scanning electron microscopic findings in a basilar tip aneurysm embolized with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18:688–90.
Shimizu S, Kurata A, Takano M, Takagi H, Yamazaki H, Miyasaka Y, et al. Tissue response of a small saccular aneurysm after incomplete occlusion with a Guglielmi detachable coil. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20:546–8.
Szikora I, Seifert P, Hanzely Z, Kulcsar Z, Berentei Z, Marosfoi M, et al. Histopathologic evaluation of aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils or matrix detachable microcoils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27:283–8.
Molyneux AJ, Ellison DW, Morris J, Byrne JV. Histological findings in giant aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. Report of two cases with autopsy correlation. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:129–32.
Su IC, Willinsky RA, Fanning NF, Agid R. Aneurysmal wall enhancement and perianeurysmal edema after endovascular treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Neuroradiology. 2014;56:487–95.
Funding
Jawid Madjidyar acknowledges funding from the German Research Foundation (DFG) through the project GRK 2154 “Materials for Brain”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
N. Larsen, C. Flüh, J. Madjidyar, M. Synowitz, O. Jansen and F. Wodarg declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, N., Flüh, C., Madjidyar, J. et al. Visualization of Aneurysm Healing. Clin Neuroradiol 30, 811–815 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-019-00854-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-019-00854-5