Abstract
Purpose
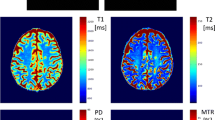
Phase imaging provides additional information on multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions and may in combination with mean diffusivity (MD) and magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) help differentiating heterogeneity of MS lesion pathology.
Methods
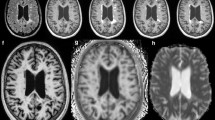
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed in 23 MS patients including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), magnetization transfer imaging (MTI), and SWI. Mean values (MTR, MD, and homodyne filtered phase) from 138 chronic MS lesions and normal appearing white matter (NAWM) were obtained and correlations examined. For explorative analysis, a divisive hierarchical clustering algorithm was applied.
Results
Phase characteristics were an independent characteristic of chronic T2 lesions, as MTR and MD were not correlated with phase values (R = − 0.23, R = − 0.18). Dependent on MTR, MD, and phase, cluster analysis led to five lesion groups. Of the two groups with phase values close to NAWM, one presented with highest MD and most severe MTR decrease (p = 0.01), the other with slight MD increase and MTR decrease. Two lesion groups with highest phase values (p = 0.01) displayed slightly increased MD and moderate decrease in MTR. Clinical data including EDSS, disease duration, and age did not differ significantly between groups.
Conclusions
Increased phase is predominantly detectable in lesions with clear MTR decrease but only moderate MD increase. Phase images seem to represent an independent parameter for MS lesion characterization and may provide additional information on MS lesion heterogeneity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daumer M, Neuhaus A, Morrissey S, Hintzen R, Ebers GC. MRI as an outcome in multiple sclerosis clinical trials. Neurology. 2009;72(8):705–11. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000336916.38629.43.
Zivadinov R. Can imaging techniques measure neuroprotection and remyelination in multiple sclerosis? Neurology. 2007;68(22 Suppl 3):S72–82. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000275236.51129.d2.
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products for the treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. European Medicines Agency. 2012; EMA/CHMP/771815/2011, Rev2.
Haacke EM, Cheng NY, House MJ, Liu Q, Neelavalli J, Ogg RJ, Khan A, Ayaz M, Kirsch W, Obenaus A. Imaging iron stores in the brain using magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;23(1):1–25. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2004.10.001.
Bagnato F, Hametner S, Yao B, van Gelderen P, Merkle H, Cantor FK, Lassmann H, Duyn JH. Tracking iron in multiple sclerosis: a combined imaging and histopathological study at 7 Tesla. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 12):3602–15. doi:10.1093/brain/awr278.
Yao B, Li TQ, Gelderen P, Shmueli K, de Zwart JA, Duyn JH. Susceptibility contrast in high field MRI of human brain as a function of tissue iron content. Neuroimage. 2009;44(4):1259–66. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.029.
He X, Yablonskiy DA. Biophysical mechanisms of phase contrast in gradient echo MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(32):13558–63. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904899106.
Li TQ, Yao B, van Gelderen P, Merkle H, Dodd S, Talagala L, Koretsky AP, Duyn J. Characterization of T(2)* heterogeneity in human brain white matter. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62(6):1652–7. doi:10.1002/mrm.22156.
Haacke EM, Makki M, Ge Y, Maheshwari M, Sehgal V, Hu J, Selvan M, Wu Z, Latif Z, Xuan Y, Khan O, Garbern J, Grossman RI. Characterizing iron deposition in multiple sclerosis lesions using susceptibility weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29(3):537–44. doi:10.1002/jmri.21676.
Eissa A, Lebel RM, Korzan JR, Zavodni AE, Warren KG, Catz I, Emery DJ, Wilman AH. Detecting lesions in multiple sclerosis at 4.7 T using phase susceptibility-weighting and T2-weighting. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30(4):737–42. doi:10.1002/jmri.21926.
Walsh AJ, Blevins G, Lebel RM, Seres P, Emery DJ, Wilman AH. Longitudinal MR imaging of iron in multiple sclerosis: an imaging marker of disease. Radiology. 2014;270(1):186–96. doi:10.1148/radiol.13130474.
Walsh AJ, Lebel RM, Eissa A, Blevins G, Catz I, Lu JQ, Resch L, Johnson ES, Emery DJ, Warren KG, Wilman AH. Multiple sclerosis: validation of MR imaging for quantification and detection of iron. Radiology. 2013;267(2):531–42. doi:10.1148/radiol.12120863.
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B. 1996;111(3):209–19.
Fox RJ. Picturing multiple sclerosis: conventional and diffusion tensor imaging. Semin Neurol. 2008;28(4):453–66. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1083689.
Seewann A, Vrenken H, van der Valk P, Blezer EL, Knol DL, Castelijns JA, Polman CH, Pouwels PJ, Barkhof F, Geurts JJ. Diffusely abnormal white matter in chronic multiple sclerosis: imaging and histopathologic analysis. Arch Neurol. 2009;66(5):601–9. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2009.57.
Schmierer K, Scaravilli F, Altmann DR, Barker GJ, Miller DH. Magnetization transfer ratio and myelin in postmortem multiple sclerosis brain. Ann Neurol. 2004;56(3):407–15. doi:10.1002/ana.20202.
Filippi M, Agosta F. Magnetization transfer MRI in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimaging. 2007;17(Suppl 1):22S–6S. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2007.00132.x.
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O'Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thompson AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol. 2011;69(2):292–302. doi:10.1002/ana.22366.
van Waesberghe JH, Kamphorst W, De Groot CJ, van Walderveen MA, Castelijns JA, Ravid R, Lycklama à Nijeholt GJ, van der Valk P, Polman CH, Thompson AJ, Barkhof F. Axonal loss in multiple sclerosis lesions: magnetic resonance imaging insights into substrates of disability. Ann Neurol. 1999;46(5):747–54.
Jenkinson M, Smith S. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal. 2001;5(2):143–56.
Hammond KE, Metcalf M, Carvajal L, Okuda DT, Srinivasan R, Vigneron D, Nelson SJ, Pelletier D. Quantitative in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of multiple sclerosis at 7 Tesla with sensitivity to iron. Ann Neurol. 2008;64(6):707–13. doi:10.1002/ana.21582.
Yao B, Bagnato F, Matsuura E, Merkle H, van Gelderen P, Cantor FK, Duyn JH. Chronic multiple sclerosis lesions: characterization with high-field-strength MR imaging. Radiology. 2012;262(1):206–15. doi:10.1148/radiol.11110601.
Droogan AG, Clark CA, Werring DJ, Barker GJ, McDonald WI, Miller DH. Comparison of multiple sclerosis clinical subgroups using navigated spin echo diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;17(5):653–61. doi:S0730-725X(99)00011-9.
Rovaris M, Gambini A, Gallo A, Falini A, Ghezzi A, Benedetti B, Sormani MP, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M. Axonal injury in early multiple sclerosis is irreversible and independent of the short-term disease evolution. Neurology. 2005;65(10):1626–30. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000184493.06254.a6.
Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR Biomed. 1995;8(7–8):333–44.
De Groot CJ, Bergers E, Kamphorst W, Ravid R, Polman CH, Barkhof F, van der Valk P. Post-mortem MRI-guided sampling of multiple sclerosis brain lesions: increased yield of active demyelinating and (p)reactive lesions. Brain. 2001;124(Pt 8):1635–45.
Bitsch A, Kuhlmann T, Stadelmann C, Lassmann H, Lucchinetti C, Bruck W. A longitudinal MRI study of histopathologically defined hypointense multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol. 2001;49(6):793–6.
Barkhof F, Bruck W, De Groot CJ, Bergers E, Hulshof S, Geurts J, Polman CH, van der Valk P. Remyelinated lesions in multiple sclerosis: magnetic resonance image appearance. Arch Neurol. 2003;60(8):1073–81. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.8.1073.
Bruck W, Bitsch A, Kolenda H, Bruck Y, Stiefel M, Lassmann H. Inflammatory central nervous system demyelination: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging findings with lesion pathology. Ann Neurol. 1997;42(5):783–93. doi:10.1002/ana.410420515.
Sahraian MA, Radue EW, Haller S, Kappos L. Black holes in multiple sclerosis: definition, evolution, and clinical correlations. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;122(1):1–8. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2009.01221.x.
van Walderveen MA, Kamphorst W, Scheltens P, van Waesberghe JH, Ravid R, Valk J, Polman CH, Barkhof F. Histopathologic correlate of hypointense lesions on T1-weighted spin-echo MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1998;50(5):1282–8.
Barkhof F, Karas GB, van Walderveen MA. T1 hypointensities and axonal loss. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2000;10(4):739–52.
Lassmann H. The pathologic substrate of magnetic resonance alterations in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2008;18(4):563–76. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2008.06.005.
Rovaris M, Gass A, Bammer R, Hickman SJ, Ciccarelli O, Miller DH, Filippi M. Diffusion MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2005;65(10):1526–32. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000184471.83948.e0.
Yablonskiy DA, Luo J, Sukstanskii AL, Iyer A, Cross AH. Biophysical mechanisms of MRI signal frequency contrast in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(35):14212–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206037109.
Wiggermann V, Hernandez Torres E, Vavasour IM, Moore GR, Laule C, MacKay AL, Li DK, Traboulsee A, Rauscher A. Magnetic resonance frequency shifts during acute MS lesion formation. Neurology. 2013;81(3):211–8. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31829bfd63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siemonsen, S., Young, K., Bester, M. et al. Chronic T2 Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis are Heterogeneous Regarding Phase MR Imaging. Clin Neuroradiol 26, 457–464 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-015-0389-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-015-0389-8