Abstract
Introduction
Stent-assisted coiling of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms has become an established treatment and has significantly benefited from the introduction of compliant, self-expanding devices, such as the Enterprise VRD (EP-VRD). We report our experiences with the successor model, the Enterprise2 (EP2) stent in stent-assisted coiling as well as in the treatment of atherosclerotic stenosis.
Materials and Methods
In 11 consecutive patients 12 EP2 were used to treat 9 intracranial aneurysms and 2 stenoses.
Results
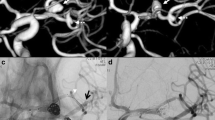
All stents could easily be delivered including partial or complete recapturing when necessary. In two cases with sharp angled curves in the carotid siphon there was kinking and flattening of the stent resulting in incomplete wall apposition of the stent. Moreover, when vascular anatomy showed curves with angles >50° it was regularly observed that the proximal stent markers were asymmetrically arranged along the vessel circumference without influence on the stent apposition. Both findings could be reproduced in a silicone flow model.
Conclusion
The EP2 performed well in our small patient cohort; however, above a critical acute angle there may be incomplete wall apposition of the stent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chalouhi N, Jabbour P, Singhal S, Drueding R, Starke RM, Dalyai RT, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez LF, Dumont AS, Rosenwasser R, Randazzo CG. Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms: predictors of complications, recanalization, and outcome in 508 cases. Stroke. 2013;44:1348–53.
Dashti SR, Fiorella D, Toledo MM, Hu Y, McDougall CG, Albuquerque FC. Proximal migration and compaction of an Enterprise stent into a coiled basilar apex aneurysm: a posterior circulation phenomenon? J Neurointerv Surg. 2010;2:356–8.
Ebrahimi N, Claus B, Lee CY, Biondi A, Benndorf G. Stent conformity in curved vascular models with simulated aneurysm necks using flat-panel CT: an in vitro study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:823–9.
Fargen KM, Hoh BL, Welch BG, Pride GL, Lanzino G, Boulos AS, Carpenter JS, Rai A, Veznedaroglu E, Ringer A, Rodriguez-Mercado R, Kan P, Siddiqui A, Levy EI, Mocco J. Long-term results of enterprise stent-assisted coiling of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2012;71:239–44, discussion 244.
Feng Z, Duan G, Zhang P, Chen L, Xu Y, Hong B, Zhao W, Liu J, Huang Q. Enterprise stent for the treatment of symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: an initial experience of 44 patients. BMC Neurol. 2015;15:187.
Gao B, Malek AM. Possible mechanisms for delayed migration of the closed cell – designed enterprise stent when used in the adjunctive treatment of a basilar artery aneurysm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:E85–E86.
Geyik S, Yavuz K, Yurttutan N, Saatci I, Cekirge HS. Stent-assisted coiling in endovascular treatment of 500 consecutive cerebral aneurysms with long-term follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:2157–62.
Heller R, Calnan DR, Lanfranchi M, Madan N, Malek AM. Incomplete stent apposition in enterprise stent-mediated coiling of aneurysms: persistence over time and risk of delayed ischemic events. J Neurosurg. 2013;118:1014–22.
Heller RS, Malek AM. Parent vessel size and curvature strongly influence risk of incomplete stent apposition in enterprise intracranial aneurysm stent coiling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:1714–20.
Heller RS, Miele WR, Do-Dai DD, Malek AM. Crescent sign on magnetic resonance angiography revealing incomplete stent apposition: correlation with diffusion-weighted changes in stent-mediated coil embolization of aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2011;115:624–32.
Jia J, Lv X, Liu A, Li Y. Enterprise stent-assisted coiling of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms: clinical and angiographic follow-up. Interv Neuroradiol. 2012;18:426–31.
Kadkhodayan Y, Rhodes N, Blackburn S, Derdeyn CP, Cross DT 3rd, Moran CJ. Comparison of Enterprise with Neuroform stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200:872–8.
Kelly ME, Turner RD 4th, Moskowitz SI, Gonugunta V, Hussain MS, Fiorella D. Delayed migration of a self-expanding intracranial microstent. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:1959–60.
Kono K, Terada T. In vitro experiments of vessel wall apposition between the enterprise and enterprise 2 stents for treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016;158:241–5.
Lavine SD, Meyers PM, Connolly ES, Solomon RS. Spontaneous delayed proximal migration of enterprise stent after staged treatment of wide-necked basilar aneurysm: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2009;64:E1012, discussion E1012.
Lee KY, Chen DY, Hsu HL, Chen CJ, Tseng YC. Undersized angioplasty and stenting of symptomatic intracranial tight stenosis with Enterprise: Evaluation of clinical and vascular outcome. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015;22:187-95.
Lobotesis K, Gholkar A, Jayakrishnan V. Early migration of a self expanding intracranial stent: case report. Neurosurgery. 2010;67:E516–E517.
Mocco J, Snyder KV, Albuquerque FC, Bendok BR, Alan S B, Carpenter JS, Fiorella DJ, Hoh BL, Howington JU, Jankowitz BT, Liebman KM, Rai AT, Rodriguez-Mercado R, Siddiqui AH, Veznedaroglu E, Hopkins LN, Levy EI. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the Enterprise stent: a multicenter registry. J Neurosurg. 2009;110:35–9.
Nishido H, Piotin M, Bartolini B, Pistocchi S, Redjem H, Blanc R. Analysis of complications and recurrences of aneurysm coiling with special emphasis on the stent-assisted technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35:339–44.
Vajda Z, Schmid E, Güthe T, Klötzsch C, Lindner A, Niehaus L, Sperber W, Peters J, Arnold G, Bäzner H, Henkes H. The modified Bose method for the endovascular treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic arterial stenoses using the Enterprise stent. Neurosurgery. 2012;70:91–101, discussion 101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
C. Herweh, S. Nagel, J. Pfaff, C. Ulfert, M. Wolf, M. Bendszus and M. Möhlenbruch declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki in its current version and the current version of ICH-GCP principles and was approved by our local ethics committee (ethics committee of the University of Heidelberg; ID: S‑247/2009). All patients gave written and informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herweh, C., Nagel, S., Pfaff, J. et al. First Experiences with the New Enterprise2® Stent. Clin Neuroradiol 28, 201–207 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-016-0545-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-016-0545-9