Abstract
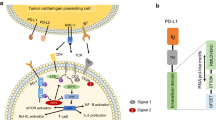
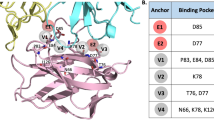
Cancer immunotherapy has achieved a leap from the laboratory to the clinic, especially for therapeutic applications based on programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) that target tumour immune escape and growth. At present, 13 PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been approved as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). However, inherent limitations of mAbs, including poor bioavailability and immunogenicity, have led researchers to pursue alternatives and develop small-molecule inhibitors with low molecular weight. Biphenyl derivatives are small-molecule inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 with advantages of oral bioavailability, high tumour penetration and better pharmacokinetic properties. In this work, we review progress and structure-activity relationship analysis of biphenyl derivatives as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. The conclusions could contribute to the design of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor candidates for cancer immunotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang YY, Zhang ZM. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17:807–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6.
Shekarian T, Valsesia-Wittmann S, Caux C, Marabelle A. Paradigm shift in oncology: targeting the immune system rather than cancer cells. Mutagenesis. 2015;30:205–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geu073.
Atkins MB, Sznol M. Cancer immunotherapy: Past Progress and Future Directions. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:518–22. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2015.05.001.
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Restifo NP. Cancer immunotherapy: moving beyond current vaccines. Nat Med. 2004;10:909–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1100.
Rosenberg SA. Raising the Bar: The Curative Potential of Human Cancer Immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3003634
Mellman I, Coukos G, Dranoff G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature. 2011;480:480–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10673.
Taefehshokr N, Baradaran B, Baghbanzadeh A, Taefehshokr S. Promising approaches in cancer immunotherapy. Immunobiology. 2020;225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2019.11.010
Ngiow SF, von Scheidt B, Akiba H, Yagita H, Teng MWL, Smyth MJ. Anti-TIM3 Antibody Promotes T Cell IFN-gamma-Mediated Antitumor Immunity and Suppresses Established Tumors. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3540–51. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-0096.
Li H, Wu K, Tao KX, Chen LB, Zheng QC, Lu XM. et al. Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;56:1342–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.25777.
Woo SR, Turnis ME, Goldberg MV, Bankoti J, Selby M, Nirschl CJ. et al. Immune Inhibitory Molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 Synergistically Regulate T-cell Function to Promote Tumoral Immune Escape. Cancer Res. 2012;72:917–27. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-1620.
Sondak VK, Smalley KSM, Kudchadkar R, Grippon S, Kirkpatrick P. Ipilimumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:411–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3463.
Tan SG, Zhang CWH, Gao GF. Seeing is believing: anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies in action for checkpoint blockade tumor immunotherapy. Sig Transd Targeted Ther. 2016;1. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2016.29.
Lin X, Lu X, Luo GS, Xiang H. Progress in PD-1/PD-L1 pathway inhibitors: From biomacromolecules to small molecules. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111876.
Ceeraz S, Nowak EC, Noelle RJ. B7 family checkpoint regulators in immune regulation and disease. Trends Immunol. 2013;34:556–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2013.07.003.
Mahoney KM, Rennert PD, Freeman GJ. Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14:561–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4591.
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpel AH. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677–704. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090331.
Chen LP. Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:336–47. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1349.
Intlekofer AM, Thompson CB. At the Bench: Preclinical rationale for CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade as cancer immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol. 2013;94:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1212621.
Lazar-Molnar E, Yan Q, Cao E, Ramagopal U, Nathenson SG, Almo SC. Crystal structure of the complex between programmed death-1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:10483–8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804453105.
Chemnitz JM, Parry RV, Nichols KE, June CH, Riley JL. SHP-1 and SHP-2 associate with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary human T cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents T cell activation. J Immunol. 2004;173:945–54. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.173.2.945.
Patsoukis N, Brown J, Petkova V, Liu F, Li L, Boussiotis VA. Selective Effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras Pathways Regulate Molecular Components of the Cell Cycle and Inhibit T Cell Proliferation. Sci Signal. 2012;5. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2002796.
Hui E, Cheung J, Zhu J, Su X, Taylor MJ, Wallweber HA. et al. T cell costimulatory receptor CD28 is a primary target for PD-1-mediated inhibition. Science. 2017;355:1428. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf1292.
Sharpe AH, Pauken KE. The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:153–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.108.
Flies DB, Sandler BJ, Sznol M, Chen L. Blockade of the B7-H1/PD-1 pathway for cancer immunotherapy. Yale J Biol Med. 2011;84:409–21.
Shi L, Chen S, Yang L, Li Y. The role of PD-1 and PD-L1 in T-cell immune suppression in patients with hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-6-74
Ledford H, Else H, Warren M. Cancer immunologists scoop medicine Nobel prize. Nature. 2018;562:20–1. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-06751-0.
Ribas A, Wolchok JD. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. 2018;359:1350. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar4060.
Chames P, Van Regenmortel M, Weiss E, Baty D. Therapeutic antibodies: successes, limitations and hopes for the future. Br J Pharmacol. 2009;157:220–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00190.x.
Beck KM, Dong JN, Geskin LJ, Beltrani VP, Phelps RG, Carvajal RD, et al. Disease stabilization with pembrolizumab for metastatic acral melanoma in the setting of autoimmune bullous pemphigoid. J Immunother Cancer. 2016;4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-016-0123-3
Weinmann H. Cancer Immunotherapy: Selected Targets and Small-Molecule Modulators. Chemmedchem. 2016;11:450–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201500566.
Musielak B, Kocik J, Skalniak L, Magiera-Mularz K, Sala D, Czub M, et al. CA-170 - A Potent Small-Molecule PD-L1 Inhibitor or Not? Molecules. 2019;24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152804
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Naremaddepalli S, Naremaddepalli SS, Nair Sasikumar PG, Setty Sudarshan N, et al. AURIGENE DISCOVERY TECHNOLOGIES LTD (REDY-C) AURIGENE DISCOVERY TECHNOLOGIES LTD (REDY-C) SASIKUMAR P G N (SASI-Individual) RAMACHANDRA M (RAMA-Individual) NAREMADDEPALLI S S S (NARE-Individual) NAREMADDEPALLI S S (NARE-Individual), assignee. New 1,3,4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole derivatives are programmed cell death-1 signaling pathway modulators useful for the treatment of e.g. bone cancer, pancreatic cancer, bacterial disease and viral disease patent WO2015033301-A1. 2015.
Sasikumar PGNB, IN), Ramachandra, Muralidhara (Bangalore, IN), Naremaddepalli, Seetharamaiah Sudarshan (Bangalore, IN), inventor Sasikumar Pottayil Govindan N.,Ramachandra Muralidhara,Naremaddepalli Seetharamaiah Sudarshan, assignee. 1,2,4-OXADIAZOLE AND THIADIAZOLE COMPOUNDS AS IMMUNOMODULATORS patent US20180044303--A1. 2018.
Sharpe AH, Butte MJ, Oyama S. HARVARD COLLEGE (HARD-C) SHARPE A H (SHAR-Individual) BUTTE M J (BUTT-Individual) OYAMA S (OYAM-Individual), assignee. New bis((hetero)aryl) sulfenyl/sulfonyl/carbonyl compounds used in pharmaceutical composition for treating or preventing e.g. herpes simplex virus infection, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and type I diabetes patent WO2011082400-A2. 2011.
Chupak LS, Zheng X, Chupak Louis S. Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C), assignee. New immunomodulating compound useful for preparing a pharmaceutical composition, and for treating a disease or disorder associated with the inhibition of the programmed cell death 1/programmed death-ligand 1 interaction, e.g. cancer patent WO2015034820-A1. 2015.
Connolly TP, Frennesson DB, Grant-Young KA, Hewawasam P, Langley DR, Meng Z, et al. Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C), assignee. New substituted aromatic compound used in pharmaceutical composition for e.g. enhancing, stimulating, modulating and/or increasing immune response, and inhibiting growth, proliferation, or metastasis of cancer cells patent WO2017066227-A1. 2017.
Zak KM, Grudnik P, Guzik K, Zieba BJ, Musielak B, Domling A, et al. Structural basis for small molecule targeting of the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1. Oncotarget. 2016;7:30323–35. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8730.
Skalniak L, Zak KM, Guzik K, Magiera K, Musielak B, Pachota M. et al. Small-molecule inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint alleviate the PD-L1-induced exhaustion of T-cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:72167–81. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20050.
Degorce F, Card A, Soh S, Trinquet E, Knapik GP, Xie B. HTRF: A technology tailored for drug discovery - a review of theoretical aspects and recent applications. Curr Chem Genom. 2009;3:22–32. https://doi.org/10.2174/1875397300903010022.
Feng Z, Chen X, Zhang L, Yang Y, Lai F, Ji M, et al. Chinese Acad Medical Sci (Msum-C), assignee. New bromo-substituted phenylether derivative used in pharmaceutical composition for manufacturing medicament useful for preventing and/or treating cancer, infectious disease and autoimmune disease patent CN107417666-A. 2017.
Yan J, YAN J (YANJ-Individual) ANHUI SHITE PHARM TECHNOLOGY CO LTD (ANHU-Non-standard), assignee. New (5-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)methanol compound is cell death receptor 1/programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitor useful in preparing antitumor medicine patent CN111320606-A. 2020.
Ma J, Wang Y, Chen R, Liu J, Wu S. Univ Huaqiao (Uyhq-C), assignee. New 2-((dimethylamino)methyl)-5-(4-quinolyloxy)phenol derivative used in preparing pharmaceutical composition for treating diseases related to programmed cell death-1/programmed death ligand-1 patent CN112979562-A. 2021.
Guo JL, Luo LL, Wang ZH, Hu NJ, Wang W, Xie F. et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Linear Aliphatic Amine-Linked Triaryl Derivatives as Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Interaction with Promising Antitumor Effects In Vivo. J Med Chem. 2020;63:13825–50. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01329.
Wang Y, Xu Z, Wu T, He M, Zhang N. GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard), assignee. New aromatic acetylene or aromatic vinyl compound used in pharmaceutical composition, and in preparation of medicament for prevention, alleviation and treatment of cancer, infections and autoimmune diseases patent WO2018006795-A1. 2018.
Wang Y, Zhang N, Wu T, He M, Wang F. GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU ZAIJI PHARM TECHNOLOGY CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (SHAN-Non-standard) GUANGZHOU MAXINOVEL PHARM CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard), assignee. New 1-phenyl-3-(2-phenylethyl)benzene derivative useful in pharmaceutical composition for preparing medicine for preventing and treating e.g. cancer and autoimmune disease patent WO2019128918-A1. 2019.
Jiang S, Hao H, Wang T, Wang M, Zhang W, Ni Y, et al. Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C) Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C), assignee. New phenyl-substituted five-membered heterocyclic compound used in pharmaceutical composition for preparing anti-tumor medicine patent CN111718310-A. 2020.
Lajkiewicz N, Wu L, Yao W, Wen-Qing Y. Incyte Corp (Inyt-C) Incyte Corp (Inyt-C) Incyte Corp (Inyt-C), assignee. New substituted phenyl-quinolin-8-yl-amine compounds are programmed cell death protein (PD) 1-PD-ligand 1 interaction inhibitors useful for e.g. treating viral infection and cancer patent CN108699001-A. 2018.
Li J, Wu L, Yao W. Incyte Corp (Inyt-C) Incyte Corp (Inyt-C) Incyte Corp (Inyt-C), assignee. New substituted heterocyclic compounds are programmed cell death protein 1/programmed death-ligand 1 interaction inhibitors useful to enhance, stimulate and/or increase immune response and to treat e.g. viral infection and cancer patent CN109641885-A. 2019.
Xiao K, Zhang F, Wu L, Yao W, Xiao KJ, Zhang FL, et al. Incyte Corp (Inyt-C) Incyte Corp (Inyt-C) Incyte Corp (Inyt-C) Incyte Corp (Inyt-C), assignee. New amido-substituted heterocyclic compound used in pharmaceutical composition useful for treating disease or disorder associated with inhibition of PD-1/PD-L1 interaction, and enhancing, stimulating or increasing immune response in patient patent CN109890819-A. 2019.
Lange C, Malathong V, McMurtrie DJ, Punna S, Singh R, Yang J, et al. Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C) Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C), assignee. New substituted phenoxyindane compounds are programmed cell death-1 protein inhibitors, used to treat e.g. infectious disease, bacterial infectious disease, viral infectious disease, fungal infectious disease, solid tumor and cancer patent WO2018005374-A1. 2018.
Lange C, Punna S, Singh R, Yang J, Zhang P. Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C) Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C), assignee. New substituted indan-1-yl-phenyl-amine compounds are used to e.g. modulate immune response mediated by the programmed cell death protein (PD)-1 signaling pathway and enhance, stimulate, modulate and/or increase the immune response patent WO2019165043-A2. 2019.
Xu Y, Huang L, Lin D, Hu H. GUANGZHOU DANKANG MEDICAL BIOLOGY CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard), assignee. New fused ring compound useful in preparing medicine for treating and preventing disease associated with programmed cell death protein-1/programmed death-ligand-1 interaction and preparing immunomodulator patent CN110092740-A. 2019.
Fu B, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Wang J, Ding L. BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard) ZHEJIANG BETA PHARMA INC (ZHEJ-Non-standard) BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard), assignee. New substituted heterocylic compounds are programmed cell death protein-1/programmed cell death-ligand1 interaction inhibitors, used to treat e.g. colon, gastric, thyroid, lung, pancreatic, brain, renal, prostate, ovarian and breast cancers patent CN112384500-A. 2021.
Qin MZ, Cao Q, Wu X, Liu CY, Zheng SS, Xie HB, et al. Discovery of the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction inhibitors bearing an indoline scaffold. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111856
Qin MZ, Meng YY, Yang HS, Liu L, Zhang HT, Wang SM. et al. Discovery of 4-Arylindolines Containing a Thiazole Moiety as Potential Antitumor Agents Inhibiting the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Interaction. J Med Chem. 2021;64:5519–34. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01958.
Chen H, Wang K, Yang Y, Huang X, Dai X, Feng Z. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction inhibitors bearing a benzo[d]isothiazole scaffold. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;217:113377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113377.
Muszak D, Surmiak E, Plewka J, Magiera-Mularz K, Kocik-Krol J, Musielak B. et al. Terphenyl-Based Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Protein-Protein Interaction. J Med Chem. 2021;64:11614–36. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00957.
Wang TY, Cai S, Wang MM, Zhang WH, Zhang KJ, Chen D. et al. Novel Biphenyl Pyridines as Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Interaction. J Med Chem. 2021;64:7390–403. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00010.
Zhang HB, Xia Y, Yu CQ, Du HJ, Liu JC, Li H, et al. Discovery of Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction via Structural Simplification Strategy. Molecules. 2021;26. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113347
Yeung K, St Laurent DR, Romine JL, Scola PM, Yang G, St LDR. Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C), assignee. New isoquionline derivatives are programmed death-1 inhibitors used to enhance, stimulate, modulate and/or increase immune response, inhibit growth, proliferation, or metastasis of cancer cells and treat infectious disease and septic shock patent WO2018183171-A1. 2018.
Ma J, Huang K, Ni X, Chen R, Yu C, Yan Q, et al. Univ Huaqiao (Uyhq-C), assignee. New coumarin derivatives useful in preparing medicine for treating and preventing cancer diseases and other proliferative diseases patent CN109232498-A. 2019.
Chen J, Cheng B. Univ Southern Medical (Unsm-C), assignee. New substituted 2-(1,1’-biphenyl-3-yl)-4H-chromen-4-one compound useful for preparing programmed cell death protein 1/programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor patent CN109336857-A. 2019.
Chen J, Cheng B. Univ Southern Medical (Unsm-C), assignee. New 2-methyl-6-((2-methylbiphenyl-3-yl)methoxy)naphthalene compound useful in preparing programmed cell death protein 1/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD1/PD-L1) inhibitor patent CN109438263-A. 2019.
Chen J, Cheng B. Univ Southern Medical (Unsm-C), assignee. New substituted biphenyl-containing chalcone derivative used for preparing programmed cell death receptor 1/programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitor patent CN109456284-A. 2019.
Sun H, Liu L, Yao Z. Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C), assignee. New 7-(biphenyl-3-ylmethoxy)-6,7-dihydro-benzo(1,2,5)oxadiazol-5-ol compounds are programmed cell death protein 1 and programmed death ligand 1 inhibitors used for tumor immunotherapy patent CN109776445-A. 2019.
Yang P, Xiao Y, Sun C, Deng H, Cheng Y, Xie S, et al. Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C), assignee. New substituted phthalimide compound used in pharmaceutical composition for treating disease including autoimmune disease, cancer and infectious disease patent CN112979532-A. 2021.
Wang Z, Fan G, Zeng Z, Wang X, Jiang R. SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI CHENGSEN PHARM CO LTD (SHAN-Non-standard), assignee. New heteroaryl compound used in pharmaceutical composition for preparing PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor to treat cancer treating cancer e.g. melanoma, lung cancer and bladder cancer, is formed by performing ring fusion of diheteroaryl compounds patent WO2019076343-A1. 2019.
Wang Z, Zhang J, Zeng Z. SHANGHAI CHENGSEN PHARM CO LTD (SHAN-Non-standard), assignee. New substituted aromatic compound used in pharmaceutical composition for preventing and/or treating disease associated with programmed cell death protein 1/programmed death-ligand 1 patent CN111039942-A. 2020.
Wang Z, Bai H, Li D, Qian A, Win BH, Lan Q. SHANGHAI CHENGSEN PHARM CO LTD (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARM CO (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARM CO (SHAN-Non-standard), assignee. New 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene compounds useful for preventing/treating diseases related to activity or expression of programmed cell death 1 receptor/ligand programmed cell death ligand 1 patent CN112457305-A. 2021.
Wang Z, Bai H, Li D, Qian A, Win BH, Lan Q. SHANGHAI CHENGSEN PHARM CO LTD (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARM CO (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARM CO LTD (SHAN-Non-standard) SHANGHAI LONGWOOD BIOPHARM CO (SHAN-Non-standard), assignee. New tricyclic aromatic heterocyclic compound used e.g. for pharmaceutical composition for preventing and treating diseases related to activity or expression amount of programmed cell death 1 receptor/programmed cell death ligand 1 patent CN112457308-A. 2021.
Venkateshappa C, Duraiswamy AJ, Putta RKVP, Rajagopal S, Putta RKV. JUBILANT BIOSYS LTD (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT BIOSYS LTD (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard), assignee. New 2-(benzyloxy)pyrimidine derivatives are programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitors used to treat and/or prevent e.g. proliferative disorder or cancer, HIV, influenza, herpes virus, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and hepatitis D patent WO2019087214-A1. 2019.
Venkateshappa C, D AJ, Pendyala M, Sivanandhan D, Rajagopal S, A JD, et al. JUBILANT BIOSYS LTD (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT PRODEL LLC (JUBI-Non-standard) JUBILANT BIOSYS LTD (JUBI-Non-standard), assignee. New bicyclic compounds are PD-1 interaction inhibitors useful for treating and/or preventing various diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases patent WO2019175897-A1. 2019.
Fan P, Lange CW, Lui RM, McMurtrie DJ, Scamp RJ, Yang J, et al. Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C) Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C), assignee. New heteroaryl-biphenyl amines are programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitors used to treat e.g. infectious disease, bacterial infectious disease, viral infectious disease, fungal infectious disease, inflammatory disease and cancer patent WO2021076688-A1. 2021.
Fan P, Lange CW, Lui RM, McMurtrie DJ, Scamp RJ, Yang J, et al. Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C) Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C), assignee. New heteroaryl-biphenyl amides derivatives are programmed death-1 inhibitors to treat e.g. infectious disease, bacterial infectious disease, solid tumor, immune disorder, inflammatory and viral infectious disease fungal infectious disease patent WO2021076691-A1. 2021.
Yang Q, Lu X, Li Z, Xin L, Song Y, Fu C. SHENZHEN CHIPSCREEN BIOSCIENCES LTD (SHEN-Non-standard) SHENZHEN CHIPSCREEN BIOSCIENCES LTD (SHEN-Non-standard) SHENZHEN CHIPSCREEN BIOSCIENCES LTD (SHEN-Non-standard), assignee. New substituted amine based urea compounds useful in medicinal composition and medicament for preventing disease associated with PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway including cancer, autoimmune diseases and chronic infectious diseases patent CN108250159-A. 2018.
Lai AC, Crews CM. Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:101–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.211.
Lim S-O, Li C-W, Xia W, Cha J-H, Chan L-C, Wu Y. et al. Deubiquitination and Stabilization of PD-L1 by CSN5. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:925–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.010.
Cheng BB, Ren YC, Cao H, Chen JJ. Discovery of novel resorcinol diphenyl ether-based PROTAC-like molecules as dual inhibitors and degraders of PD-L1. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112377.
Chamberlain PP, Hamann LG. Development of targeted protein degradation therapeutics. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:937–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0362-y.
Zeidner JF, Knaus HA, Zeidan AM, Blackford AL, Montiel-Esparza R, Hackl H. et al. Immunomodulation with pomalidomide at early lymphocyte recovery after induction chemotherapy in newly diagnosed AML and high-risk MDS. Leukemia. 2020;34:1563–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-019-0693-4.
Wang YB, Zhou YY, Cao S, Sun Y, Dong ZQ, Li C, et al. In vitro and in vivo degradation of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) by a proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC). Bioorg Chem. 2021;111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104833
Frennesson DB, Grant-Young KA, Hewawasam P, Langley DR, Meng Z, Mull E, et al. Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C), assignee. New immunomodulatory derivative used for treating cancer and infectious diseases, where additional agent is antimicrobial agent, antiviral agent, cytotoxic agent, gene expression modulatory agent or immune response modifier patent CN109863146-A. 2019.
Feng Z, Chen X, Yang Y, Zhou C, Lai F, Ji M, et al. Chinese Acad Medical Sci (Msum-C), assignee. New bromo-substituted phenylether derivative used in pharmaceutical composition for manufacturing medicament useful for preventing and/or treating cancer, infectious disease and autoimmune disease patent CN107417564-A. 2017.
Xu Y, Huang L, Lin D, Hu H. GUANGZHOU DANKANG MEDICAL BIOLOGY CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard), assignee. New chlorobenzene compound useful in preparing medicine for preventing/treating diseases related to interaction solid cancer and advanced solid cancer (e.g. non-small cell lung cancer) and for preparing medicine and immunomodulators patent CN111747927-A. 2020.
Sun H, Liu L, Wang S, Yao Z, Xie T, Wu G, et al. Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C) Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C), assignee. New substituted 5-((3-(((1,1’-biphenyl)-3-yloxy)methyl)phenoxy)methyl)-2H-1,3-benzodiazole compound used in pharmaceutical composition for preparing immunomodulator drugs used for preventing or treating tumors or autoimmune diseases patent CN111909108-A. 2020.
Guzik K, Zak KM, Grudnik P, Magiera K, Musielak B, Torner R. et al. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) Interaction via Transiently Induced Protein States and Dimerization of PD-L1. J Med Chem. 2017;60:5857–67. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00293.
Yeung K, Grant-Young KA, Sun L, Langley DR, St Laurent DR, Scola PM, et al. Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C) Bristol-Myers Squibb Co (Brim-C), assignee. New substituted phenyl compounds are programmed death-ligand 1-programmed death 1 interaction inhibitors used to e.g. enhance, stimulate, and/or increase immune response, and inhibit growth, proliferation or metastasis of cancer cells patent WO2018118848-A1. 2018.
Yu J, Xin L, Shan S, Wang X, Fu C, Li Z, et al. SHENZHEN CHIPSCREEN BIOSCIENCES LTD (SHEN-Non-standard) SHENZHEN CHIPSCREEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD (SHEN-Non-standard), assignee. New biphenyl compounds are programmed cell death receptor-1 and PROGRAMMED cell death protein ligand-1 inhibitors used for e.g. improving, stimulating, regulating and increasing immune response, and treat infectious disease caused by virus patent WO2020043154-A1. 2020.
Liu B, Yang T, Yu X, Sun D, Zhang Y. Sunshine Lake Pharma Co Ltd (Susn-C) Guangdong Dongyangguang Pharm Co Ltd (Gddy-C), assignee. New substituted phenol compound useful in medicinal composition for treating, preventing and improving cancer in which immortalized cell exists in organ/body tissue including e.g. bone cancer, infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases patent WO2019174533-A1. 2019.
Liu B, Zhang Y, Yang T, Yu X, Sun D. DONGGUAN HEC NEW DRUG RES & DEV CO LTD (DONG-Non-standard) GUANGDONG DONGYANGGUANG PHARM CO LTD (GDDY-C), assignee. New programmed cell death protein 1/programmed cell death protein 1 and its ligand small molecule inhibitor i.e. substituted aromatic compound in preparing medicine for treating e.g. cancer, infectious disease and autoimmune disease patent CN111793077-A. 2020.
Du Z, Graupe M, Machicao Tello PA, Medley JW, Metobo SE, Parkhill EQ, et al. Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C) Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C) Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C) Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C), assignee. New substituted heterocyclic compounds are programmed death-1 inhibitors, used to treat e.g. pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, renal cancer, hepatocellular cancer, lung and ovarian cancers patent WO2020086556-A1. 2020.
Xu Y, Zhang H, Zhu Q, Du H, Xia Y, Yu C, et al. Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C), assignee. New biphenyl compound useful in preparing programmed cell death protein 1 and programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor medicine and in preparing medicine for treating tumor patent CN113135895-A. 2021.
Zhang H, Zhou J, Zhang J, Zhu P, Wang T. Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C), assignee. New heterocyclic substituted biphenyl compound is programmed cell death protein 1/programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor, useful in preparing medicine for preventing and treating e.g. solid tumor, late solid tumor and melanoma patent CN113307779-A. 2021.
Basu S, Yang J, Xu B, Magiera-Mularz K, Skalniak L, Musielak B. et al. Design, Synthesis, Evaluation, and Structural Studies of C-2-Symmetric Small Molecule Inhibitors of Programmed Cell Death1/Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Protein-Protein Interaction. J Med Chem. 2019;62:7250–63. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00795.
Wu L, Qian D, Lu L, Lajkiewicz N, Konkol LC, Li Z, et al. INCYTE CORP (INYT-C) INCYTE CORP (INYT-C) LU L (LULL-Individual) ZHANG F (ZHAN-Individual) LI J (LIJJ-Individual) WANG H (WANG-Individual) XIAO K (XIAO-Individual), assignee. New heterocyclic compound used in pharmaceutical composition treating disease or disorder associated with inhibition of PD-1/PD-L1 interaction patent CN110267953-A. 2019.
Aktoudianakis E, Appleby T, Cho A, Du Z, Graupe M, Guerrero JA, et al. Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C) Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C) Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C) Gilead Sci Inc (Gile-C), assignee. New substituted heterocyclic compounds are programmed cell death-1 inhibitors, used to treat cancer e.g. cancer of pancreatic, bladder, colorectal, breast, prostate, renal, hepatocellular, lung, ovarian, cervical, gastric and esophageal patent WO2018195321-A1. 2018.
Wang Y, Fu B, Zhang Y, Liu X, Wang J, Ding L. BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard) ZHEJIANG BETA PHARMA INC (ZHEJ-Non-standard) BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard) BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard) BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard), assignee. New substituted 1,1’-biphenyl-3,3’-diamine compounds are PD-1-PD-L1 interaction inhibitors used for treating cancer of e.g. gastric, thyroid, lung, renal, and prostate and enhancing, stimulating and/or increasing immune response patent WO2019192506-A1. 2019.
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Fu B, Wang J, Ding L, Chen K, et al. BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard) ZHEJIANG BETA PHARMA INC (ZHEJ-Non-standard) BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard) BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard) BETA PHARM CO LTD (BETA-Non-standard), assignee. New substituted fused cyclic compounds are programmed cell death-1/programmed death-ligand 1 interaction inhibitor, used to treat e.g. colon cancer, brain cancer and melanoma, and enhancing, stimulating and/or increasing immune response patent WO2020156323-A1. 2020.
Malathong V, Mali VR, McMurtrie DJ, Punna S, Roth HS, Singh R, et al. Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C) Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C), assignee. New substituted fused cyclic compounds are programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitors, used to e.g. modulating immune response mediated by PD-1 signaling pathway, increasing immune response and inhibiting metastasis of cancer cells patent WO2021007386-A1. 2021.
Jiang S, Xiao Y, Hao H, Wang T, Zhang K, Wang M, et al. Univ China Pharm (Uycp-C), assignee. New five-membered heterocyclic substituted biphenyl compounds are programmed cell death ligand inhibitor and immune checkpoint inhibitors, useful in preparing medicine for treating cancer patent CN113121464-A. 2021.
Xu Y, Huang L, Lin D, Hu H. GUANGZHOU DANKANG MEDICAL BIOLOGY CO LTD (GUAN-Non-standard), assignee. New (phenoxymethyl)benzene-containing derivative used for treating and/or preventing programmed death-1/programmed death-ligand 1 interaction-related diseases patent CN110092799-A. 2019.
Malathong V, McMahon J, McMurtrie DJ, Punna S, Roth HS, Singh R, et al. Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C) Chemocentryx Inc (Chcx-C), assignee. New macrocyclic immunomodulator used for inhibiting growth, proliferation, or metastasis of cancer cells, and treating disease or disorder mediated by programmed cell death protein 1 signaling pathway, e.g. immune disorder or cancer patent WO2019032547-A1. 2019.
Price C, Zhou X, Li W, Wang L. Real-Time Measurement of Solute Transport Within the Lacunar-Canalicular System of Mechanically Loaded Bone: Direct Evidence for Load-Induced Fluid Flow. J Bone Min Res. 2011;26:277–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.211.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Beijing [2022-ZZ-025].
Author contributions
YLW and SRW designed the research; SRW performed the collection and analysis of data; SRW and HY drafted the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, Y. & Yan, H. Progress on biphenyl derivatives as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Med Chem Res 32, 2089–2115 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-023-03127-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-023-03127-6