Abstract
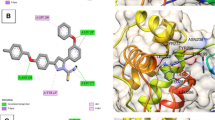
A novel class of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitors derived from 1,5,6,7-tetrahydro-4H-indazol-4-ones was designed. Virtual screening based on molecular docking followed by molecular dynamics simulation and MM/GBSA calculations was used for selecting compounds for synthesis and an evaluation. After testing 29 prepared compounds for activity against Mpro, two hits with IC50 values bellow 60 μM were found with the best result of 27.31 μM for racemic amide 9m. SAR and further possibilities for hit optimization were discussed. The effectiveness of different approaches (MM/GBSA and alchemical ABFE) for protein–ligand binding affinity prediction was assessed on the basis of obtained experimental data. The best convergence was achieved when we carried out long molecular dynamics simulations (200 ns) of complexes from docking followed by calculations of free binding energies with MM/GBSA method and explicit accounting of entropy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Liu Q, Guo D. Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J Med Virol. 2020;92:418–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25681.
Ye ZW, Yuan S, Yuen KS, Fung SY, Chan CP, Jin DY. Zoonotic origins of human coronaviruses. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16:1686–97. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.45472.
de Wit E, van Doremalen N, Falzarano D, Munster VJ. SARS and MERS: recent insights into emerging coronaviruses. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14:523–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.81.
Anand K, Ziebuhr J, Wadhwani P, Mesters JR, Hilgenfeld R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science. 2003;300:1763–7. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1085658.
Hilgenfeld R. From SARS to MERS: crystallographic studies on coronaviral proteases enable antiviral drug design. FEBS J. 2014;281:4085–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12936.
Liu Y, Liang C, Xin L, Ren X, Tian L, Ju X, et al. The development of Coronavirus 3C-Like protease (3CL(pro)) inhibitors from 2010 to 2020. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;206:112711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112711.
Cannalire R, Cerchia C, Beccari AR, Di Leva FS, Summa V. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 proteases and polymerase for COVID-19 treatment: state of the art and future opportunities. J Med Chem. 2022;65:2716–46. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01140.
Owen DR, Allerton CMN, Anderson AS, Aschenbrenner L, Avery M, Berritt S, et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science. 2021;374:1586–93. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abl4784.
Zhang L, Lin D, Sun X, Curth U, Drosten C, Sauerhering L, et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved alpha-ketoamide inhibitors. Science. 2020;368:409–12. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb3405.
Lockbaum GJ, Reyes AC, Lee JM, Tilvawala R, Nalivaika EA, Ali A, et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease in complex with the non-covalent inhibitor ML188. Viruses. 2021;13:174. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020174.
Stille JK, Tjutrins J, Wang G, Venegas FA, Hennecker C, Rueda AM, et al. Design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel SARS-CoV-2 3CL(pro) covalent inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2022;229:114046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.114046.
Han SH, Goins CM, Arya T, Shin WJ, Maw J, Hooper A. et al. Structure-based optimization of ML300-derived, noncovalent inhibitors targeting the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3CL protease (SARS-CoV-2 3CL(pro)). J Med Chem. 2022;65:2880–904. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00598.
Shcherbakov D, Baev D, Kalinin M, Dalinger A, Chirkova V, Belenkaya S, et al. Design and evaluation of bispidine-based SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022;13:140–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00299.
Ghosh AK, Raghavaiah J, Shahabi D, Yadav M, Anson BJ, Lendy EK, et al. Indole chloropyridinyl ester-derived SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors: enzyme inhibition, antiviral efficacy, structure-activity relationship, and X-ray structural studies. J Med Chem. 2021;64:14702–14. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01214.
Chen R, Gao Y, Liu H, Li H, Chen W, Ma J. Advances in research on 3C-like protease (3CL(pro)) inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 since 2020. RSC Med Chem. 2023;14:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2md00344a.
Li Z, Li X, Huang YY, Wu Y, Liu R, Zhou L, et al. Identify potent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors via accelerated free energy perturbation-based virtual screening of existing drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:27381–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2010470117.
Ghahremanpour MM, Tirado-Rives J, Deshmukh M, Ippolito JA, Zhang CH, Cabeza de Vaca I, et al. Identification of 14 known drugs as inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11:2526–33. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00521.
Zhang CH, Stone EA, Deshmukh M, Ippolito JA, Ghahremanpour MM, Tirado-Rives J, et al. Potent noncovalent inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 from molecular sculpting of the drug perampanel guided by free energy perturbation calculations. ACS Cent Sci. 2021;7:467–75. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.1c00039.
Luttens A, Gullberg H, Abdurakhmanov E, Vo DD, Akaberi D, Talibov VO, et al. Ultralarge virtual screening identifies SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors with broad-spectrum activity against coronaviruses. J Am Chem Soc. 2022;144:2905–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c08402.
Cantini N, Crocetti L, Guerrini G, Vergelli C, Lamanna S, Schepetkin IA, et al. Molecular manipulation of the 1,5,6,7-tetrahydro-4H-indazol-4-one scaffold to obtain new human neutrophil elastase (HNE) inhibitors. J Mol Struct. 2022;1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133140.
Okawa Y, Hideshima T, Steed P, Vallet S, Hall S, Huang K, et al. SNX-2112, a selective Hsp90 inhibitor, potently inhibits tumor cell growth, angiogenesis, and osteoclastogenesis in multiple myeloma and other hematologic tumors by abrogating signaling via Akt and ERK. Blood. 2009;113:846–55. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-04-151928.
Sulur M, Sharma P, Ramakrishnan R, Naidu R, Merifield E, Gill DM, et al. Development of scalable manufacturing routes to AZD1981. Application of the Semmler–Wolff aromatisation for synthesis of the indole-4-amide core. Org Process Res Dev. 2012;16:1746–53. https://doi.org/10.1021/op300173z.
Alhossary A, Handoko SD, Mu Y, Kwoh CK. Fast, accurate, and reliable molecular docking with QuickVina 2. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:2214–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv082.
Wang E, Sun H, Wang J, Wang Z, Liu H, Zhang JZH, et al. End-point binding free energy calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: strategies and applications in drug design. Chem Rev. 2019;119:9478–508. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00055.
Muegge I, Hu Y. Recent advances in alchemical binding free energy calculations for drug discovery. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023;14:244–50. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00541.
Shen C, Ding J, Wang Z, Cao D, Ding X, Hou T From machine learning to deep learning: advances in scoring functions for protein–ligand docking. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci. 2019;10. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcms.1429.
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, et al. GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX. 2015;1-2:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001.
Valdes-Tresanco MS, Valdes-Tresanco ME, Valiente PA, Moreno E. gmx_MMPBSA: a new tool to perform end-state free energy calculations with GROMACS. J Chem Theory Comput. 2021;17:6281–91. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.1c00645.
Strakova I, Kumpiņa I, Rjabovs V, Lugiņina J, Belyakov S, Turks M. Resolution, absolute configuration, and synthetic transformations of 7-amino-tetrahydroindazolones. Tetrahedron Asymmetry. 2011;22:728–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetasy.2011.03.010.
Tian J, Yue H, Yang P, Sang D. One-pot cleavage of aryl alkyl ethers by aluminum and iodine in acetonitrile. ChemistrySelect. 2019;4:38–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201803469.
Khlebnicova TS, Piven YA, Baranovsky AV, Lakhvich FA, Shishkina SV, Zicane D, et al. Synthesis of novel lupane triterpenoid-indazolone hybrids with oxime ester linkage. Steroids. 2017;117:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2016.08.002.
Piven YA, Yastrebova MA, Khamidullina AI, Scherbakov AM, Tatarskiy VV, Rusanova JA, et al. Novel O-acylated (E)-3-aryl-6,7-dihydrobenzisoxazol-4(5H)-one oximes targeting HSP90-HER2 axis in breast cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 2022;53:116521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116521.
Andrianov AM, Nikolaev GI, Shuldov NA, Bosko IP, Anischenko AI, Tuzikov AV. Application of deep learning and molecular modeling to identify small drug-like compounds as potential HIV-1 entry inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40:7555–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1905559.
Sulimov AV, Shikhaliev KS, Pyankov OV, Shcherbakov DN, Chirkova VY, Ilin IS, et al. Development of antiviral drugs based on inhibitors of the SARS-COV-2 main protease. Biomed Khim. 2021;67:259–67. https://doi.org/10.18097/PBMC20216703259.
Sander T, Freyss J, von Korff M, Rufener C. DataWarrior: an open-source program for chemistry aware data visualization and analysis. J Chem Inf Model. 2015;55:460–73. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci500588j.
O’Boyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C, Vandermeersch T, Hutchison GR. Open Babel: an open chemical toolbox. J Cheminform. 2011;3:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-33.
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009;30:2785–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256.
Sousa da Silva AW, Vranken WF. ACPYPE – AnteChamber PYthon Parser interfacE. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5:367. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-367.
Hawkins GD, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG. Parametrized models of aqueous free energies of solvation based on pairwise descreening of solute atomic charges from a dielectric medium. J Phys Chem. 1996;100:19824–39. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp961710n.
Aldeghi M, Heifetz A, Bodkin MJ, Knapp S, Biggin PC. Accurate calculation of the absolute free energy of binding for drug molecules. Chem Sci. 2016;7:207–18. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5sc02678d.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Belarusian Republican Foundation for Basic Research (project Х21КОВИД-003). YAP would like to thank Anatoli A. Piven for assistance in automation of virtual screening processes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Piven, Y.A., Zinovich, V.G., Shcherbakov, D.N. et al. Computer-aided design, synthesis and evaluation of new SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors based on 1,5,6,7-tetrahydro-4H-indazol-4-one scaffold. Med Chem Res 33, 151–163 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-023-03174-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-023-03174-z