Abstract
Purpose
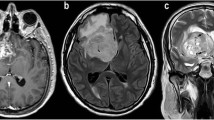
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the pivotal diagnostic step in patients with brain tumors, and is performed before histological diagnosis is available. We hypothesized that conventional MRI is as accurate as tumor histology in differentiating malignant from benign clinical course.
Methods
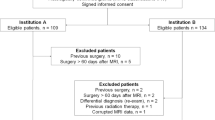
Two neuroradiologists blinded to any clinical information evaluated the first diagnostic MRI of 244 brain tumor patients before any treatment, using a self-developed standardized list of image criteria and prospectively determined world health organization (WHO) tumor grade and tumor entity. All patients were examined with at least T1- and T2-weighted spin echo sequences before and after contrast injection on 1 and 1.5-T MRI scanners. Following the patients prospectively for 8–13 years after diagnosis, we were able to use nonsurvival at 5 years as a criterion for malignity and reference for the prognostic accuracy of both MRI and tumor tissue histology.
Results
The accuracy for predicting nonsurvival at 5 years was 91 % (95 % confidence interval (CI): 87–94 %) for MRI and 92 % (95 % CI: 88–95 %) for histology. The Kaplan–Meier survival curves of patients with benign and malignant brain tumors as diagnosed by MRI or histology differed significantly (p < 0.001). Histology confirmed benignity or malignity in 201 patients (82 %, 95 % CI: 77–87 %). Sources of misdiagnosis were metastases diagnosed as astrocytoma WHO IV, atypical meningiomas, and low-grade astrocytoma with malignant transformation.
Conclusion
MRI appears as accurate as histology in predicting survival at 5 years after diagnosis. Histological diagnosis may be more specific, however, and is needed to assess the tumor’s specific biology.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young RJ, Knopp EA. Brain MRI: tumor evaluation. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24(4):709–24.
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114(2):97–109.
Westphal M, Lamszus K. The neurobiology of gliomas: from cell biology to the development of therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12(9):495–508.
Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas. 1960;20:37–46.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159–74.
Berry CC. A tutorial on confidence intervals for proportions in diagnostic radiology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154(3):477–80.
Outcomes of cancer treatment for technology assessment and cancer treatment guidelines. American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). J Clin Oncol 1996; 14(2): 671-9.
Ocana A, Tannock IF. When are “positive” clinical trials in oncology truly positive? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103(1):16–20.
McKee AE, Farrell AT, Pazdur R, Woodcock J. The role of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration review process: clinical trial endpoints in oncology. Oncologist. 2010;15(Suppl. 1):13–8.
Lutterbach J, Bartelt S, Momm F, Becker G, Frommhold H, Ostertag C. Is older age associated with a worse prognosis due to different patterns of care? A long-term study of 1,346 patients with glioblastomas or brain metastases. Cancer. 2005;103(6):1234–44.
Ramnarayan R, Dodd S, Das K, Heidecke V, Rainov NG. Overall survival in patients with malignant glioma may be significantly longer with tumors located in deep grey matter. J Neurol Sci. 2007;260(1–2):49–56.
McGirt MJ, Chaichana KL, Attenello FJ, Weingart JD, Than K, Burger PC, Olivi A, Brem H, Quinoñes-Hinojosa A. Extent of surgical resection is independently associated with survival in patients with hemispheric infiltrating low-grade gliomas. Neurosurgery. 2008;63(4):700–7. Author reply 707–8.
Grisold W, Krauseneck P, Müller B. Praktische Neuroonkologie. 1st ed. Wien: Springer-Verlag; 2000.
Kaye AH, Laws ER. Brain tumors: an encyclopedic approach. London: Churchhill Livingstone; 2001.
Al-Okaili RN, Krejza J, Woo JH, Wolf RL, O’Rourke DM, Judy KD, Poptani H, Melhem ER. Intraaxial brain masses: MR imaging-based diagnostic strategy—initial experience. Radiology. 2007;243(2):539–50.
Arvinda HR, Kesavadas C, Sarma PS, Thomas B, Radhakrishnan VV, Gupta AK, Kapilamoorthy TR, Nair S. Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of diffusion and perfusion imaging. J Neurooncol. 2009;94(1):87–96.
Fayed N, Davila J, Medrano J, Olmos S. Malignancy assessment of brain tumours with magnetic resonance spectroscopy and dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2008;67(3):427–33.
Law M, Yang S, Wang H, Babb JS, Johnson G, Cha S, Knopp EA, Zagzag D. Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(10):1989–98.
Möller-Hartmann W, Herminghaus S, Krings T, Marquardt G, Lanfermann H, Pilatus U, Zanella FE. Clinical application of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the diagnosis of intracranial mass lesions. Neuroradiology. 2002;44(5):371–81.
Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N. Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of cerebral gliomas. Neuroradiology. 1992;34(6):463–9.
Dean BL, Drayer BP, Bird CR, Flom RA, Hodak JA, Coons SW, Carey RG. Gliomas: classification with MR imaging. Radiology. 1990;174(2):411–5.
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Martinez AJ. Unreliability of contemporary neurodiagnostic imaging in evaluating suspected adult supratentorial (low-grade) astrocytoma. J Neurosurg. 1993;79(4):533–6.
Forsting M, Jansen O. MRT des Zentralnervensystems. Stuttgart: Thieme; 2006.
Hanft S, Canoll P, Bruce JN. A review of malignant meningiomas: diagnosis, characteristics, and treatment. J Neurooncol. 2010;99(3):433–43.
Warmuth-Metz M, Bison B, Leykamm S. Neuroradiologic review in pediatric brain tumor studies. Klin Neuroradiol. 2009;19(4):263–73.
Johannesen TB, Langmark F, Lote K. Progress in long-term survival in adult patients with supratentorial low-grade gliomas: a population-based study of 993 patients in whom tumors were diagnosed between 1970 and 1993. J Neurosurg. 2003;99(5):854–62.
Okamoto Y, Di Patre PL, Burkhard C, Horstmann S, Jourde B, Fahey M, Schüler D, Probst-Hensch NM, Yasargil MG, Yonekawa Y, Lütolf UM, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H. Population-based study on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations of low-grade diffuse astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2004;108(1):49–56.
Claus EB, Black PM. Survival rates and patterns of care for patients diagnosed with supratentorial low-grade gliomas: data from the SEER program, 1973–2001. Cancer. 2006;106(6):1358–63.
Tortosa A, Viñolas N, Villà S, Verger E, Gil JM, Brell M, Caral L, Pujol T, Acebes JJ, Ribalta T, Ferrer I, Graus F. Prognostic implication of clinical, radiologic, and pathologic features in patients with anaplastic gliomas. Cancer. 2003;97(4):1063–71.
Shaw EG, Scheithauer BW, O’Fallon JR. Supratentorial gliomas: a comparative study by grade and histologic type. J Neurooncol. 1997;31(3):273–8.
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P. Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol. 2007;170(5):1445–53.
Hakyemez B, Yildirim N, Erdogan C, Kocaeli H, Korfali E, Parlak M. Meningiomas with conventional MRI findings resembling intra-axial tumors: can perfusion-weighted MRI be helpful in differentiation? Neuroradiology. 2006;48(10):695–702.
Saloner D, Uzelac A, Hetts S, Martin A, Dillon W. Modern meningioma imaging techniques. J Neurooncol. 2010;99(3):333–40.
Shiroishi MS, Habibi M, Rajderkar D, Yurko C, Go JL, Lerner A, Mogensen MA, Kim PE, Boyko OB, Zee CS, Law M. Perfusion and permeability MR imaging of gliomas. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2011;10(1):59–71.
Morita N, Harada M, Otsuka H, Melhem ER, Nishitani H. Clinical application of MR spectroscopy and imaging of brain tumor. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2011;9(4):167–75.
Gerstner ER, Sorensen AG. Diffusion and diffusion tensor imaging in brain cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2011;21(2):141–6.
Schneider T, Mawrin C, Scherlach C, Skalej M, Firsching R. Gliomas in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011;107(45):799–807. Quiz 808.
Tilgner J, Herr M, Ostertag C, Volk B. Validation of intraoperative diagnoses using smear preparations from stereotactic brain biopsies: intraoperative versus final diagnosis—influence of clinical factors. Neurosurgery. 2005;56(2):257–65. Discussion 257–65.
Muragaki Y, Chernov M, Maruyama T, Ochiai T, Taira T, Kubo O, Nakamura R, Iseki H, Hori T, Takakura K. Low-grade glioma on stereotactic biopsy: how often is the diagnosis accurate? Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2008;51(5):275–9.
Klingebiel R, Bohner G. Neuroimaging. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2009;171:175–90.
Juratli TA, Kirsch M, Robel K, Soucek S, Geiger K, von Kummer R, Schackert G, Krex D. IDH mutations as an early and consistent marker in low-grade astrocytomas WHO grade II and their consecutive secondary high-grade gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2012;108:403–10.
Hall WA. The safety and efficacy of stereotactic biopsy for intracranial lesions. Cancer. 1998;82(9):1749–55.
Kreth FW, Muacevic A, Medele R, Bise K, Meyer T, Reulen HJ. The risk of haemorrhage after image-guided stereotactic biopsy of intra-axial brain tumours—a prospective study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001;143(6):539–45. Discussion 545–6.
Soo TM, Bernstein M, Provias J, Tasker R, Lozano A, Guha A. Failed stereotactic biopsy in a series of 518 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1995;64(4):183–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klingelhöfer, L., Mucha, D., Geiger, K. et al. Prognostic Value of Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Adult Patients with Brain Tumors. Clin Neuroradiol 25, 281–289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0309-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0309-3